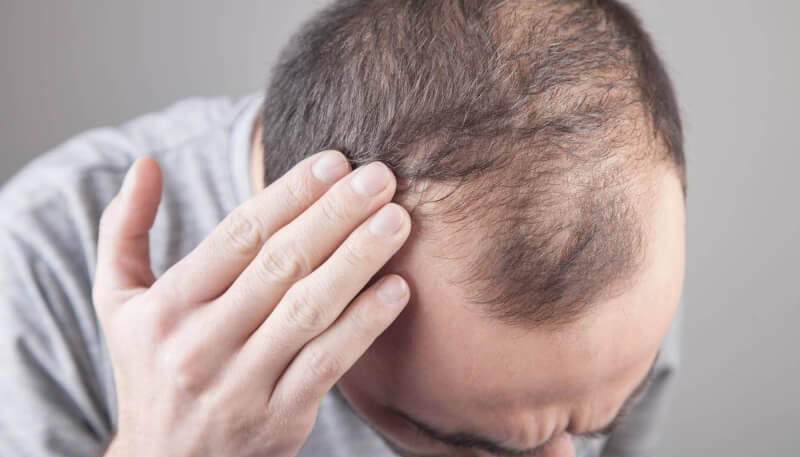
Hair loss is a necessary process for healthy hair to grow. With the loss of weakened hair, hair with healthier and thicker strands grows instead. However, these spills are considered normal up to a certain amount. If the hair loss is 10% or more of the total hair, then a dermatologist should be consulted.
The average person has between 100 and 150 thousand hair strands. If hair loss is more than 100-150 per day, it is called hair loss, regardless of whether it is regional or generalized.
Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss in men starts with the end of puberty. Due to the fact that male genetics are suitable for hair loss, hair begins to fall out at an early age.
Hair loss problems are less common in women. Other causes of hair loss in women, usually due to gene differences, include factors such as birth control pills, stressful life, birth process, thyroid hormone imbalance, breastfeeding and menopause.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Hair loss due to genetic causes is mostly seen in men and postmenopausal women. Hair loss due to genetic reasons starts mostly from the forehead and temple area in men and from the crown area in women.
Lichen Planus
Lichen disease can cause permanent hair loss. To prevent this, the disease must be diagnosed and treated at an early stage.
Psychological Causes
Hair loss is also a consequence of a psychological illness called trichotillomania. Hair loss is treated with psychological therapy.
Hormone Dysregulation
Hormonal imbalances due to reasons such as thyroid diseases cause hair loss.
Pregnancy
Hair loss is frequently observed in women during pregnancy due to changing hormone levels. Hair loss observed during this period is temporary.
Anemia
The most common cause of hair loss, especially in women, is anemia.
Lifestyle
Conditions such as inadequate and unbalanced nutrition or exposure to excessive stress cause hair loss. In addition, some lifestyle habits also cause hair loss.
Wrong Hair Care
Constantly tightly packed hair, excessive use of chemicals or improper washing habits can cause hair loss.
What is seasonal hair loss?
One of the most common causes of hair loss, called seasonal hair loss, is intense hair loss that occurs especially at the end of summer and the beginning of autumn and lasts an average of 2 weeks. Although seasonal hair loss worries many people, it is important for the natural cycle of hair to remain healthy.
The reason for seasonal shedding is thought to be the limitation of the melatonin hormone caused by sun exposure in the summer months. Due to melatonin deficiency, the first two phases of the hair life cycle are quickly passed and the last phase, the weakening of the hair strands, begins. As a result, the lifespan of the hair strands is reduced and more hair loss occurs.
Things to Do to Reduce the Impact of Seasonal Shedding
Two important points to be less affected by seasonal hair loss are to ensure that the hormone melatonin is secreted more and to protect the hair from sunlight. Foods such as bananas and oranges can be used for increased secretion of the hormone melatonin. In addition, consuming fruits and fruit juices with antioxidant properties will also prolong the life of the hair.
In order to protect the hair from the negative effects of the sun, physical protection should be used. In addition, there should be no vitamin D deficiency and supplements should be taken if available.
How to Prevent Hair Loss?
Early intervention plays a key role in male pattern hair loss. In this way, hair loss can be stopped without the need for hair transplantation operations. One of the methods to be applied for this is to limit the formation of DHT. After DHT formation is classified with medical applications, topical lotion applications and laser application can be used for faster hair growth. In addition to these, PRP application also stops hair loss to a great extent and provides the formation of new hair. Since there is no method that completely stops hair loss in today’s medicine, the methods to be applied should be determined according to the needs of the patients.
Treatments to prevent hair loss are not only for the hair. This one In addition, the general health, age and diet of the patients also play an important role in protecting the hair. In addition, attention should be paid to the adequate intake of vitamins and minerals such as selenium, vitamin B and zinc in the diet.
How is Hair Loss Diagnosed?
When hair loss is encountered, it is first necessary to determine whether this loss is a normal part of the hair shaft. If there is hair loss beyond what is expected, then the necessary tests are used to determine the underlying causes of hair loss.
Hair Loss Treatment
In order to treat hair loss, the underlying cause must first be identified and eliminated. Hair loss should first be examined by a dermatologist. Afterwards, treatments are applied both for the cause and for the prevention of hair loss and new hair growth.
In male pattern hair loss, treatment options should be evaluated according to the size of the area of loss. Treatment methods such as PRP or mesotherapy are applied to hair loss that can be covered. Hair transplantation is applied to hair loss spread over a large area.
In other hair loss, priority is given to vitamin and mineral values. In case of deficiencies, necessary reinforcements are made. In addition, mesotherapy and PRP injections are used to nourish the hair follicles and strengthen the hair.
Hair Transplant
Hair transplantation treatment is performed to treat hair loss permanently. In this method, healthy hair follicles are transferred to the area where hair loss occurs. The hair follicles to be transferred are taken from the nape and the areas above the ear. Because these are the areas that are insensitive to DHT. With the method called FUE, healthy hair follicles are collected. It is then placed into the micro channels in the area of hair loss. This method, also known as non-surgical hair transplantation because it is an incisionless procedure, is performed under local anesthesia in a period of 4 to 5 hours. The transplanted hair follicles grow gradually within 3 months. Within a year, patients regain the appearance of their natural hair.
Things to Consider After Hair Transplantation
The first three days after hair transplantation the treated area should not be touched. The first wash should be performed at least 3 days after the hair transplant and, if possible, by a physician. It is recommended to stop smoking, alcohol and caffeine consumption after hair transplantation. A hat should be worn for 2 weeks as external factors will damage the newly transplanted hair. After transplantation, crusting and itching may be observed both in the transplanted area and in the area where the hair is removed. During this phase, which lasts up to 2 weeks, care should be taken not to itch and hit these areas.
Shock Spill
Following the shedding of the crusts formed after hair transplantation, the transplanted hair is also expected to fall out. This so-called shock shedding is normal and while the hair used in transplantation is shed, the transplanted follicles are not damaged. This shedding makes room for new hair growth.