30-Second Summary
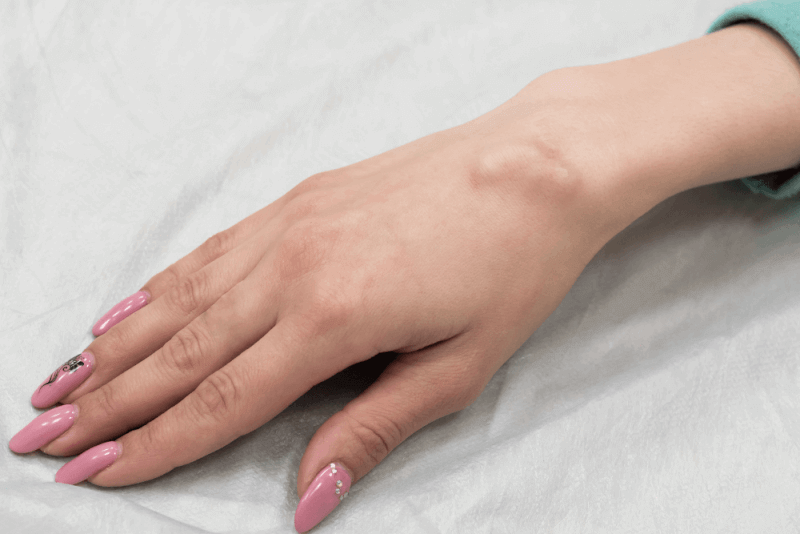
- Lumps that usually appear along the tendons or joints of the wrists and hands are called ganglion cysts. They may also occur in the ankles and feet.
- If ganglion cysts press on nearby nerves, pain may occur. In some cases, movement may also be affected.
- The cause of ganglion cysts is unknown. They grow from the lining of a joint or tendon and resemble a small water balloon on a stalk. The cysts contain a thick fluid, which may also be found around tendons or joints.
- Although they are most common in women between the ages of 20 and 40, they can occur in individuals of any age or gender.
What Is a Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst?
Lumps that usually appear along the tendons or joints of the wrists and hands are called ganglion cysts. They may also occur in the ankles and feet. These cysts are oval or round in shape. These tissues are not cancerous and are filled with a jelly-like fluid.
Smaller ones are about the size of a pea, but their size varies among patients. If ganglion cysts press on nearby nerves, pain may occur. In some cases, movement may also be affected.
If the cyst causes problems, the doctor may recommend draining it with a needle. It is also possible to surgically remove the cyst. However, if the cyst does not cause any problems, treatment is not recommended. Cysts typically enlarge and shrink, and some disappear on their own.
What Causes a Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst?
The cause of ganglion cysts is unknown. They grow from the lining of a joint or tendon and resemble a small water balloon on a stalk. The cysts contain a thick fluid, which may also be seen around tendons or joints.
Risk Factors for Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst
Risk factors that may lead to ganglion cyst formation include:
- Although they are most common in women between the ages of 20 and 40, they can occur in individuals of any age or gender.
- Wear or tear from arthritis in the joints closest to the fingernails increases the risk.
- Injured joints or tendons have a higher likelihood of developing a ganglion cyst.
Symptoms of Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst
Common features of ganglion cysts include:
Location
Ganglion cysts typically develop along the tendons or joints of the wrists or hands. The next most common location is the ankles and feet. These cysts grow near joints.
Shape and Size
Ganglion cysts are round or oval in shape. Some are too small to be felt externally, while others are larger. Therefore, sizes may vary. Joint movement influences the growth of cysts.
Pain
Patients often do not feel any pain. However, the cyst may press on nerves or other tissues. As a result, patients may experience numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness.
Diagnosis Criteria for Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst
During physical examination, the doctor may apply pressure to the cyst to determine whether it causes pain. Shining light on the cyst helps determine whether it is solid or fluid-filled.
Imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI are used during diagnosis. These tests also help detect conditions like arthritis or tumors. Additionally, fluid can be drawn from the cyst with a needle. If it is a ganglion cyst, the fluid will be thick and clear.
Treatment Methods for Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst
Ganglion cysts usually do not require treatment if they don’t cause discomfort. The doctor may suggest monitoring the cyst for changes. If the cyst causes pain or affects joint movement, various treatment options may be recommended.
Restricting Joint Movement
Joint mobility can cause ganglion cysts to grow. Therefore, a brace or splint may be used to immobilize the joint for a period of time. As the cyst shrinks, it may relieve pressure on the nerves and reduce pain. However, prolonged use of a brace or splint may weaken nearby muscles.
Aspiration of the Cyst
To drain the cyst, a needle is used to remove the fluid inside. However, the cyst may return afterward.
Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst Surgery
If other approaches do not work, surgery becomes an option. Surgery involves removing the cyst and its stalk that connects it to the joint. In rare cases, surgery may damage nearby nerves, blood vessels, or tendons. The cyst may also return after surgery.
Surgical Methods for Ganglion Cysts
These surgeries, called ganglionectomy, use arthroscopic surgery to remove the cyst, stalk, and surrounding area. If minimal invasion is not sufficient, a larger incision may be required. Both methods are outpatient procedures.
Benefits of Ganglion Cyst Surgery
Ganglion cyst surgeries help relieve pain and improve restricted movement in patients.
Complications of Ganglion Cyst Surgery
Complications in ganglion cyst surgeries are extremely rare. However, surgery may potentially damage nerves, muscles, and tendons around the cyst.
What Happens If a Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst Bursts?
If the cyst is punctured by the patient or bursts on its own, serious health issues may occur. These include nerve damage and infection.
Recovery Process After Ganglion (Wrist) Cyst Surgery
The recovery period after ganglion cyst surgery typically lasts 2 to 6 weeks. A splint may be applied to protect the surgical site during this time. The chance of recurrence after surgery is less than 15%.
Types of Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are classified based on their location.
Wrist Ganglion Cyst
Cysts on the back of the wrist often disappear without treatment. Those on the front side of the wrist are commonly seen in young individuals or elderly people with arthritis.
Finger Ganglion Cyst
These cysts are usually located at the fingertip, just below the cuticle, and are known as mucous cysts. This type of cyst is more common in middle-aged or older adults.
Thumb Ganglion Cyst
These are rarer than ganglion cysts seen on other fingers. Movement of the thumb may cause locking or catching, as well as joint pain and stiffness.
Elbow Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion cysts in the elbows are extremely rare. They may limit joint movement and cause pain.
Foot Ganglion Cyst
Ganglion cysts may grow on the top of the foot or ankle. They often result from bone spurs or damage to joints or tendons due to arthritis.
Volar Ganglion Cyst
These are pea-sized lumps in the palm or base of the fingers. They can cause pain when gripping objects. Volar ganglion cysts usually appear suddenly and do not change in size. About half of the cases resolve without treatment.