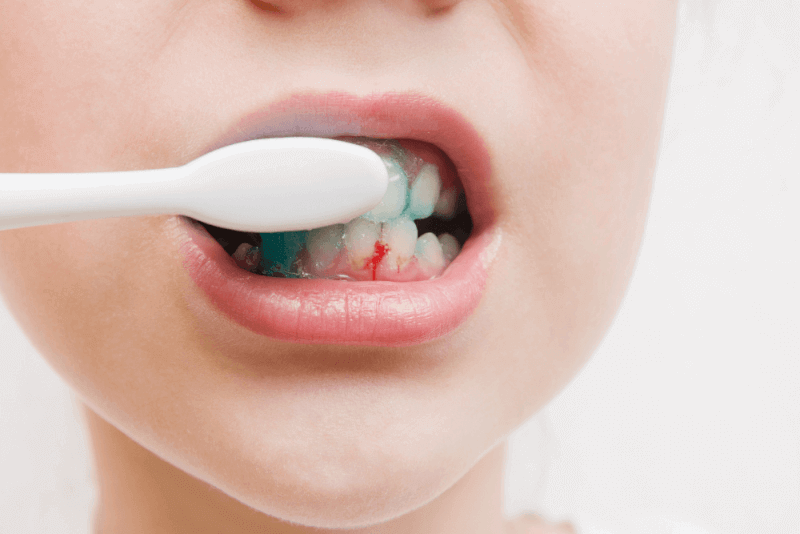
The gums are a connective tissue extremely rich in blood vessels. For this reason, in case of any damage, the connective tissue is damaged and bleeding gums occur.
Symptoms Accompanying Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums occur as a result of various oral health problems. In some cases it is the first symptom to appear, while in other cases it is accompanied by concomitant symptoms. Symptoms that can be seen with bleeding gums are as follows.
- Bad breath that cannot be eliminated despite brushing the teeth,
- Incomplete fit of the partial denture,
- Pain during chewing,
- The development of plaque, inflammation or tartar between the tooth and gum,
- Distortion of the bite structure,
- Movement or loosening of the tooth,
- Gum recession,
- Separation of tooth and gum,
- Edematous, red, swollen and sensitive gums
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can be a harbinger of serious health problems or can be seen in healthy individuals due to physiological conditions. The factors that cause bleeding gums are as follows:
Oral Hygiene Habits
The most common cause of bleeding gums is oral hygiene habits. It occurs when individuals brush their teeth hard or use a hard toothbrush, brush their teeth with excessive pressure and the wrong technique. In addition, incomplete oral hygiene and the use of different oral health products or techniques can also cause bleeding gums.
Dentures
In people whose prosthetic teeth do not fully adapt to the oral structure, prostheses damage the gums and cause bleeding.
Pregnancy
Hormonal changes in women during pregnancy cause increased edema in the gums and more blood supply to the gums. This makes the gums more prone to bleeding.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis, inflammation of the gums, occurs for various reasons and makes the gums fragile. This causes bleeding in the gums.
Periodontitis
Inflammation of the tissue that connects the tooth to the gums and the surrounding jawbone. Periodonitis, caused by causes such as gingivitis or tooth decay, causes damage to the gingival palate and bleeding gums.
Bleeding Disorders
Various reasons, such as low thromboacid counts in the blood or hemophilia, cause the gums to be more prone to bleeding. These diseases cause the gums to bleed severely even with mild impacts.
Diabetes
The tissues of people with diabetes are more prone to bleeding. This also affects the gums and bleeding gums are more common in diabetics.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiency of vitamins K and C causes gingival bleeding to occur more intensely and frequently. Vitamin K has a role in regulating bleeding and vitamin C has a role in gum health.
Dietary habits
When individuals consume foods that can damage the gums, the gums are damaged. to see it. Improper consumption of hard or crusted foods often causes bleeding gums.
Cigarette Use
Smoking causes damage to the gums and therefore makes them more prone to bleeding.
Blood Diseases
Blood diseases cause a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood, making the gums prone to bleeding.
Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases such as liver or kidney failure can cause bleeding disorders.
Side Effects of Medicines
Gum bleeding is a side effect of many medications, especially blood thinners such as coumadin or aspirin.
How is Bleeding Gums Diagnosed?
Bleeding gums are usually a consequence, not a cause. For this reason, it is among the symptoms of many health problems. In order to prevent this result, it is necessary to get help from a specialist and ensure oral hygiene. Bleeding gums can be easily detected by a physical examination performed by the dentist. During this examination, it is important for patients to also mention any additional complaints.
Gum Treatment
The first step in gum treatment is to ensure regular dental hygiene. If there is a previously diagnosed dental problem, patients should continue their regular check-ups. Individuals brushing their teeth with the right techniques and flossing correctly will minimize the formation of plaque, which will reduce the risk of bleeding gum
Antiseptic mouthwashes are used in the treatment of bacterial infections that often cause bleeding gums. In addition, regular gargling with warm and salty water will also provide relief for the gums.
People with bleeding gums should pay attention to the toothbrushes they use. These people should pay attention to the soft tip. In addition, electric toothbrushes are more effective in ensuring oral hygiene and preventing pressure.
If gingival bleeding is severe and this interferes with patients’ daily lives, nutrition and oral hygiene, then medication is administered. Mouthwashes, special toothpastes and painkillers are used for this. If the dentist’s recommendations are followed, bleeding gums heal in a short time.