What is Kartagener Syndrome?
Kartagener syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive or single gene inherited genetic disorder. It occurs when both parents carry the disease gene and pass it on to their children. It is a syndrome characterized by ciliary dyskinesia and situs invertus.
The human respiratory tract consists of the nose, sinuses, middle ear, eustachian tubes, throat, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles. The respiratory tract is lined with special cells called cilia, which have hair-like projections. It sweeps foreign substances such as inhaled dust, smoke and bacteria out of the respiratory tract. In the case of primary ciliary dyskinesia associated with Kartagener's syndrome, the cilia are defective and do not function correctly. Mucus and bacteria in the lungs cannot be expelled, resulting in frequent lung infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
Cilia are also found in the ventricles of the brain and in the reproductive system. People with Kartagener syndrome can develop headaches and problems with fertility. The sperm's camper and tail are also associated with the cilia, and infertility can occur in Kartagener patients as a result of poor sperm motility. Situs Invertus occurs when the fetus is in the uterus. It causes organs to change their normal position in the body. In some cases all organs can be mirror images, in other cases only certain organs are displaced.
Diagnostic Criteria for Kartagener Syndrome
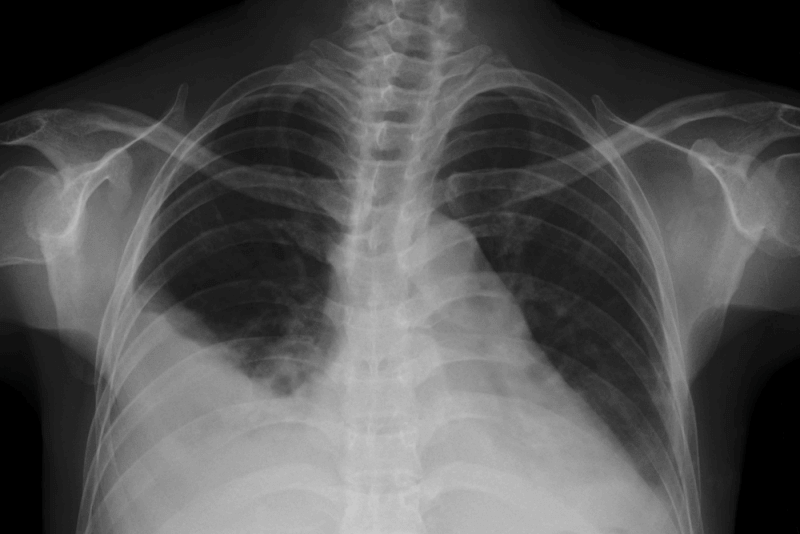
For the diagnosis of Kartagener syndrome, physical examination and history of symptoms are taken. Chronic sinusitis, bronchiectasis and situs inversus are the three main symptoms of Kartagener syndrome. Chest X-ray or computed tomography scans can detect the lung changes characteristic of the syndrome.
Biopsies of the trachea, lungs or sinuses allow microscopic examination of airway cells and cilia can be observed. The diagnosis can be made by hearing test, nasal nitric oxide measurement or nasal ciliary biopsy.
Symptoms of Kartagener Syndrome
- Bronchiectasis The cilia in the respiratory tract help to clear mucus, dust and germs. Defective cilia in Kartagener syndrome can lead to infections that can damage the walls of the airways, causing bronchiectasis.
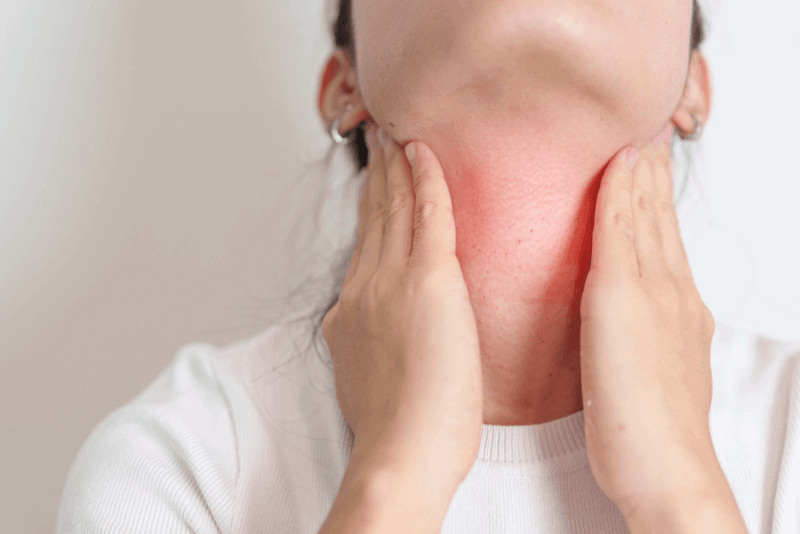
- Recurrent Sinusitis: Because the cilia are not working properly, germs cannot be removed and the infection repeats itself.
- Chronic Ear Infections: The sinuses and middle ear are connected, which causes recurrent sinusitis to lead to ear infections.
- Hearing Loss It is a symptom that occurs when there is a problem with the transmission of sound waves everywhere through the outer ear, eardrum or middle ear. People with Kartagener syndrome may present with chronic infections, particularly in the middle ear, which cause hearing loss.
- Situs Invertus It is an inversion of the mirror image of the organs in the chest and abdominal cavity. The tip of the heart may face towards the right side of the chest instead of the left side. Most patients have no signs or symptoms and a chest X-ray will reveal it.
- Ectopic Pregnancy The cilia are involved in the transportation of the egg through the fallopian tube. The fertilized egg is expected to move into the uterus 3-4 days after fertilization. In patients with Carthagener syndrome, the egg in the fallopian tube cannot travel to the uterus due to defective cilia and ectopic pregnancy can occur.
- Immobilized Sperm: The tail and the campesus of the sperm are connected to the cilia. Failure of the cilia to function can stop the movement of the sperm.
- Decreased Female and Male Fertility: In males with Kartagener syndrome, sperm motility is restricted, and in females, reduced fertility can be seen due to the inability to transfer eggs.
Causes of Kartagener Syndrome
Kartagener syndrome is a genetic disorder in which two parents with the disorder pass on a mutated gene to their child. Mutations in the 5p15.1 and 9p13.3 bands of the DNAH5 and DNA11 genes are known to cause the syndrome. If parents with a child with Kartagener syndrome are considering a second child, genetic diagnosis is important. Prenatal diagnosis can detect 65% of gene mutations.
Kartagener Syndrome Treatment Methods
There is no known cure for Kartagener syndrome. The overall aim of treatment is to keep the airways clear and relaxed and to get rid of extra mucus and discharge. It helps to keep the lungs and lung tissues healthy for as long as possible.
- Regular sinus washings
- Regular ear canal washings
- Mucolytic drugs are used to thin and expel the mucus layer
- Antibiotics stop the progression of infections
- Steroids
- Bronchodilators are used to relax the lung muscles for easy breathing
- Hearing aids
- Speech therapy
- In advanced cases, lung transplantation is performed.
People with Kartagener syndrome should get vaccinated to prevent serious illnesses, including the flu vaccine. Smoking and exposure to cigarette smoke should be avoided. For patients with fertility problems, microinjection or IVF treatments may be preferred.