What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis, which is one of the most common diseases affecting the quality of life of patients, is also known as eczema. Permanent and recurrent attacks are observed, especially in the types seen from childhood onwards. Atopic dermatitis is also a harbinger of allergies.
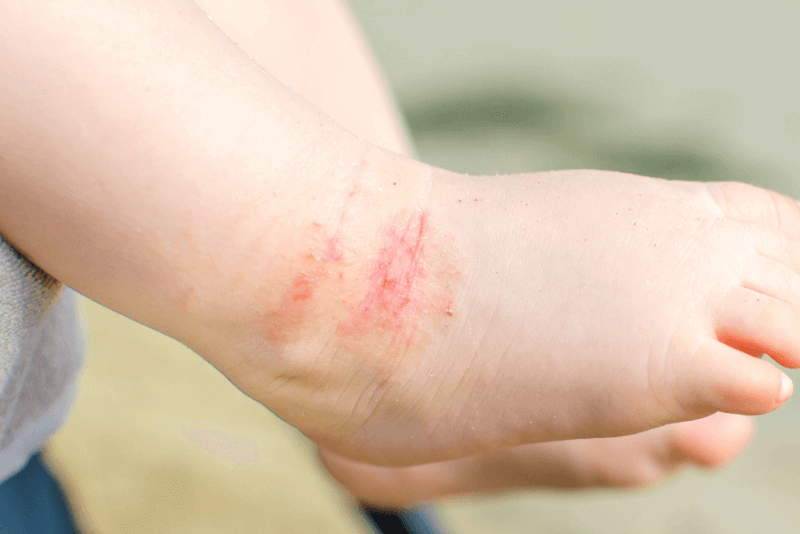
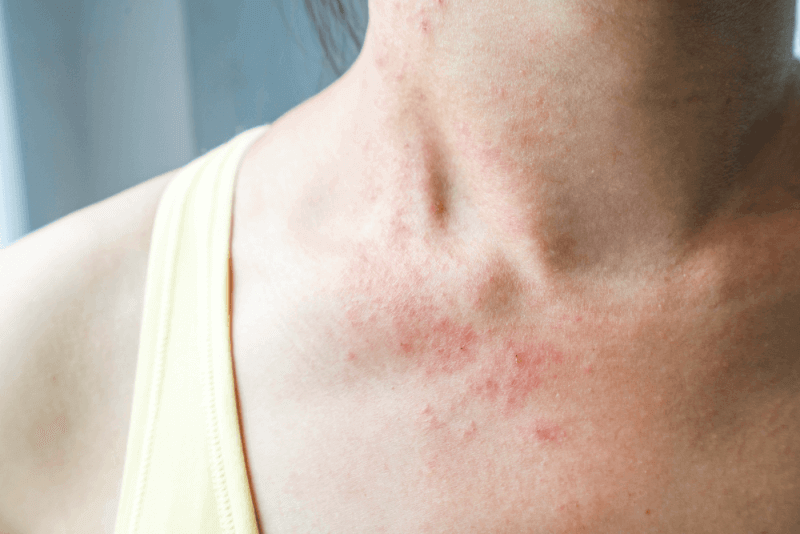
Usually seen in people with allergic constitution, atopic dermatitis is a disease characterized by itching, redness and dryness in various parts of the body. Atopic dermatitis, which is one of the chronic diseases, usually starts to be seen from childhood. Atopic dermatitis, which has an autoimmune origin, causes other autoimmune diseases such as hay fever and asthma in patients in the future due to this feature.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis occur in attacks. The spread and severity of the symptoms in the body varies according to the patient. Common symptoms include itching, very dry skin, redness, tenderness and, due to secondary infections, increased skin temperature, pain and discharge.
Symptoms appear on the scalp, arms, legs and cheeks in patients in infancy. With the advancing age of the patients, the symptoms begin to appear around the elbows, knees, neck and eyes. If the lesions are scratched, the tissues may harden and darken in color. In adult patients, widespread eczema and rashes may be observed with the influence of environmental factors.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
Studies on atopic dermatitis, one of the diseases with an unknown cause, have led to the discovery of some factors that are effective in the development of the disease. Since the skin integrity of patients with atopic dermatitis is impaired, certain environmental conditions facilitate the development of the disease. These are:
- Mold,
- Pollen
- Perfume,
- Physical stress,
- Emotional stress,
- Wool clothes,
- Synthetic clothing,
- Irritants such as mud, sand, smoke or dust,
- Factors that cause skin irritation, such as soap and detergents,
- Dry air
- The weather is too hot or too cold,
- Sweating
- Prolonged itching of the skin,
- Showering with very hot or cold water,
How is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Atopic dermatitis is usually diagnosed by physical examination. However, some tests can be used to rule out other allergic problems. Patients can also undergo a patch test to determine the cause of the allergy. If the allergen can be identified, avoiding these allergens in daily life makes it easier to control the disease.
Atopic Dermatitis Treatments
Current treatment methods are not able to cure atopic dermatitis. Instead, treatment is aimed at alleviating the symptoms and halting the progression of the disease. For this, lifestyle changes are recommended along with medication.
Medication Therapy
The first group of drugs used is the group of drugs used to reduce patients' complaints of itching. This treatment prevents patients from scratching the lesions, further destroying them and causing infections. The drug groups used for this are corticosteroid-containing drugs. These medicines, which are usually used as creams, can be supplemented with oral medicines if the itching is excessive. Antihistamines can also be added to these medicines.
In case of secondary infections, antibiotic treatment is also administered to patients. If cases do not respond to treatment, immunosuppressive drugs are used.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medication, patients should pay attention to some points even during periods without attacks. The first of these points is that the shower water should be warm. In addition, constant and regular moisturizing of the skin will also help reduce attacks. Another change that patients should make in their lives is to consume plenty of water. In addition, care should be taken to ensure that the air in the environment is humid. Patients should prefer loose and cotton clothes. In addition, if there is a known allergy, this allergen should be avoided.
Atopic Dermatitis Nutrition
Patients with atopic dermatitis should also pay attention to their diet. Because the food consumed also plays a role in triggering attacks. The main rules that patients should pay attention to in their nutrition are as follows.
- Fresh and unprocessed foods should be consumed,
- Application of the elimination method to determine which foods cause the reaction,
Milk
Milk and other foods derived from milk are the leading foodborne causes of atopic dermatitis. Although sheep and goat milk is better tolerated than cow's milk, caution should be exercised if patients have sensitivities.
Gluten
Patients should avoid gluten consumption. Gluten found in cereals can also be found in lentils, spices or oats.
Egg
Eggs are one of the biggest triggers of eczema. For this, patients are advised to consume goose or quail.
Soya
Consumption of soy and soy milk, which are often found in processed foods, should also be avoided.
Pistachio
Peanuts and peanut oil are the most common causes of allergy.
Nuts
Hazelnuts are generally well tolerated, but other nuts can cause allergies.