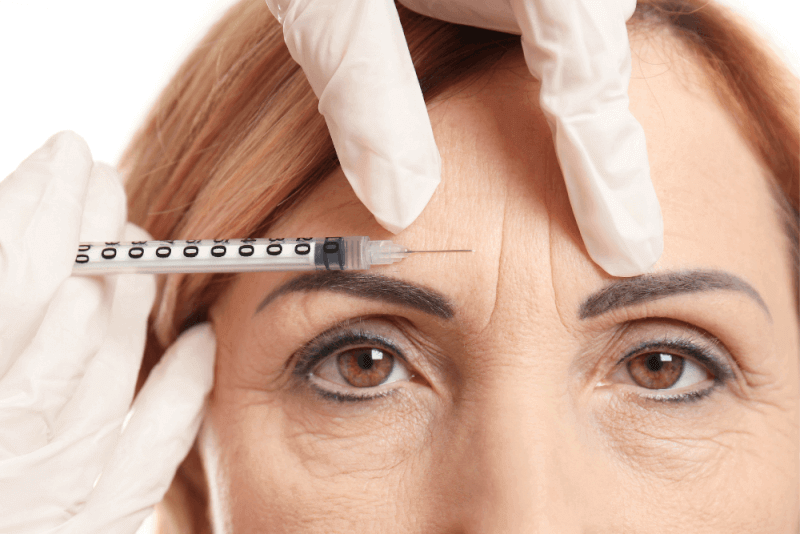
What is Botox?
Botox, which prevents the targeted muscle from moving for a certain period, is commonly used to remove facial wrinkles. It also has other applications such as treating migraines, preventing sweating, and managing an overactive bladder.
The drug used in Botox injections is derived from a toxin called botulinum, which can cause food poisoning. However, forms of botulinum toxin purified by experts meet medical standards, making bacterial toxins used for medical purposes safe.
Botox applications help alleviate symptoms associated with some health issues. However, these procedures do not cure the underlying health condition.
How does Botox work?
Botox works by blocking the signals from the nerves to the muscles. As a result, the injected muscle doesn’t contract, which helps wrinkles to relax and soften.
Types of Botox
The Botox toxin used in treatment is divided into two subtypes, each used for different purposes in various areas. The following are types of Botox toxin:
Type A Botox
Type A Botox is generally used to eliminate wrinkles on the face.
Type B Botox
Type B is used for injections into muscles, such as in cases of neck spasms.
Botox Types by Area
Botox can be applied to various areas of the body for different purposes. The most commonly treated areas include:
Jaw Botox
Jaw Botox refers to the injection of Botox into the chewing muscles. It is often used to treat teeth grinding issues, which can damage the teeth and jaw muscles. This is also known as masseter Botox.
Lip Botox
Lip Botox is the term for using Botox to smooth out wrinkles above the lips. Since the goal is to remove wrinkles, the injection is applied under the skin.
Eyebrow Botox
Also known as brow lift Botox, this procedure is performed to give the eyebrows a more youthful appearance. By temporarily paralyzing the eyebrow muscles, Botox allows the eyebrows to appear more lifted.
Facial Botox
Facial Botox is the use of Botox toxin to reduce wrinkles caused by repetitive facial expressions.
Glabellar Botox
Glabellar Botox is applied to remove deep wrinkles between the eyebrows, helping to control the muscles. By keeping the eyebrows still, this treatment not only eliminates existing wrinkles but also prevents new ones from forming.
Eye Area Botox
Eye area Botox is used to eliminate wrinkles at the corners of the eyes.
Hand Sweating Botox
Botox is used when sweating occurs despite not being hot or engaging in activities that cause sweating. This application is mainly used for the hands but can also be used for sweating problems in other areas of the body.
Migraine
Botox injections can help reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. Botox for migraines is typically applied to individuals experiencing migraine attacks that last more than 15 days. To benefit from this treatment, it needs to be repeated approximately every three months.
Eye Botox
The most common cause of lazy eye is an imbalance in the muscles used to move the eye. Lazy eye can also lead to strabismus.
Cheek Botox
There is no specific type of Botox applied directly to the cheeks. However, in procedures aimed at giving the face a V-shape, Botox is applied to the lower part of the cheeks.
Crow’s Feet Botox
Also known as eye area Botox.
Masseter Botox
Also known as jaw Botox.
Neck Spasms
Botox is also used for neck spasms, which involve uncontrolled muscle contractions that can cause significant pain. This prevents the head from turning into an uncomfortable position, a condition also known as cervical dystonia.
Other Muscle Spasms
Cerebral palsy and other neurological diseases can cause limbs to pull towards the center of the body. Botox injections are used to alleviate these muscle contractions.
Botox Application
Botox applications typically do not cause much pain. However, if applied to the hands or feet, the pain can be significant, in which case local anesthesia may be used. Anesthesia can be applied using ice or massage.
Botox applications are performed in a clinical setting. Doctors apply the appropriate amount of Botox to the skin or muscles based on the patient’s needs, using a very fine needle. In some cases, ultrasound imaging is used to accurately guide the needle.
Botox Risks
Botox injections should be administered by licensed doctors. However, the procedure is not always performed by licensed individuals, which can lead to improper application and potential harm. Possible side effects of Botox include:
- Swelling, pain, and bruising at the injection site
- Infection
- Headache or flu-like symptoms
- Drooping eyelids
- Tearing
- Dry eyes
- Asymmetrical eyebrows
- Crooked smile
- Drooling
Additionally, Botox may spread to areas of the body where it shouldn’t go, causing symptoms in those areas. Therefore, side effects can appear hours or even weeks after the procedure. If any of the following symptoms occur after a Botox procedure, it is necessary to consult a doctor:
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty speaking
- Vision problems
- Difficulty swallowing
- Breathing problems
- Loss of bladder control
- Allergic reaction
Botox Side Effects
Some temporary side effects may occur after Botox injections. These side effects include:
- The most common side effect is bruising.
- Headaches typically resolve within 24 to 48 hours.
- Drooping eyelids resolve on their own within 3 weeks.
- Crooked smile
- Dry eyes
- Drooling
- Severe tearing
- Mild pain or swelling at the injection site
- Flu-like symptoms
- Nausea
- Weakness in nearby muscles
Who Should Not Have Botox?
Botox is generally a safe procedure. However, it should not be used on pregnant or breastfeeding women, or individuals with neurological disorders. Additionally, people who are allergic to cow’s milk protein should avoid Botox.
How Long Does Botox Take to Settle?
The results of Botox injections start to become visible within 1 to 3 days after the procedure, but it can take a week or longer for full effects to be seen.
Depending on the treated issue, the effects may last 3 to 4 months. To maintain the effect, it is necessary to repeat the treatment at least every 3 months.
Post-Botox Care
After a Botox procedure, it is important to follow certain guidelines:
- The treated area should not be rubbed or massaged on the first day after the procedure.
- Avoid lying down for 2 to 4 hours after the injection to prevent the Botox from spreading to unwanted areas.
Factors That Reduce Botox Effectiveness
Several factors may cause the effects of Botox to wear off more quickly. Therefore, it is important to be mindful of these factors after the procedure. With proper care, the results can last longer.
- Do not bend down for a few hours after the injection to allow the toxin to settle.
- Do not wrinkle the skin in the treated area.
- Applying too much pressure to the treated area after the procedure can prevent the Botox from settling.
- Excessive physical exercise after the procedure can cause the Botox to spread to unwanted areas.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
- Protect the treated area from sunlight.
- Do not apply excessive heat to the treated area.
- Avoid using aspirin and blood thinners after the procedure.
- Do not apply makeup for at least 1 week after the procedure.
- Consult a doctor if any issues arise during the recovery period.
Botox Swelling Process
A slight swelling may occur after a Botox procedure. This is expected and usually resolves on its own within 24 to 48 hours.
Where is Botox Used?
The areas where Botox is commonly used include:
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Jaw pain
- Neuralgia
- Sciatic pain
- Neuropathy
- Pelvic pain
- Chronic myofascial pain
- Osteoarthritis
- Joint pain
- Jaw joint pain
- Strabismus
- Excessive muscle contraction
- Excessive sweating
- Eyelid twitching
- Chronic migraine
- Overactive bladder
- Pediatric upper limb spasticity
- Adult spasticity
- Blepharospasm
- Cervical dystonia