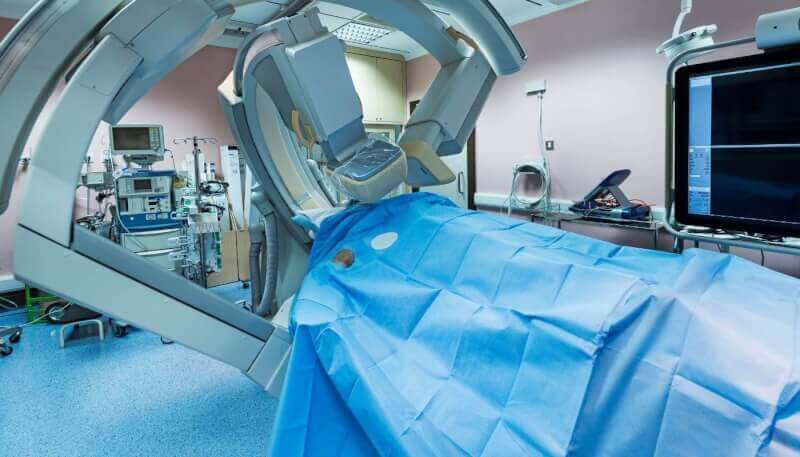
What is Angiography?
Today, the number of cardiovascular patients is increasing rapidly due to irregular nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, stress and the use of harmful substances such as smoking. The most important method used in the diagnosis of these diseases is angiography.
This procedure, called coronary angiography in medical language, is called angiography among the public. This method, which allows the vessels that blood and nourish the heart to be visualized with the help of a dyed liquid, briefly provides a film of the coronary vessels.
Discovered between 1950 and 1960, angiography is a Latin name. Angio means vein in Latin, while grafi means picture. In the early days of angiography, the artery had to be cut to perform the procedure. However, today this procedure can only be performed using a needle. Thanks to angiography, which is a minimally invasive operation, it does not cause almost any deterioration in the general condition of the patients. For this reason, it is an easy procedure that cannot be called surgery.
Angiography is not only used in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases but also in the treatment of diseases such as heart spasm, heart attack and cholesterol. In fact, its use in the treatment of these diseases increases patients' chances of survival.
Thanks to the angiography procedure performed in catheter laboratories, it is easy to determine whether there is any narrowing or blockage in the vessels. In the operations performed, the safety of both patients and healthcare professionals is at the highest level.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery: 30 Minutes-2 Hours
Anesthesia Method: Local, Sedation,
Hospitalization Duration: 1 Day
Return to Work Period: 1-3 Days
In which cases is angioplasty performed?
If patients' complaints suggest the possibility of cardiovascular diseases, angiography is among the tests performed. Blood tests and ECG are usually performed in patients' complaints. After the results of these examinations are obtained, an angioplasty procedure is performed if deemed necessary by the physician. The complaints that are effective in the angioplasty procedure are as follows.
- Heart valve problem requiring surgery
- Abnormal results seen on stress ECG or echocardiography
- Congenital heart diseases
- Pain in the left arm of unknown origin that does not go away
- Shortness of breath when climbing stairs
- Chest pain
In which diseases is angioplasty performed?
Angiography is used to detect conditions related to heart and vascular problems. For this reason, the diagnosis of many different diseases is possible thanks to the angiography procedure. These health problems include the following.
- To check the status of patients who have previously undergone stent or balloon application
- To assess the condition of the vessels supplying the heart
- Assessment of heart muscle function
- Identification of vascular occlusion
- After a heart attack
- Checking the cardiovascular health of individuals over 40 years of age before undergoing major surgery
- Checking the condition of those who have undergone bypass operations
- Cardiovascular health checks of diabetic patients before undergoing an important operation
- Identification of valvular heart disease
- Suspicious results of computerized angiography
- Suspicion of coronary artery disease in previous examinations
- Irregularities in the heart muscle during echo
- A positive effort test result
- Presence of signs of coronary stenosis
- Presence of severe chest pain
- Detection of vascular dilatation
- Detection of an aneurysm
- Detection of the vessel causing the stroke
- Determining which vessel the tumor is pressing on in some types of cancer
- Stenting a blocked vessel
Who cannot have angioplasty?
Although the success rate of diagnosis by angiography is close to 100%, this procedure should not be performed on patients with certain characteristics except in emergencies. The groups to which this procedure should not be applied are as follows.
- Patients taking certain blood thinners
- In case the patient has a fever
- Those with left heart failure
- Patients with renal failure
How is an angioplasty performed?
Angiography is usually performed by accessing the artery in the right groin area. However, if this vein is completely blocked or cannot be used, the access is performed by entering the artery in the left groin area, elbow artery, armpit artery, right or left wrist artery.
The catheters used in the angioplasty procedure are determined according to the characteristics of the vessel to be treated. In this way, any damage to the vessel is prevented. Another feature of these catheters is that they do not cause clot formation. For example, Judkins catheters are used for access through the left and right inguinal arteries, while the type of catheter used to visualize the thoracic arteries of bypass patients is the IMA.
After intravenous access, 2 to 3 exposures are used to visualize the right arteries and 5 exposures are used to visualize the left arteries. In order to visualize the left ventricle, which acts as the pump of the heart, 2 exposures are made in this area as well as the use of dyestuff ranging from 15 to 25 cc.
Angiography procedures usually take between 10 and 20 minutes. However, this period may be prolonged depending on the anatomical condition of the entered vessel. In addition, the duration of the angioplasty procedure for patients with by-pass varies between 20 and 30 minutes.
Before starting the angioplasty procedure, local anesthesia is applied to the area to be treated. This way, patients do not feel any pain or soreness during the procedure. After the angioplasty procedure is completed, which is usually uneventful, the cannula at the entry site is withdrawn and pressure is applied to the entry site for 15 to 20 minutes to stop the bleeding. After stopping the bleeding, the area is wrapped with a tight bandage and a weight is placed on it. Patients are allowed to lie down and rest for 4-6 hours in this way. At the end of 6 hours, the patient is stood up and discharged if there are no problems.
Patients can shower the next day. If there is no disturbing swelling or bruising in the treated area, they can return to their normal lives after a day.
Risks of angioplasty
Angioplasty is one of the minimally invasive interventions, and the likelihood of complications is almost zero, especially when performed by specialists in the field. However, as with all other procedures in medicine, there is a small chance of complications after angioplasty. These complications include the following.
- Patients are at risk of heart attack and stroke during the angioplasty procedure. However, there is no evidence that this risk is directly linked to the angioplasty procedure. For this reason, it is also possible that the blocked vessel can cause these problems.
- During the angioplasty procedure, the access vessel may be damaged.
- Pain, swelling or bruising may occur at the site where the cannula is inserted. As these symptoms are often signs of infection, you should consult your doctor immediately.
- During angioplasty, patients may experience impaired kidney function. However, this is usually temporary. Permanent kidney damage occurs in a very small proportion of patients. Therefore, in these cases, the patient needs urgent intervention.
- Patients may experience nausea and dizziness due to prolonged fasting.
- Patients may feel warmth and burning at the procedure site.
- Patients may be allergic to the contrast material used during the angioplasty procedure. In this case, patients may experience mild allergic reactions such as redness and itching.
- In inguinal access procedures, bleeding may occur if the patient moves or if the pressure is not applied well. In case of bleeding, there is extensive bruising on the leg of the patients.
Things to consider before angiography
Before angioplasty, patients need to make the necessary preparations for the procedure. These preparations will reduce the risk of complications and make the procedure more comfortable. The points that patients should pay attention to before the angioplasty procedure are as follows.
- Medications used before angiography should be reported to the physician. It may be requested to discontinue medications such as blood thinners that may pose a risk during the procedure. Medicines that do not have any effect on the procedure can continue to be used.
- You should not eat or drink anything in the 5 hours before the angioplasty procedure.
- The night before the angioplasty procedure, you should not consume foods that increase the pulse rate, such as tea, coffee and energy drinks.
- Patients should inform their physician if they have kidney failure or allergies.
- Patients should bring the results of their previous tests with them to the angioplasty procedure.
- The patient should bring water with them when entering the procedure.
Things to consider after angioplasty
In order to minimize the risk of complications after the angioplasty procedure, patients should pay attention to some points and strictly follow the recommendations of their physicians. The points that patients should pay attention to after angiography are as follows.
- To minimize the damage to the kidneys caused by the contrast agent used in the angioplasty procedure, patients should drink plenty of water after the angioplasty procedure. If there is no health problem that prevents patients from consuming too much water, then patients should consume 2 liters of water within 2 hours after the operation.
- After the angioplasty procedure, a sandbag is placed at the point where the catheter is removed to prevent bleeding. The sandbag should not be moved for 6 hours after the angioplasty procedure.
- Patients should also not move their legs on the side of the insertion to avoid the risk of bleeding.
- Patients should not get up if they need to use the toilet and should get help to do so.
- In movements that may cause bleeding, such as coughing or sneezing, extra pressure should be applied to the area with the hand.
- In case of swelling, pain or edema in the treated area after leaving the hospital, you should consult a doctor.
Types of angioplasty
The angioplasty procedure varies according to the area treated. It is commonly used to examine the vessels of the heart, brain, lungs, eyes and kidneys.
Coronary CT Angiography (Virtual Angiography)
This procedure, also called cardiac angiography, is used to visualize the vessels that feed the heart and the vessels around the heart. In this angiography technique, 3D imaging is provided with computerized imaging systems.
Standard (Conventional) Angiography
In this procedure using a catheter, imaging is performed using contrast material and X-rays. It is also called cine angiography because the images are recorded in motion.
Angiography side effects
Some side effects may occur after an angioplasty procedure. Although the incidence of these side effects is extremely low, the risk can be reduced by paying attention to some points.
Bruising after angiography
The most common side effect after angioplasty is bruising. Some of the bruises cause a serious clinical picture. These are usually due to failure to stop bleeding or failure to apply pressure properly. However, this is rare. In addition, even if there is no aneurysm or hematoma after angiography, the skin may bruise. This is a natural consequence of the process.
Increased blood pressure after angiography
Patients may experience a drop in blood pressure after the angioplasty procedure and this is expected. However, patients are not expected to have high blood pressure. For this reason, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Shortness of breath after angiography
If shortness of breath, chest pain, fever and swelling of the area develop after the angioplasty procedure, urgent medical attention is required.
Nutrition after angioplasty
After the angioplasty procedure, patients need to pay more attention to their nutrition. Because heart diseases are closely related to nutrition. For this reason, it is necessary to seek help from a nutritionist if necessary and switch to a healthier and heart-friendly diet.







L** O** | 23 Feb 2025
G** T** | 06 Apr 2025