What is Gout?
For many years, gout, also known as sultan's disease in both medical and colloquial circles, has been associated with irregular diet and excessive alcohol consumption. In fact, while there are different factors behind this disease, this disease, also known as rich disease, is a class of rheumatic disorders, but also among metabolic disorders.
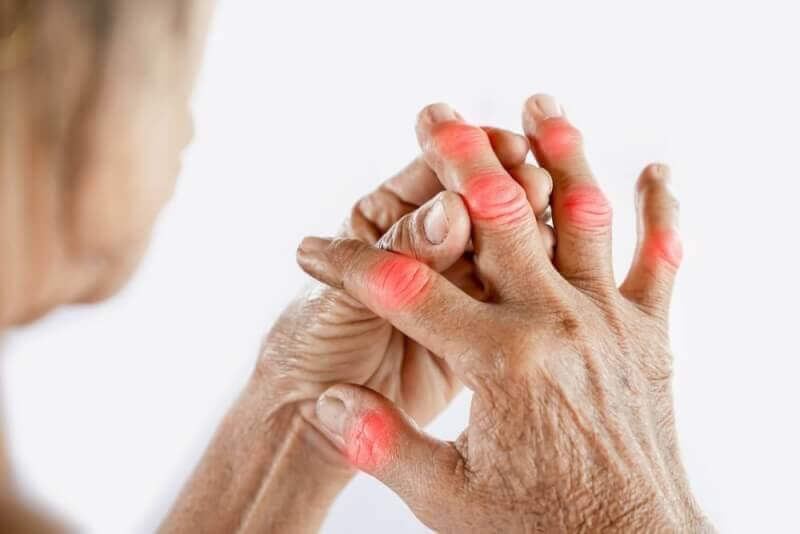
Gout is actually a very common joint inflammation that is clearly chronic in nature. This condition, which has been known since ancient times, is known as a rheumatologic disorder that can be controlled today, but it is seen with the accumulation of monohydrate crystals, called monosodium urate, in the organs.
Under normal conditions, after proteins are digested in the human body, some of the substances in them are converted into uric acid and excreted from the body through urine. If uric acid is not excreted adequately and is overproduced, it can build up in the blood and body. When this build-up reaches a high level in the joints, the inflammatory condition is called gout.
What is pseudogout?
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease is commonly referred to as pseudo-gout. A variant of this disease, abbreviated CPPD, which causes calcium to build up in the joints, is called pseudo-gout. However, CPPD is a much broader disease. This variety is so named because it causes complaints similar to gout.
CPPD basically has 4 different types. Among these, Aseptomic CPPD causes no complaints in patients and therefore calcium deposits are incidentally seen on joint radiographs. In the type of osteoarthosis with CPPD, patients complain of arthrosis and calcium deposits are seen on radiographs. The chronic form of CPPD causes involvement of one or more joints and is characterized by chronic symptoms that can last for months. It also has inflammatory symptoms. In addition, acute CPPD is a type of gout whose symptoms are similar to those of gout and is therefore misdiagnosed as gout. This form, also called pseudogout, is characterized by joint inflammation. However, pseudogout differs from gout in that calcium crystals deposited in the joints initiate the inflammation. People with this disease may have involvement of more than one joint and symptoms may last for months. In addition, the involvement of the joints can also impede their movement.
What are the Symptoms of Gout?
Although it is a disease that develops without causing very intense symptoms, the discomfort that becomes severe in gout can cause deformation in the body. Although different symptoms may occur in each patient, they are among the common symptoms of gout;
-
There are joint pains that occur during attacks of the disease and are followed by severe pain. These pains may develop depending on the duration of the attacks.
-
Gout, especially in the big toe joint, can also occur in other joints. Although it is generally seen in the ankle, elbow, knee, wrist and finger joints, intense joint pain that can last up to 12 hours can be experienced in all these joints.
-
Another symptom is swelling and redness in the joint areas during attacks. However, restriction in joint movements may be encountered in progressive diseases.
Who Has Gout?
Gout is more common in men than women in all populations. When we look at the likelihood of developing the disease, it is more prominent in advanced ages, while the probability increases at high ages such as 75 years. In women, gout is generally more common after menopause.
How is Gout Diagnosed?
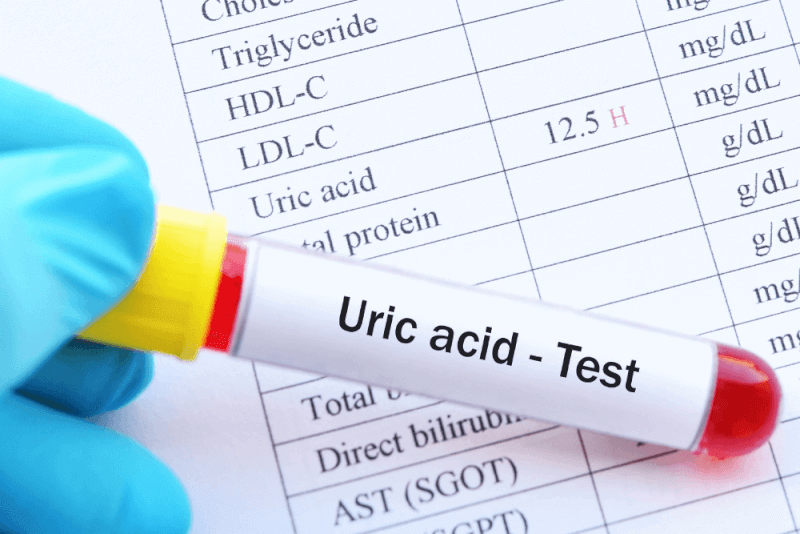
Gout, unlike many other diseases, cannot be diagnosed with a practical blood test. This is because high uric acid levels, the main cause of the disease, can occur for many different reasons. In this context, in order to diagnose gout, fluid is taken from the joint where the disease is suspected to be present and pathological examination is performed in this fluid.
The joint fluid is examined under a polarized microscope for the presence of monosodium urate crystals. In addition, different methods such as blood tests, X-rays, ultrasound and MRI are used to diagnose gout. Gout causes weakness in the joints where it settles and can cause joint damage after a long period of time. Therefore, a correct diagnosis is absolutely necessary.
Blood Test
When the disease is suspected, a blood test is performed to measure the levels of uric acid and creatinine in the blood. However, sometimes the test results can be misleading and the patient cannot be directly diagnosed with gout even if they have a high uric acid level.
X-ray
In addition to the diagnosis of gout, this method is also used to detect different diseases that can actually cause joint inflammation.
Ultrasound
In order to examine the musculoskeletal joints that may be associated with gout, ultrasound can be used to visualize inflammation and urate crystals at these points.
MR
With the use of magnetic resonance imaging, urate crystals in the suspected joints can be clearly seen.
Gout Treatment
In order to establish a treatment for the disease, it is necessary to identify the factor that increases the amount of uric acid. In this respect, firstly, the disease is diagnosed and then the uric acid level is measured depending on the diagnosis. If patients have a uric acid level above 7 mg/dl, a definitive diagnosis is made with the specified diagnostic methods.
Once a definitive diagnosis has been made, the acute period in which the person is in for the treatment of gout is taken into consideration. This is because gout is characterized by certain stages of the disease. If these phases are briefly mentioned;
-
In the acute attack phase, the disease suddenly appears in the joints and lasts for about 5-10 days.
-
In the intercritical attack phase, the symptoms are gone. However, attacks may occur again afterwards.
-
In the chronic gout stage, the interval between two attacks is now progressively shorter and requires prompt treatment. Otherwise, one or more joints may become permanently swollen and painful.
-
In the so-called tofus gout stage, uric acid begins to accumulate in the surrounding tissues as well as the joints and swellings called tofus appear. This complication, called tofus, can occur particularly at the points of the metacarpal bone, the upper part of the fingers, elbows and big toes.
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used in new attacks, given the stages of the disease. After the acute phase is over, the patient is prescribed gout medication on a regular basis. The main purpose of medicines is to support the removal of excess uric acid from the body and to reduce the production of uric acid. In addition to drug treatment, patients should be provided with nutritional and lifestyle adjustments along with doctor control for the treatment of gout.
Gout medication
Drugs used in the treatment of gout are prescribed to control attacks. In addition, various medications are prescribed to prevent future attacks.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
This group of medicines, also called NSAIDs, includes over-the-counter medicines such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium, as well as more powerful prescription medicines such as indomethacin and celecoxib.
Colchicine
Colchicine, an anti-inflammatory drug that provides rapid relief of gout pain, is one of the drugs used in the treatment of gout. However, the medicine has side effects such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
Corticosteroids
It is a group of medicines to control gout inflammation and pain. It can be used orally or injected into the joint. Side effects of corticosteroids include increased blood pressure, mood changes and increased blood sugar levels.
Gout Diet
In the treatment of gout, an appropriate diet program should be prepared specifically for each patient. Diet programs reduce the number of attacks and normalize uric acid levels. In particular, alcohol intake is completely cut out in this diet program. Increase fluid consumption, prefer healthy milk consumption and ensure a protein-based diet.
In the gout diet, quality carbohydrates are preferred for carbohydrates, and frequent and small food consumption is ensured. Fruits and vegetables with natural sugars are selected, fermented foods are abandoned, natural fats are used. While purine-containing foods are preferred in this diet program, potatoes, peas, green leafy vegetables, eggplant, eggs, nuts, coffee, tea, green tea and vegetable oils can be found.
What people with gout should eat
Gout is one of the diseases directly affected by diet. For this reason, patients need to regulate their diet. Within these dietary patterns, foods that will cause gout to progress should be removed, while foods that will reduce uric acid should be added to the diet. Patients should also follow generally accepted healthy dietary guidelines and maintain a healthy weight. Among the foods that gout patients should consume are the following:
- Apple cider vinegar
- Celery
- Lemon juice
- It is important to consume mineral water to help lower uric acid.
- Walnut
- Cherry
- Strawberry
- Blueberries
- Pumpkin
- Cucumber
- Olive Oil
- Hazelnut oil
- Abundant water consumption
In addition, there are some foods that gout patients do not need to completely exclude from their diet, but should pay attention to limited consumption. These foods include the following:
- Lean beef
- Lean chicken meat
- Turkey meat
- Legumes
- Cauliflower
- Purslane
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Chard
- Brussels sprouts
- Peas
- Asparagus
- Mushroom
- Bulgur
What gout patients should not eat
In the treatment of gout, it is important to organize the diet in accordance with the disease and to make this diet a lifestyle for the patient. In order to control the disease, patients should avoid or limit the consumption of the following foods:
- Ready-to-eat and packaged foods with unknown ingredients
- Alcoholic beverages
- Foods cooked by frying
- All pastries
- Sugary foods such as molasses and jam
- Whole grain, rye or wholemeal bread
- Caviar
- Mussel
- Calamari
- Lobster
- Anchovy
- Sardine
- Offal
- Sausage
- Salam
- Bacon
- Sausage
- Game meat
- Fatty broths and dishes prepared with them
- Kaymak
- Cream
- Mayonnaise
- Whole milk and dairy products
- Interior and tail fat
Exercise for Gout
Exercise is very important in gout and should be done regularly. However, at this point, light-paced exercises and sportive activities should be preferred to heavy sports and exercises in order to lower uric acid levels.
Adequate Water Consumption
One of the foods that the body needs most in gout is, of course, the basic food product water. For this reason, patients should pay attention to water consumption in order to prevent the progression of the disease during the treatment process and in the future. Regular water consumption helps to prevent gout attacks and reduces pain and discomfort. In this respect, attention should be paid to drinking between 8 and 16 glasses of water daily.
Attention to Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption, which is one of the most important risk points of gout, should be absolutely abandoned during and after the disease. Because it becomes difficult to remove uric acid after alcohol consumption, and attacks may increase as a result of more uric acid accumulation in the blood.
What is good for gout?
Gout patients should make the doctor's recommendations a lifestyle. In this way, the progression of the disease can be stopped and complaints can be relieved. The list of suggestions that will be good for gout disease is as follows:
- Medicines prescribed by a physician should be used without interruption. Care should be taken not to overdose when using medicines and the physician should be contacted in case of external medication. Patients should be especially careful not to use aspirin or blood thinners to relieve pain.
- Ice compresses can be applied to relieve the pain felt in inflamed areas.
- Avoid using shoes that will cause the feet to get stuck. Especially patients with gout that causes foot pain should pay more attention to this point.
- Gout patients should regularly and continuously practice light sports. This is because sport not only helps to maintain the overall health of the body, but also facilitates the weight loss process.
- Patients who prefer to eat eggs should prefer boiled or hard-boiled eggs instead of fried.
- Patients struggling with gout can also get help from apple cider vinegar. For this, it will be sufficient to add 2 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water 2 to 3 times a day and consume it in this way.
- Full-fat products and carbohydrate food group should be avoided. Especially in the consumption of milk and dairy products, low-fat products should be preferred.
- It is recommended that patients consume parsley juice every 3 days to remove uric acid.
- Patients can take vitamin C supplements.
- Foods such as dried beans, chickpeas and lentils should be consumed no more than 7 spoons a day.
- The oils used in cooking should be changed to olive oil or hazelnut oil. Butter, suet and margarine are foods that should be completely excluded from the diet.
- Yeast foods should be avoided.
- Gout patients are recommended to consume white bread instead of wholemeal or whole grain bread.
- Cherry. Fruits and vegetables rich in water content, especially blueberries and strawberries, should be consumed.
- Drinks containing fructose and acids should be completely excluded from the diet.
- Alcohol consumption is completely prohibited.
- Patients need to eat often but little by little.
- Patients who are above a healthy weight should lose weight. However, it is recommended to take this weight loss process slowly. Because uric acid levels can increase suddenly during weight loss.
- Finally, patients should pay attention to water consumption between 8 and 16 glasses a day.
Is gout fatal?
Gout is not a disease that directly causes death. However, complications caused by gout can be life-threatening. These include cardiovascular problems such as stroke, heart failure and heart attack, as well as serious health problems such as damage to blood vessels due to uric acid build-up.
What happens if gout is not treated?
If gout is left untreated, the pain felt by patients may worsen and joint damage may occur. In addition, complications caused by gout can lead to a decrease in the quality of life of patients and even a risk to life.
Is gout contagious?
Gout is one of the autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases are defined as the immune system attacking healthy cell tissues. Gout is not a contagious disease because it is autoimmune.