What is biotinidase deficiency?
Biotinidase deficiency is one of the genetically inherited diseases. The important point in biotinidase deficiency, which is a health condition that needs to be taken under control, is early diagnosis and rapid treatment. Because it poses a life risk if left untreated.
Biotinidase deficiency, also called BIOT, is when the body is unable to recycle or reuse the vitamin biotin. Biotin’s role in the body is to break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the food we take in. If biotin is deficient, there is less processing of macronutrients that are important for individuals.
There are two different variants of BIOT. Both types are life-threatening if left untreated. Since BIOT is a birth defect, it is examined during heel prick screening of newborns. By diagnosing and treating babies from the moment they are born, it is possible for them to continue their normal development.
Types of biotinidase deficiency
Biotinidase deficiency is divided into 2 main types. BIOT varies because the severity of symptoms varies.
Deep biotinidase deficiency
BIOT is used to describe a severe form of the disease. In children with deep biotinidase deficiency, symptoms such as developmental delay, respiratory problems, poor muscle tone, vision loss, balance and movement problems, hair loss, skin problems and vision loss are observed. In particular, children in this group face serious risks such as coma and life-threatening conditions if they do not receive treatment.
Partial biotinidase deficiency
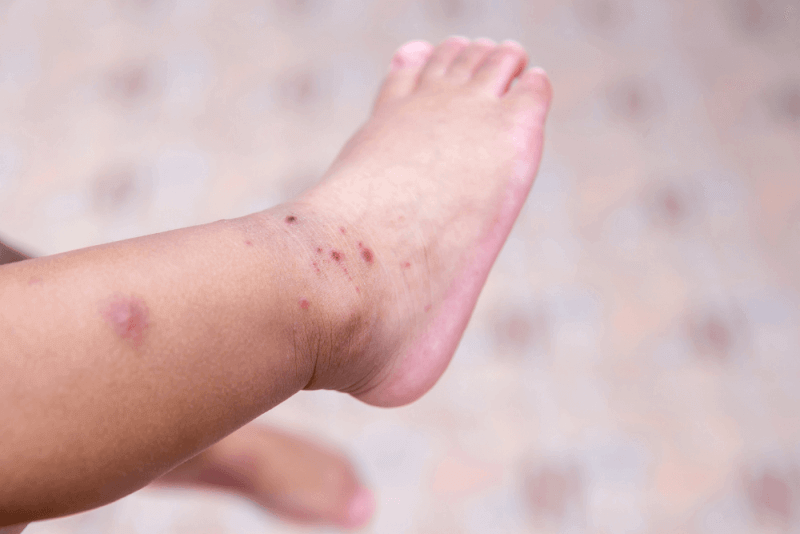
In this form of biotinidase deficiency, the symptoms are milder. Untreated patients with partial biotinidase deficiency experience hair loss, poor muscle tone and skin rash. In some patients, these symptoms occur during stressful times or with infections.
Biotinidase deficiency diagnosis
Babies are tested at birth to determine whether they have biotinidase deficiency. If the result of this heel prick test is out of range, the pediatrician will order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis.
However, BIOT can be difficult to diagnose because it is a genetic and rare disease. For this, specialists order additional tests. These tests include the following:
- The Genetic Testing Registry, called GTR, provides information for this disease. It is especially instructive for healthcare providers and researchers.;
- The protocol to be followed for infants with the possibility of BIOT in neonatal testing has been established. Experts should proceed in accordance with this protocol.
Symptoms of biotinidase deficiency
The symptoms of BIOT vary depending on the variety. The type of BIOT with severe symptoms is called profound biotinidase deficiency, while the type with mild symptoms is called partial biotinidase deficiency.
The first symptoms of BIOT usually start a few months after birth. In some patients, symptoms do not appear until early childhood. Therefore, it is important to perform BIOT screening in the neonatal period.
Early symptoms of BIOT include the following:
- Seizures
- Generalized myoclonic seizures
- Metabolic ketoacidosis
- Poor muscle tone
- Baldness
- Ataxia
- Difficulty breathing
- Skin rash
- Hair loss
- Loss of balance
- Candidiasis fungus
- Skin wounds
- Developmental delay
- Hearing disorders
- Visual disturbances
Causes of biotinidase deficiency
Biotinidase, which is involved in the breakdown and decomposition of nutrients entering the body, makes it possible to reuse and recycle vitamin biotin. Biotin is involved in the breakdown of macronutrients in the diet.
In the case of BIOT, not enough biotinidase is produced in the body or the biotinidase produced does not work. In this case, biotin cannot be recycled. In the absence of biotin in the body, carbohydrates, fats and proteins in food begin to accumulate in the blood.
BIOT is a genetic disease. For a child to be born with BIOT, both the mother and the father must be BIOT carriers. People who are carriers of BIOT do not recognize it because it is asymptomatic. Although it is unlikely that both parents are BIOT carriers, it is possible for BIOT carrier couples to have more than one child with BIOT.
Treatment of biotinidase deficiency
Vitamin biotin is used to treat biotinidase deficiency. Although it is normally present in foods, this amount is insufficient for children with BIOT. For this reason, patients must use vitamin biotin throughout their lives. The correct dose adjustment is made by the physician.