What is gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea, one of the sexually transmitted diseases, is a bacterial disease. The bacteria that cause gonorrhea can infect the female reproductive system, urethra, mouth, throat, rectum or eyes. These bacteria, which are transmitted especially during oral, vaginal and anal sexual activity, can also be transmitted to babies during their birth. In infants, gonorrhea especially affects the eyes.
Gonorrhea in men
Gonorrhea is more common in people who were assigned male at birth. Symptoms caused by gonorrhea are also more common in men. However, in some cases it takes 1 to 2 weeks for symptoms to appear. Late onset of symptoms also increases the risk of transmission.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in men
Symptoms that can be seen in case of gonorrhea in men include the following.
- Yellow, green or white discharge from the penis
- Testicular pain
- Severe pain or burning when urinating
- Swelling of the testicles
Gonorrhea in women
People who were assigned as women at birth usually do not experience the symptoms caused by gonorrhea. For this reason, it is recommended that people get tested if they think they have been exposed to the bacteria that cause gonorrhea.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women
In cases where the symptoms of gonorrhea are seen, the most common symptoms are as follows.
- Unusual discharge of yellow or white color
- Bleeding between periods
- Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Pain and burning during urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
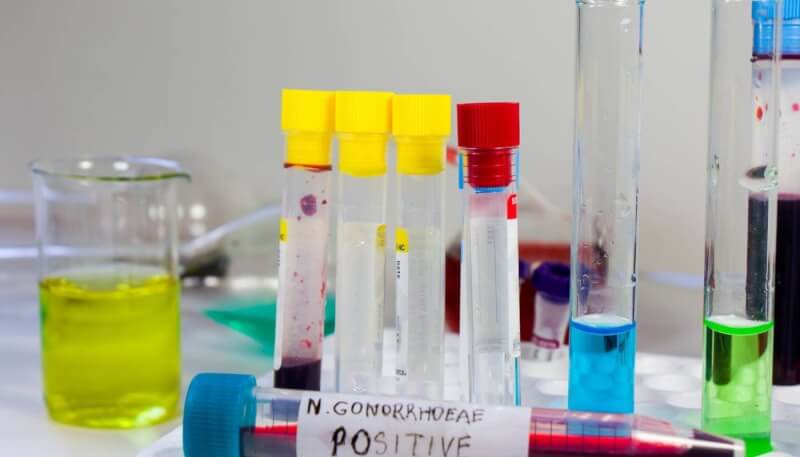
Diagnostic criteria for gonorrhea
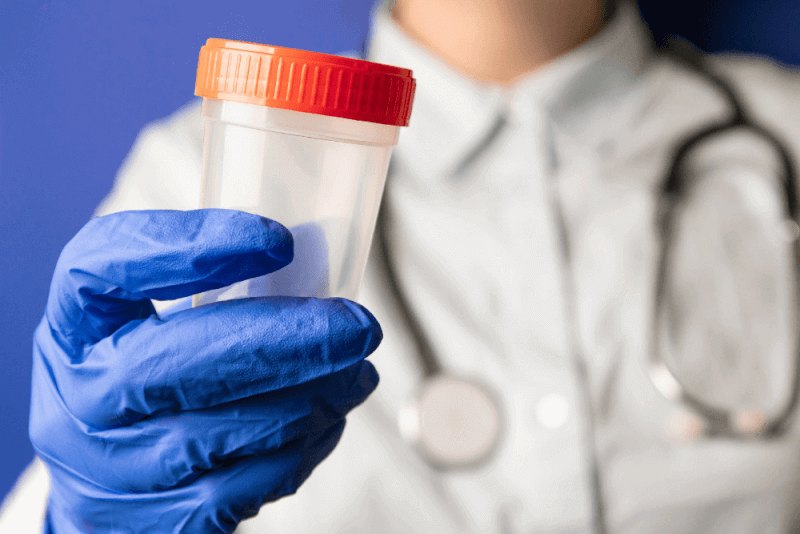
Cell sample analysis is required for the diagnosis of gonorrhea. These tests include the following.
- Urine test for identification of bacteria in the urethra
- Sample from the area affected by the bacteria causing gonorrhea
- In rare cases, a blood culture test is performed. However, this test is not conclusive.
Causes of gonorrhea
The bacterium that causes gonorrhea is Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The bacteria are transmitted from person to person during oral, vaginal and anal intercourse.
Gonorrhea treatment methods
Since gonorrhea is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are used in its treatment. However, it is recommended to treat it with the antibiotic ceftriaxone, as the bacterium becomes resistant to the drug over time. In this treatment, the antibiotic is injected as a single dose.
For 7 days after the injection of the antibiotic, patients can transmit the bacteria to their partners. For this reason, patients should avoid sexual intercourse during this period. 3. after treatment month, patients need to be retested. The reason for repeating the test is to check for transmission from new partners after treatment or from untreated partners.
Treatment for partners
In the case of gonorrhea, partners also need to be treated. For this reason, it is recommended that all partners with whom patients have had sexual intercourse in the last 60 days should be tested, even if there are no symptoms. In the case of gonorrhea in people who do not get tested, it spreads rapidly.
Treatment of gonorrhea in infants
Babies born to mothers with gonorrhea can be infected with the bacteria during birth and newborn babies can also get gonorrhea. Antibiotics are also used to treat these cases.
Ways of transmission of gonorrhea
The bacterium that causes gonorrhea is a bacteria that can be transmitted from person to person. The transmission route is the body fluids of the infected person. Transmission therefore occurs during oral, anal or vaginal intercourse.
Does gonorrhea go away on its own?
Symptoms caused by gonorrhea may go away over time. However, this does not mean that the patient is completely free of bacteria. For this reason, there is no spontaneous cure for gonorrhea.
Gonorrhea in other parts of the body
Gonorrhea does not only affect the reproductive system. Infection can also occur in the following areas
Rectum
Symptoms that can be seen if the bacteria causing gonorrhea infects the rectum include the following.
- Anal itching
- Pus-like discharge from the rectum
- Bright red color in the stool
- Difficulty during bowel movements
Eyes
Especially in infants, gonorrhea affects the eyes. However, the bacteria that cause gonorrhea can also infect the eyes in adults. Symptoms that can be seen when the eyes are infected include the following.
- Eye pain
- Photosensitivity
- Pus-like discharge from one or both eyes
Throat
Symptoms that can be seen when the bacteria causing gonorrhea infects the throat include the following.
- Sore throat
- Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck
Joints
The bacteria that cause gonorrhea can also affect patients' joints. If this situation occurs, the symptoms that can be seen include the following.
- Increased heat during movement in the affected joints
- Swelling of the joint
- Pain in the joints
Risk factors for gonorrhea
Among the factors that can lead to an increased risk of getting gonorrhea are the following.
- Men and women under 25 who are sexually active
- Having a new sex partner
- Previous history of gonorrhea or any other sexually transmitted disease
- Having a sex partner with other partners
- Having multiple sex partners
Complications of gonorrhea
If left untreated, gonorrhea can cause some serious complications. These complications include the following.
Infertility
Infertility is a complication in women and men with gonorrhea. It causes infertility in women because the bacteria spread to the fallopian tubes and uterus, causing pelvic inflammatory disease. This causes scar formation in the tubes, leading to increased complications in pregnancy and infertility.
The reason why gonorrhea causes infertility in men is that it causes inflammation of the epididymal tube, which is located behind the testicles and contains the sperm ducts. This inflammation is called epididymitis. Untreated epididymitis causes infertility in men.
Infection affects other parts of the body
The bacteria that cause gonorrhea can enter the bloodstream and infect different parts of the body. If this occurs, patients may experience fever, rash, stiffness and skin sores.
Increased risk of HIV/AIDS
People with gonorrhea become more susceptible to HIV. In addition, people with both gonorrhea and HIV can pass the infection to their partners more quickly.
Complications in infants
If gonorrhea is transmitted to babies during birth, they can develop scalp sores and infection, as well as blindness.
How to prevent gonorrhea?
In order to reduce the risk of getting gonorrhea, the following points should be considered.
- Using condoms during sexual intercourse
- Limiting the number of sex partners
- Testing both partners for sexually transmitted diseases
- Not having sexual intercourse with people who have sexually transmitted diseases
- Regular gonorrhea screening
What does not cause gonorrhea?
Although gonorrhea is a contagious disease, not all intimate behaviors can transmit the disease. Although it is often thought otherwise, it is not possible to transmit gonorrhea in the following cases.
- Kissing
- Hug
- Holding hands
- Sharing food or drinks
- Sharing the same kitchen utensils
- Sharing the toilet with others
- Inhalation of droplets after a sick person coughs or sneezes