What is a gastric balloon?
The gastric balloon, which provides a non-surgical solution to the problem of obesity, which is increasing rapidly all over the world, is extremely important in preventing complications caused by obesity as well as ensuring that patients reach their healthy weight.
Gastric balloon, which is one of the most frequently applied methods in obesity patients, especially in obesity patients where successful results cannot be achieved with diet and exercise, enables patients to reach their ideal weight in a short time.
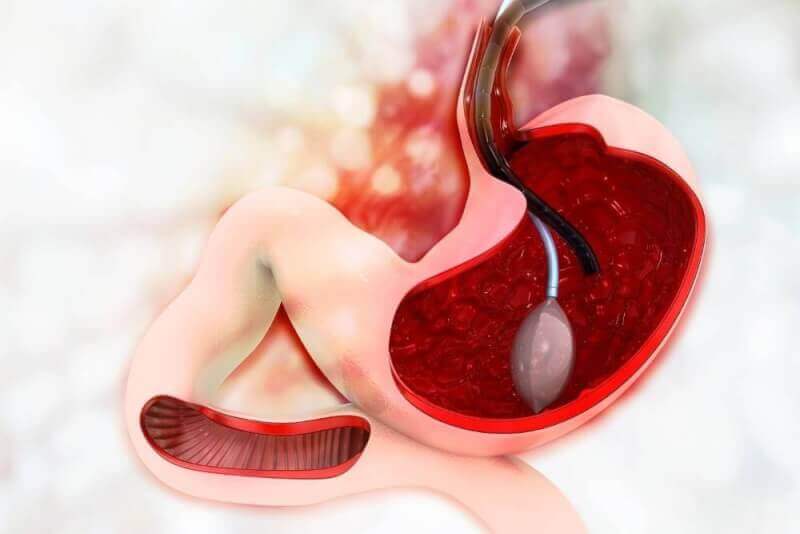
The gastric balloon, which is recommended for people with a body mass index above 30, has different types, but it is generally a silicone balloon with water inside. Gastric balloons, which are inflated after being placed in the stomach, enable patients to experience a feeling of satiety with less food by reducing their stomach capacity. In this way, the amount of calories taken in each meal is reduced and patients lose weight easily. No incision is required during the placement and inflation of the gastric balloon.
Who can have a gastric balloon?
It is not recommended to apply the gastric balloon to everyone with excess weight. For this reason, the most important criterion for gastric balloon application is the body mass index of the patients. Gastric balloon is not applied for people with a body mass index below 30 and above 40. However, in cases where the patient needs to lose weight in a short period of time in serious diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, these criteria are exceeded. In these cases, the expert makes the decision.
Who is not eligible for gastric ballooning?
Although the gastric balloon is a highly effective and event method in the treatment of obesity, it is not a method that can be applied to everyone. Among the people to whom the gastric balloon cannot be applied are the following.
- Alcohol and drug addicts
- Pregnant women and those planning a pregnancy
- People with serious heart, kidney and liver disease
- Previous stomach or esophageal surgery
- Those with a stomach hernia
- People with reflux
- People with stomach and duodenal ulcers
Types of gastric balloons
Gastric balloon is divided into types in terms of application method and features. There are basically 4 different types of gastric balloons used.
Medsil balloon
The Medsil balloon, also called 6-month gastric balloon, stays in the stomach for 6 months. The Medsil balloon placed in the stomach with endoscopic methods is inflated with liquid. The Medsil balloon, which has the highest level of tightness, also has a removal kit.
Orbera balloon
The Orbera balloon, which allows patients to lose between 9 and 14 kilograms on average, allows approximately ¾ of the stomach to be filled. Obera, which contains saline in a silicone balloon, is also inserted into the stomach by endoscopic methods. Then, depending on the size of the stomach, an amount of saline water ranging from 400 to 700 ml is injected to inflate the balloon. The duration of the Obera balloon in the stomach is limited to 6 months.
At the end of the 6th month, the balloon must be removed. The body mass index required for the application of the Obera balloon is between 30 and 35. If it is applied to people with a higher body mass index, the expected success may not be achieved. In addition, it is applied to patients with a lower body mass index if the physician deems it appropriate.
Spatz 3 balloons
The biggest feature that distinguishes the Spatz 3 gastric balloon from others is its 1-year usage period. In addition, it is sufficient for patients to have a body mass index above 27 for the application to be performed. For this reason, it can be easily applied to patients who are not suitable for other gastric balloon treatments.
Thanks to the ability to adjust its size during the treatment process, the risk of early intolerance seen in gastric balloon patients is also prevented. In cases where the gastric balloon causes complaints, patients can continue treatment by reducing its size in the stomach. In cases where weight loss stops during treatment, the volume of the balloon is increased so that it takes up more space in the stomach. In this way, patients continue to lose weight by eating less.
In addition to these advantages, the Spatz 3 gastric balloon eliminates the risk of intestinal obstruction and patients maintain their weight loss within the first 2 years after treatment.
Allurion ellipse swallowable balloon
Allurion Elipse, also known as swallowable gastric balloon, is the first method that does not require anesthesia and endoscopy. Although they work on the same principle as other gastric balloons, they are not inserted into the stomach by endoscopic methods.
Allurion Elipse is in capsule form and can be easily swallowed with water. After the patients swallow the capsule, it is checked by X-ray to see if the capsule is in place and then inflated with a thin tube. When the 16-week use of Allurion Ellipse expires, the valve on it is opened and the empty capsule is naturally excreted from the intestines.
Allurion Elipse has many advantages over other types of gastric balloons:
- Since it is made of polyurethane material, it has a smoother structure compared to other gastric balloons. Thanks to this structure, it has fewer side effects compared to other gastric balloon options.
- It allows patients to lose 10% to 15% of their weight.
- Idea balloon treatments are effective in the first 4 months. The duration of use of the Allurion Ellipse is also adjusted accordingly.
- Since no endoscopic procedure is required for both insertion into the stomach and removal, patients do not need anesthesia.
- The rate of patients maintaining their ideal weight within 1 year after balloon removal is 95%.
How is a gastric balloon inserted?
Except for the swallowable gastric balloon type, gastric balloons are placed endoscopically. However, patients should stop eating and drinking 6 to 8 hours before the procedure is performed.
Before the application, sedo anesthesia is applied by anesthesiologists so that the patients do not feel any discomfort. Sedo anesthesia is a type of anesthesia that prevents patients from feeling pain or pain without fully sleeping.
The stomach and duodenum of the anesthetized patients are first checked to see if there are any obstacles to the procedure. If the patient is suitable for gastric balloon application, the gastric balloon is delivered into the stomach by endoscopy.
The saline flask is then filled with saline stained with a substance called methylene blue. The volume of the balloon depends on the patient's weight and stomach size. The reason for sending blue water in the balloon is to ensure that patients can recognize this in their urine in case the gastric balloon is damaged and its contents are emptied.
The gastric balloon procedure takes approximately 20 minutes. The patient is then awakened and kept under observation for 2 to 3 hours. If all is well, the patient is discharged.
How to remove a gastric balloon?
Each type of gastric balloon has a specific duration of use. After this time, the balloon must be removed. If a swallowable gastric balloon is not used, the balloon must be removed endoscopically. Before this procedure, sedo anesthesia is applied so that patients do not feel any discomfort. However, patients should start a liquid diet 3 days before the removal procedure to clean the solid foods adhering to the balloon and continue this diet for 3 days.
In the gastric balloon removal procedure, the fluid in the balloon is drained first. After this process is carried out with a special apparatus sent inside the balloon, the gastric balloon is taken out of the stomach. After this procedure, which takes approximately 15 minutes, patients are awakened and kept under observation for 1 to 2 hours.
Harm of gastric balloon
Gastric balloon is not considered as one of the surgical procedures because it is applied with endoscopic methods. Therefore, the risks are very low. However, although rarely seen, gastric balloon applications have some risks.
Bleeding
As with all other operations, there is a risk of bleeding in gastric balloon procedures. However, although this risk is extremely rare, it is sufficient to act very slowly and carefully during entry and exit into and exit from the stomach to minimize the risk. If a sudden movement is made, the likelihood of bleeding increases. In case of bleeding, it is corrected with additional intervention treatments.
Anesthesia risks
Anesthesia itself is one of the factors that create risk. In order to minimize these risks, the health status of patients should be assessed. If patients have previously developed reactions due to anesthesia, the drugs used in anesthesia should be learned.
Leaking gastric balloon
The most feared gastric balloon risk is the bursting or leaking of the gastric balloon. Although it is a rare condition, it requires urgent intervention in case of an explosion.
In case of gastric balloon leakage, patients can see the blue color in their feces or urine, creating a chance for early intervention. In this case, it is necessary to intervene as soon as possible. Leakage can be prevented by intervention.
Vomiting and nausea
Vomiting and nausea, which are not among the harms of the gastric balloon but one of its side effects, can be seen in many patients. The immune system is activated by the presence of a foreign body in the stomach. However, nausea and vomiting last for 2 to 3 days. Rarely, this period is prolonged in some patients.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, one of the side effects of the gastric balloon, is seen in almost every patient. This pain, which is limited to a few days, also causes some patients to have difficulty digesting.
Benefits of the gastric balloon
It is one of the most frequently used methods in the treatment of obesity recently. The biggest reason for this is the advantages it provides to patients. These advantages include the following.
- Since it is not a surgical treatment method, patients are discharged within 3 to 4 hours.
- After the operation, patients return to their normal lives in a short time.
- Processing time is limited to 20 minutes.
- It is a reversible process.
- In case of an unexpected situation, the gastric balloon is easily neutralized.
- It does not affect any organs and has no effect on their function.
- It achieves results quickly with diet and exercises after the procedure.
- After removal of the gastric balloon, the stomach easily regains its former shape.
- It is more cost-effective than other operations.
- If the first application is not successful, it can be repeated.
Nutrition after gastric balloon
After the placement of the gastric balloon, patients need to make a serious change in their diet. This change should be planned by nutritionists. The diet usually applied after gastric balloon applications is as follows.
First 2 days
After the gastric balloon is placed in the stomach, patients should start drinking water sip by sip. Afterwards, you can start consuming herbal teas and fruit juice. Afterwards, milk, meat broths and grain-free chicken broth soup can be consumed.
It should be ensured that at least 1.5 liters of water is consumed in the first 2 days. However, small sips should be taken when consuming liquids and care should be taken that the drinks are not too hot or cold. Paying attention to these points will prevent symptoms such as cramps, nausea and bloating.
2 to 5 days
It is recommended that harvests consume soft foods on these days. The doctor's approval is required for the transition to soft foods. The soft diet includes vegetable and fruit purees, whole grains, meat, fish, olives, chicken, cheese, turkey. This plan should be planned by a dietitian.
Meat used in the diet should be passed through a blender. Meals should be eaten extremely slowly. For this reason, maximum time should be allocated to mealtimes. It is also important to ensure that meat products are cooked very well and that there is at least 1 hour between meals.
Gastric balloon diet
Although the diet applied during the adaptation period is general, the program prepared afterwards varies according to the patients. In achieving the desired results, it is extremely important to eat in accordance with the prepared program. However, the most important point that patients should pay attention to during this period is not to consume liquid and solid foods together. For this reason, liquid foods should be consumed at least half an hour before or after meals. If solid and liquid foods are consumed together, the volume of the stomach increases, putting pressure on the balloon.
Dietary considerations
As long as patients have a gastric balloon, there are some points that they should pay attention to in their nutrition, apart from their plans. Among these points are the following:
- Foods that increase stomach acid should not be consumed. These include all acidic drinks, fruits with high acidity, alcohol, vegetables that cause gas, and all foods cooked with unhealthy cooking methods.
- Urine should be monitored to adjust water consumption. At this follow-up, the urine color is expected to be light yellow. If the urine is dark in color, then it means that you are not drinking enough water.