What is a Gynecological Examination?
A gynecological examination is conducted to check the health of the reproductive organs. As part of a regular check-up, a cervical examination may be performed. However, not all women need an annual check-up. Some doctors recommend a gynecological exam only when there is vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, other symptoms, or specific reasons.
A cervical examination usually takes a few minutes. During this examination, the doctor checks the vagina, cervix, ovaries, uterus, and rectum for any changes. A Pap smear test, which is a screening for cervical cancer, is also performed during a gynecological exam.
How is a Gynecological Examination Performed?
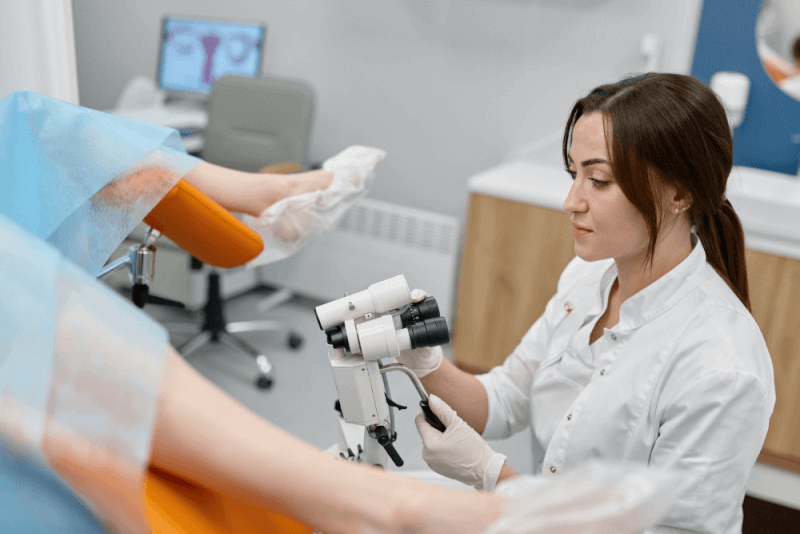
First, you will lie on your back on the examination table. Your feet are usually placed on the corners of the table or on supports called stirrups. You will be asked to slide your body to the edge of the table and open your knees. A gynecological examination typically includes the following:
- An external visual examination is performed to check for unusual symptoms. During this examination, the vulva is inspected. Unusual symptoms may include skin lesions, changes in skin color, sores, and swelling.
- Next, the doctor will use a hinged plastic or metal instrument called a speculum to open the walls of the vagina. This allows the doctor to see the vagina and cervix more easily. The speculum is shaped like a duck’s bill. To make the patient more comfortable, it may be warmed before insertion. The speculum may cause pressure that could be uncomfortable. It is important to try to relax as much as possible to ease the discomfort, but if pain occurs, it should be reported to the doctor immediately.
- A cell sample may be collected for a Pap smear test before the speculum is removed.
- The pelvic organs, including the uterus and ovaries, cannot be seen from the outside of the body. For this part of the examination, the doctor will need to feel the cervix through the abdomen. The doctor will perform a manual examination. During this part of the examination, the size and shape of the uterus and pelvic organs are checked. Any tender areas or abnormal growths are noted. After the vaginal examination, the doctor may insert a gloved finger into the rectum. This is done to check for tenderness, growths, or other unusual symptoms. Throughout the cervical examination, the doctor will explain what is being done, helping the patient feel more at ease.
Who Should Have a Gynecological Examination?
The purposes of a gynecological examination include:
- It is performed to monitor sexual and reproductive health. Additionally, a gynecological examination may be part of a routine physical check-up. Symptoms of ovarian cysts, some sexually transmitted infections, uterine cancer, or early-stage cancers may be detected.
- The examination is also performed during the first prenatal care visit in pregnancy.
- If there is any condition affecting the reproductive system, routine gynecological examinations are recommended.
- A gynecological examination is also conducted to determine the cause of symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge, skin changes, painful intercourse, or urinary issues.
Gynecological Examination During Pregnancy
A gynecological examination is performed during the first three months of pregnancy. It may also be conducted outside this period if a cervical screening test or bleeding occurs.
If there are no complications during the rest of the pregnancy, a gynecological examination is not performed. However, if labor induction is recommended during pregnancy, a vaginal examination may be conducted.
Hospital policies regarding gynecological examinations during childbirth vary. In addition, it is generally recommended that delivery care providers perform vaginal examinations. A gynecological examination is recommended under the following conditions:
- Within 4 hours after delivery
- Every 4 hours as long as active labor continues
- If there is any clinical concern
If there is a suspected delay in the progression of labor, the doctor may perform a vaginal examination before the routine 4-hour period. If the stage of labor is not clear, a gynecological examination will help in decision-making and planning for delivery. Ideally, whether during pregnancy or childbirth, gynecological examinations are kept to a minimum and are performed only with the patient's consent.
Gynecological Examination for Menstrual Irregularities
When a patient visits the doctor for menstrual irregularities, the patient's medical history is first reviewed. A gynecological examination is then performed. During the gynecological examination, ultrasound examinations are conducted. The pelvic organs, including the ovaries and uterus, are examined through ultrasound. In some cases, blood tests or MRI imaging may be requested to confirm the diagnosis. Additionally, a biopsy may be performed to understand the cause of menstrual irregularities.
Gynecological Examination for Virgins
Whether for routine check-ups or to diagnose a gynecological problem, the first gynecological examination can be daunting for those who are not sexually active. However, there are many reasons why sexually inactive women may need to visit a gynecologist. These include menstrual pain, menstrual irregularities, itching, and vaginal discharge.
Vaginal examinations are not performed on women who are not sexually active. Instead, an ultrasound examination is conducted through the abdominal area. For the best results from the examination, it is recommended that the patient has a full bladder. Additionally, if there is a specific reason, an external genital examination may be performed.
In countries where virginity is important, no instruments are used during the examination to preserve the hymen. Instead, the external genital organs are visually examined. If necessary, a manual examination may also be performed. Additionally, a vaginal culture can be taken without damaging the hymen.
Preparations Before a Gynecological Examination
There is no special preparation needed before a gynecological examination. However, for the patient's comfort, it is better to schedule the examination on a day when they are not menstruating. Additionally, the bladder should be emptied before the examination.
The gynecological examination is performed in the doctor's office and usually takes just a few minutes. You may be asked to remove your clothes and wear a special gown. A sheet may be provided to cover yourself for added privacy. Before the gynecological examination, the doctor may listen to your heart and lungs and check your abdomen, back, and breasts.
A chaperone may be present in the room during the examination. This person is usually a nurse or medical assistant. If a chaperone is not provided, patients have the right to request one. Additionally, patients may bring a friend or relative to the gynecological examination.