What is Colposcopy?
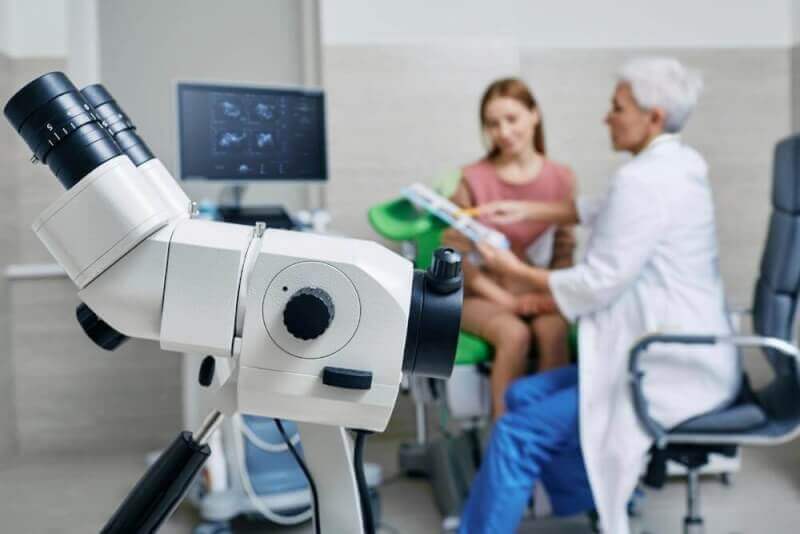
Colposcopy is a procedure used to examine the cervix with a medical device that has a light and magnification feature of up to 40 times. This allows for a clearer assessment of the cervix. The colposcope, which resembles binoculars, helps in identifying signs that cannot be seen with the naked eye during a gynecological examination. If a suspicious area is detected during the evaluation of the vagina, a colposcopic biopsy can also be performed.
Why is Colposcopy Performed?
Colposcopy is one of the methods used for diagnosing gynecological diseases. It is particularly important in the diagnosis of early-stage cancers. Colposcopy is especially used in the diagnosis of cervical cancer, which may not present clinical symptoms. Due to its slow-progressing nature, cervical cancer can be evaluated more comfortably with colposcopy. Other conditions where colposcopy is used include:
- Vulvar cancer
- Abnormalities detected during a smear test or pelvic examination
- Vaginal cancer
- Genital warts
- Precancerous changes of the vulva
- Cervical inflammation
- Cervical cancer
- Evaluation of suspicious lesions on the vulva
- Persistent itching of the vulva
- During pregnancy
- Before performing surgery on the cervix
- To diagnose the cause of infertility
Conditions Requiring Colposcopy
The colposcopy procedure, used for examining the inner wall of the cervix and vagina, is applied to detect the following health issues.
Detection of Cancer Cells in the Cervical Region
It is used for the early diagnosis of cervical cancer when there are abnormal results from Pap and smear tests. Additionally, samples are taken from the cervical canal. If abnormal cells are detected in the biopsy samples taken, additional procedures may be carried out to remove the abnormal structures from the area.
Other Tumors Detected in the Cervical Region
Colposcopy is one of the most important diagnostic methods, particularly in detecting benign tumors called cervical polyps. It also helps in diagnosing tumors found in the glands in the cervical region. This and other tumors are then treated accordingly.
Vaginal Tumors
It is used to detect polyps and benign or malignant tumors in the vaginal wall.
Bleeding and Pain After Sexual Intercourse
Colposcopy is performed when post-coital bleeding, especially if it resembles broth, raises suspicions of cervical cancer. It is also used to detect other health issues that may cause these symptoms.
Genital Warts
Genital warts caused by HPV infection can also spread to the cervical and vaginal canal. The colposcopy method is used to detect these warts.
Cervical or Vaginal Infections
Colposcopy is also used to diagnose infections that may occur in the cervix and vaginal canal due to various reasons.
How is Colposcopy Performed?
Before performing colposcopy, patients should be informed about the procedure and the reasons for it. There are certain points that patients need to be mindful of before the procedure. These include:
- Avoid vaginal douching within 24 to 48 hours before the procedure.
- Do not use tampons.
- Discontinue the use of vaginal medications.
- Avoid sexual intercourse.
- Patients using blood thinners or those with bleeding disorders should inform their doctor. As a biopsy may be needed during the procedure, complications related to bleeding should be prevented.
- Patients who may be pregnant should also consult their doctor before undergoing the procedure.
The colposcopy procedure takes a maximum of 20 minutes. No anesthesia is required during the procedure. The patient is seated on a gynecological examination chair in a position called lithotomy. The doctor begins by inserting an instrument called a speculum into the vagina, which stretches the vaginal wall to allow a clear view of the cervix. The colposcopy device is then placed a few centimeters away from the vulva.
During the procedure, the cervix wall, vagina, and tissues are cleaned with special solution-soaked cotton. Additionally, the doctor may use various staining methods. This allows the abnormal cells to be distinguished from the healthy ones.
Tissue samples are taken from the stained tissue area and the canal opening into the cervix. These samples are then sent to the laboratory for examination. If necessary, a biopsy sample can be taken directly from the tissue. Mild bleeding is expected if a biopsy is taken. Therefore, the doctor takes the necessary steps to stop the bleeding.
Colposcopy usually does not cause pain for patients. However, some patients may experience discomfort and bleeding after the procedure. Pain relief medication can be used to alleviate discomfort. In addition, the area can be numbed to relieve discomfort.
If a vaginal biopsy is performed, patients may experience pain depending on the area where the procedure is performed. Patients do not feel pain when the procedure is done near the cervix. However, when the procedure is performed on lower areas, it may cause pain. Therefore, local anesthesia is applied first.
Post-Colposcopy Care
Colposcopy usually does not cause any complaints in patients. However, if a biopsy is performed, it can lead to bleeding or spotting. Patients may need 1-2 days to return to their normal lives after the biopsy.
Various methods are applied to stop the bleeding during the biopsy. Depending on the method used, brown discharge may occur. This is expected. Patients should avoid sexual intercourse for three days. After that, they can resume their normal activities. Pain relievers can be used if pain occurs.
What Does the Colposcopy Result Mean?
The results obtained from the colposcopy procedure are evaluated by the doctor, and necessary treatments are initiated accordingly. If the abnormal stained tissues were not completely removed during the biopsy, additional methods need to be applied. If cervical cancer development is suspected, early treatment procedures should be initiated. These procedures include:
- A cone-shaped layer of abnormal cells in the cervix is removed, a procedure known as conization.
- Cryotherapy involves the use of freezing gases like liquid nitrogen to treat the tumor. This method is also used for the treatment of genital warts.
- Finally, the LEEP method, similar to conization, removes the abnormal tissue in the cervix using electrocautery. During the procedure, a small portion of the cervical canal may also be removed to ensure the complete removal of abnormal cells.
Risks of Colposcopy
Colposcopy is a very safe procedure. However, although rare, some risks may occur due to the biopsy samples taken during the colposcopy. These risks include:
- Groin pain
- Heavy bleeding
- Infection
If any of the following occur after colposcopy, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Unusual bleeding during menstruation