30 Second Summary
- Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in the brain, resulting in increased intracranial pressure.
- Hydrocephalus can occur prenatally, postnatally or in adulthood.
- Common symptoms of hydrocephalus include headache, vomiting, tendency to sleep and enlargement of the head.
- Hydrocephalus is usually treated with surgery.
What is Hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is a health problem in which Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) begins to accumulate in the cavities of the brain, causing increased pressure on the skull. The disease can occur after birth, during childhood or in adults.
In healthy individuals, this fluid is produced by the spinal cord and brain and protects the brain and spinal cord against environmental factors. If the fluid increases, pressure on various parts of the brain and spinal cord will increase, which can lead to nerve and brain dysfunction. Symptoms may differ depending on the location of the pressure in the brain.
There are different treatments for hydrocephalus, such as medication to relieve symptoms and surgical removal of intracranial fluid. It is a condition that can lead to death if left untreated.
Diagnostic Methods for Hydrocephalus
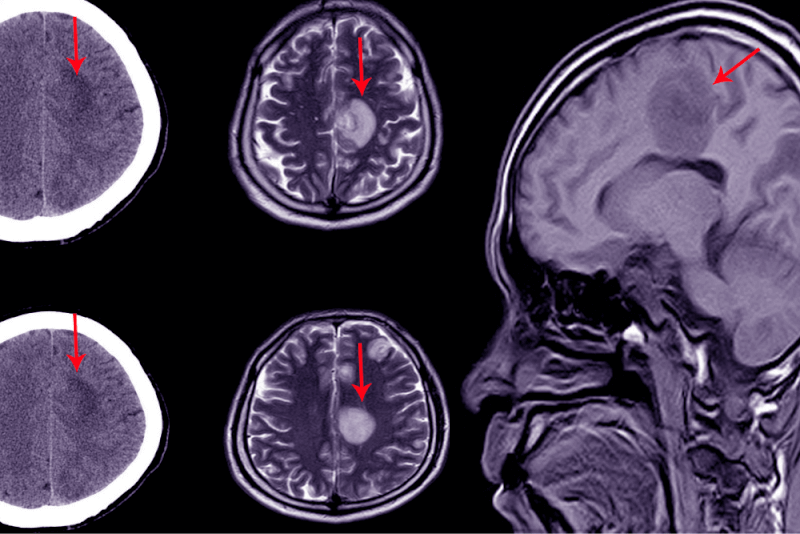
Computerized Tomography and MRI techniques are used in hydrocephalus. These radiological scans can show changes in brain tissue and where the fluid is concentrated. A definitive diagnosis of the disease can be made by evaluating other findings.
Congenital Hydrocephalus
The baby may have had hydrocephalus in the womb. The condition is usually diagnosed by obstetricians and gynecologists while the baby's development is observed by the physician during regular ultrasound scans.
With the MRI technique to be applied to the baby after birth, the cause of hydrocephalus can be determined and treatment can be planned accordingly.
Causes of Hydrocephalus
The causes of hydrocephalus can be divided into three categories: congenital, occurring in childhood and occurring in adulthood.
Causes of Congenital Hydrocephalus
- The baby has a problem that may cause a problem in the flow of CSF (Cerebrospinal Fluid)
- Some rare genetic diseases
- Mutation on the X chromosome
- Presence of health problems such as Spina Bifida in the baby
- Cysts between the arachnoid membrane and the spinal cord
Causes of Hydrocephalus in Children and Adults
- Stroke
- Infections of the spinal cord or meninges, such as meningitis
- Brain tumor
- Brain hemorrhage
- Venous thrombosis (blood clot) in the brain
- Late symptoms in case of stenosis in the channels where the cerebrospinal fluid circulates
Causes of Hydrocephalus in the Elderly
- Brain hemorrhage
- Damage to the brain
- Some infections
- Some chronic diseases that negatively affect blood flow (high cholesterol, diabetes, heart disease, etc.)
- It can also develop in an idiopathic (unknown cause) manner.
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus develops in different age groups due to different causes and the age factor is of great importance in its symptoms.
Symptoms of Congenital Hydrocephalus
- Skull cavities are wider than normal
- Vomiting
- The head becomes larger than normal by collecting water
- The veins are very prominent, shiny and thin
- Swelling and tightening of the fontanel
- Vomiting
- Irritability
- Nutrition problems
- Sara attack-like seizures
- Constant sleepiness
- Slipping of the eyes
- Vision problems
- Rigidity and muscle spasms in the feet and legs
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus in Children and Adults
- Headache, especially severe when waking up in the morning or aggravated by prolonged rest
- Neck pain
- Blurred or double vision
- Neck pain
- Difficulty walking
- Fatigue and weakness
- Mind fuzziness and confusion
- Developmental delay in children
- High-pitched, short crying spells in children
- Urinary incontinence and fecal incontinence
- Increased sleepiness as the disease progresses
- Significant change in head and face shape
- Limitation of movement or slowing of movements
- Sudden and frequent mood swings
- Epileptic seizures
- Feistiness
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus in the Elderly
Hydrocephalus seen in the advanced age group is also called 'Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus'. The most obvious symptom of this condition is a fall with sudden loss of consciousness. Other symptoms are;
- Impairments in mental functions (memory problems, forgetfulness, etc.)
- Incontinence of urine and feces
- Headache
- Difficulty walking (patients feel as if there is a magnetic force on the ground).
Hydrocephalus Treatment Methods
Although the diagnosis of Congenital Hydrocephalus is made while the baby is still in the womb, there is no treatment that can be applied in the womb before birth. Postpartum treatment is performed surgically. During the operation, the cause of the blockage that prevents the Cerebrospinal Fluid from circulating freely throughout the body is removed. The technique to be used during the operation is determined according to the underlying cause of the disease. There is no drug treatment for the disease.
Hydrocephalus Surgery
Hydrocephalus surgery can be performed with shunt placement or ETV technique.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery 1-2 Hours
Anesthesia Method: General
Hospitalization Duration: 2-4 Days
Return to Work Period: 2-4 Weeks
Shunt Insertion
To open the blockage, the shunt method is used to remove excess fluid from the brain with the help of a tube. The shunt is then placed in the baby's head to create a drainage system. It looks like a flexible and long tube and is fixed under the scalp, behind the ear. Thanks to the system installed, the excess Cerebrospinal Fluid is directed to the lungs, abdomen or heart and absorbed by the body.
Since the body naturally absorbs excess Cerebrospinal Fluid, there is no need for a battery. Intracranial pressure returns to normal thanks to the excretion of excess fluid.
ETV Technique
In this technique, called endoscopic third ventriculostomy, the surgeon enters the brain with a tube with a camera at the end. A hole is made in the atrium here and the blockage is removed. Excess Cerebrospinal Fluid then passes through this hole into the bloodstream and is absorbed by the body.
With this operation technique, there are risks such as infection, bleeding, fever and sudden closure of the opening.
Postoperative period after hydrocephalus surgery
Antibiotic treatment is started after the operation to prevent the risk of infection. The physician explains the symptoms of the emergency and what can be done in this situation to the relatives of the individual. As soon as the symptoms are noticed, the operating physician should be contacted immediately.
The individual's complaints usually improve after the operation. However, if there is permanent damage to the brain during the course of the disease, mental retardation, vision problems and impaired brain function may occur.
Parents whose babies were born with hydrocephalus can have genetic testing when they want to have another baby and can be followed more closely during pregnancy.