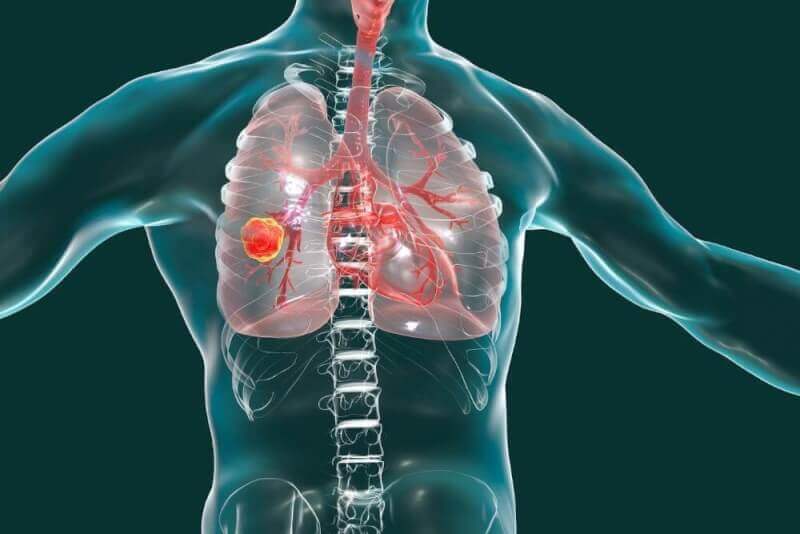
Lung cancer is a disease caused by the uncontrolled growth of cells in the lung tissues. This uncontrolled growth can lead to the invasion of surrounding tissues or metastasis by spreading to organs outside the lungs. According to the WHO (World Health Organization) report, lung cancer is the most commonly observed and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Approximately 1.6 million people die from lung cancer each year globally.
The death rate from this type of cancer is quite high and varies globally depending on smoking habits. Lung cancer is currently considered an epidemic disease worldwide. Today, it is more commonly seen in men. Since 1987, lung cancer has been the leading cause of cancer deaths in women in the United States. In 1996, approximately 64,000 women died from lung cancer and about 44,000 women died from breast cancer in the United States. The increase in lung cancer cases in the 1990s in the U.S. is believed to be linked to the rapid rise in smoking among women after the 1960s.
In many highly developed countries outside the U.S., lung cancer is also observed as the leading cause. Globally, it ranks first among men and second among women, following breast cancer. The World Health Organization reported that in 1985, 300,000 women in developing countries died from smoking-related diseases, with 21.1% of these deaths attributed to lung cancer.
However, in the past, lung cancer was observed as an extremely rare disease at the beginning of the 20th century. The transformation of tobacco into cigarettes and its widespread use led to the emergence of a lung cancer epidemic in the 1940s. This lung disease epidemic continues to increase rapidly worldwide.
Types of Lung Cancer
There are several different types of lung cancer. Some of these types originate in the lung tissue, while others develop in the chest wall. The most common types of lung cancer that form in the lung tissue include the following.
Large Cell Lung Cancer
Large cell lung cancer, the most common type of lung cancer, grows and spreads more slowly than small cell lung cancer. Large cell lung cancer is divided into three different types based on the cell types in the tumor.
Adenocarcinoma
This is the most common type of lung cancer and usually starts along the outer parts of the lungs. It is also the most common type of lung cancer seen in people who have never smoked.
Large Cell Carcinomas
This group of cancers consists of large and abnormal-looking cells. They can start anywhere in the lung and tend to grow rapidly.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Also known as epidermoid carcinoma, this type is usually found in the bronchi near the center of the lungs.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Nearly all cases of small cell lung cancer are caused by smoking. This type of cancer spreads much faster than other types of cancer and is divided into two subtypes. One of these subtypes is oat cell cancer, which accounts for a significant portion of small cell carcinoma cases. The other subtype is combined small cell carcinoma.
Mesothelioma
This is a cancer of the chest lining, usually caused by exposure to asbestos. It accounts for about 5% of lung cancer cases. There is a 30 to 50-year latency period between asbestos exposure and the onset of cancer. Many of these patients worked in environments where they were exposed to asbestos fibers.
Causes of Lung Cancer
The primary cause of lung cancer today is smoking, as approximately 80-90% of all lung cancers have developed solely due to smoking. The risk of lung cancer varies from person to person, depending on the duration of smoking, the total amount smoked, the age at which smoking began, and the type of cigarettes consumed. Studies have shown that a woman's risk of developing lung cancer is 1.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a non-smoker. Additionally, women exposed to the same amount of tobacco smoke have a 1.5 to 3 times higher risk of developing lung cancer compared to men.
After active smoking, the second most significant risk factor for lung cancer is passive smoking, also known as environmental tobacco smoke exposure. Passive smoking alone is observed to increase the risk by an average of 1.2 to 1.3 times. Genetic predisposition should also be considered in lung cancer. Having a family history of lung cancer increases a person's risk of developing the disease. A woman with a family history of lung cancer who has never smoked has a 2.8 times higher risk of developing lung cancer, while a woman with no family history of lung cancer who smokes regularly has an 11.3 times higher risk.
Most Notable Causes
- Tobacco products
- Asbestos
- Radon
- Scarring in the lung
- Inorganic arsenic
- Chronic Interstitial
- Halogen ethers
- Air pollution
- Radioisotopes
- Heavy metals
- Nickel
- Chromium
- Vitamin A and B deficiencies
- Mustard gas
Prevalence of Lung Cancer
Small cell lung cancer is known to be the fastest-growing type of lung cancer. The most significant factor triggering this type of lung cancer is smoking. Today, adenocarcinoma is observed as the most common type of lung cancer in humans.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Wheezing while breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Hearing wheezing sounds
- Coughing up blood or blood-streaked phlegm
- Swelling in the neck and face
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite, fatigue, and sudden weight loss
- Arm and shoulder pain
- Difficulty exercising
- Bone pain
- Difficulty swallowing and feeling a lump
- Irregular heartbeats
- Anemia (lack of red blood cells)
- Lymphadenopathy
- Fever
- Drooping of the eyelid, sunken eye
- Facial fullness and redness
- Skin and subcutaneous nodules
- Jaundice
If any of the symptoms listed above are observed, they should seek medical attention without delay.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Like other types of cancer, lung cancer is divided into four main stages. The TNM system is used for staging. Although there are many other staging systems, TNM is the most commonly used. T represents the size of the tumor, N indicates whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, and M denotes whether it has metastasized to distant areas.
Occult Cancer
At this stage, the primary tumor cannot be evaluated in the lungs for any reason. However, cancer cells are found in samples taken from sputum or other lung fluids. No metastasis is observed in nearby lymph nodes or distant areas, and cancer is not diagnosed through other tests.
Stage 0
At this stage, the tumor is confined to the upper layers of cells lining the airways. No cancer cells are found in deeper lung tissues.
Stage 1
The first stage of lung cancer is divided into three different groups. Stage 1A1 has two different definitions. In the first definition, the cancer is minimally invasive adenocarcinoma.
The tumor is not larger than 3 centimeters in diameter, and the portion that has spread to deeper lung tissues is less than half a centimeter in diameter. In the second scenario of stage 1A1, the tumor is smaller than 1 centimeter, has not reached the lung pleura, and has not affected the main branches of the bronchi.
In stage 1A2, the tumor is larger than 1 centimeter but smaller than 2 centimeters. Tumor cells that have not reached the lung pleura also do not affect the main branches of the bronchi.
In stage 1A3, the tumor is larger than 2 centimeters but smaller than 3 centimeters. The tumor has not reached the lung pleura, and the bronchi are not affected.
In stage 1B, the tumor has one or more of the following characteristics:
- The tumor is larger than 3 centimeters but smaller than 4 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor has spread to the main bronchus but has not spread to the point where the left or right main bronchus divides from the trachea.
- The tumor has grown towards the lung pleura.
The airways are partially blocked.
Stage 2
The second stage of lung cancer also has several sub-stages. The first is stage 2A. In stage 2A, the tumor has one or more of the following characteristics:
The tumor is larger than 4 centimeters but smaller than 5 centimeters in diameter.
The tumor has spread to the main bronchus but has not reached the point where the left and right main bronchi divide from the trachea.
The tumor has grown towards the lung pleura.
The tumor partially blocks the airways.
In stage 2B of lung cancer, several scenarios are possible. In the first scenario, the tumor is not larger than 3 centimeters and has not grown towards the lung pleura or affected the main branches of the bronchi.
At this stage, cancer has spread to the lymph nodes within the lung and/or around the area where the bronchus enters the lung. The affected lymph nodes are on the same side as the cancer.
In the second scenario of stage 2B, the following are observed:
- The tumor is larger than 3 centimeters but smaller than 5 centimeters in diameter.
- Cancer cells are found in the main bronchus but not at the point where the trachea divides into the main bronchi.
- The tumor has grown towards the lung pleura.
- The airways are partially blocked.
- Cancer is also found in the lymph nodes within the lung.
- In the final stage of 2B, the following are observed:
The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters but smaller than 7 centimeters in diameter.
The tumor has grown into the chest wall, the inner lining of the chest wall, the phrenic nerve, or the membrane surrounding the heart.
There are two or more separate tumor nodules in the same lobe of the lung.
Stage 3
In stage 3A of lung cancer, one possible scenario is that the cancer is smaller than 3 centimeters in diameter. The tumor has not spread to the lung pleura or affected the main branches of the bronchi. Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes below the point where the trachea divides into the left and right bronchi or to the space between the lungs. The affected lymph nodes are on the same side as the primary lung tumor.
In the second scenario of stage 3A, the following are observed:
- The tumor is larger than 3 centimeters but smaller than 5 centimeters in diameter.
- Cancer is found in the main bronchus but not at the point where the trachea divides into the main bronchi.
- The tumor grows towards the lung pleura.
- The airways are partially blocked.
Another scenario that may occur in stage 3A of lung cancer is as follows:
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters but smaller than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor grows into the chest wall, the inner lining of the chest wall, the phrenic nerve, or the membrane surrounding the heart.
- There are two or more separate tumor nodules in the same lobe of the lung.
The final scenario observed in stage 3A is as follows:
- The tumor is larger than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor has grown close to the heart, involving large blood vessels, the trachea, the esophagus, and the space between the esophagus and the small intestine. Tumors may also be seen in the diaphragm and spine.
- There are two or more separate tumor nodules in different parts of the same lobe of the lung.
In stage 3B of lung cancer, the first scenario observed is as follows:
- The cancer is smaller than 3 centimeters in diameter.
- It does not spread to the lung pleura or affect the main branches of the bronchi.
- Cancer spreads to lymph nodes above the clavicle on both sides of the body.
- It spreads to contralateral hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes.
In the second scenario of stage 3B, the following are observed:
- The tumor is larger than 3 centimeters but smaller than 5 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor is found in the main bronchus but not at the point where the trachea divides into the main bronchi.
- The tumor grows towards the lung pleura.
- The tumor partially blocks the airways.
The third scenario observed in stage 3B includes the following:
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters but smaller than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor grows into the chest wall, the inner lining of the chest wall, the phrenic nerve, or the membrane surrounding the heart.
- There are two or more separate tumor nodules in the same lobe of the lung.
The final characteristics of this stage include the following:
- The tumor is larger than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor has spread to the lung, heart, large blood vessels close to the heart, esophagus, the space between the small intestine and esophagus, diaphragm, and spine.
- There are two or more separate tumor nodules in different parts of the same lung.
In stage 3C of lung cancer, the first scenario observed includes the following:
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters but smaller than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- The tumor grows into the chest wall, phrenic nerve, or the membrane surrounding the heart.
- There are two or more separate tumor nodules in the same lobe of the lung.
In the second scenario of this stage, the following are observed:
- The tumor is larger than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- Cancer cells spread to the heart, large blood vessels close to the heart, trachea, esophagus, diaphragm, spine, or the muscle at the point where the trachea divides into the left and right main bronchi.
- There are two or more separate tumor nodules in different parts of the same lung.
Stage 4
The fourth stage of lung cancer is also divided into two sub-stages. The first scenario observed in stage 4A is as follows:
At this stage, the cancer may be of any size and may or may not have grown into nearby structures. It may also have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Additionally, the following situations may be observed in patients:
- The cancer has spread to the other lung.
- The cancer has spread to the lung pleura or the membrane surrounding the heart.
- Cancer cells are found in the fluid around the lungs.
- Cancer cells are found in the fluid around the heart.
The second scenario observed in stage 4A is as follows:
- The cancer may be of any size.
- The cancer may or may not have grown into nearby structures.
- The cancer may or may not have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- It has spread as a single tumor to a distant lymph node or organ, such as the liver, bones, or brain.
The final stage of lung cancer, stage 4B, includes the following:
- The cancer may be of any size.
- It may or may not have grown into nearby structures.
- It may or may not have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- The cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes and/or other organs such as the liver, bones, or brain.
Treatment Methods for Lung Cancer
Various treatment options are available for lung cancer patients, which is now quite common. From a clinical treatment perspective, primary lung cancers are known as small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Another type, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), is divided into two types of cancer. Determining the cell type in lung cancer is crucial for planning treatment and prognosis. After determining the stage and histological type of the disease, the patient's age and condition are also considered in planning the treatment.
Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
For diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer without metastatic disease, surgical treatment with curative intent is attempted in the majority of cases.
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer
This is one of the most common and most dangerous types of cancer. If the disease is at a very limited stage, surgical treatment is applied. However, in cases where the disease has progressed significantly, chemotherapy should be administered.
Lung Cancer Surgery
Surgery is often the best option for treating lung cancer, depending on the type, location, and stage of the cancer. If lung cancer is treated with surgery, some lung tissue surrounding the tumor and often the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed.
Tumor removal surgery is considered the best option, especially when the cancer is localized and the risk of spread is low. This includes early-stage large cell lung cancer and carcinoid tumors.
Methods of Lung Cancer Surgery
Lung cancer surgeries are generally performed through four different procedures. These procedures include the following:
Lobectomy
The right lung has 3 lobes, and the left lung has 2 lobes. Lobectomy involves removing the affected lobe of the lung due to lung cancer. Lobectomy is the most common surgical procedure for lung cancer. The lobectomy procedure can also be performed as bilobectomy. This method is only applied to the right lung because it involves removing two adjacent lobes. Additionally, there is a procedure called sleeve lobectomy.
This procedure is applied when one of the lung lobes is affected, as well as the main bronchus of that lung. Subsequently, a sleeve resection is performed to remove the cancerous lobe and part of the main bronchus leading to that lung. Afterward, the remaining unaffected bronchus is reconnected to the unaffected bronchi in the other lobes. This method reduces the need for pneumonectomy.
Segmentectomy
The lobes in the lungs are divided into 2 to 5 lung segments. The segmentectomy method involves removing 1 to 4 segments of a specific lobe. This preserves the other healthy tissues in the lung lobe.
Wedge Resection
This procedure involves removing a small wedge-shaped section of lung tissue surrounding the cancerous tissues.
Pneumonectomy
In this procedure, the entire affected lung is removed. This option is generally applied when the cancer cannot be completely removed with a lobectomy or when the lesion is centrally located.
Complications of Lung Cancer Surgery
Various complications can develop after lung cancer surgeries. Most of these complications are minor and rarely occur. However, some can be life-threatening. It is important to treat these complications as soon as possible. Complications that may occur after lung cancer surgeries include the following:
Feeling Tired and Weak
It is expected that many patients will feel tired after surgery. The duration of feeling weak and lacking energy varies. If these feelings last longer than a few weeks, patients should consult a doctor and seek necessary support, such as physical therapy.
Collapsed Lung
A difficult-to-detect complication, air leaks, and collapsed lungs occur due to air leaking into the pleural space. A chest drain is needed to help re-expand the lung. Therefore, in some patients, the chest drain inserted at the end of surgery may need to remain in place longer.
Shortness of Breath
It is expected that patients will experience some shortness of breath after surgery. The severity of this symptom varies depending on the type of surgery and the patient's physical condition. However, it is a complication that can be easily managed over time, especially with exercise.
Infection
Surgical procedures carry a risk of infection. Antibiotics are used to reduce this risk. However, in some cases, infection may occur despite all precautions. Signs of infection include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Cold sweats
- Generally feeling unwell
- Cough
- Swelling or redness around the wound
- Warmth around the wound
- Foul-smelling discharge from the wound
- Fluid leakage from the wound
- Loss of appetite
- Blood clot
Blood clots that may form after surgery can block normal blood flow in the veins. Clots, especially in the legs, can cause swelling, warmth, redness, or pain. There is also a risk that a blood clot may break loose and travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, causing a blockage. This condition, known as pulmonary embolism, can present the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Dizziness
- Bleeding
Bleeding may occur immediately after surgery. This may be due to leakage from the blood vessel suture or improper blood clotting. The treatment for this complication varies depending on the cause.
Long-Term Pain
Patients may experience prolonged pain due to nerve damage during surgery. The pain is usually felt along the incision line. As the nerves heal, the intensity of the pain typically decreases within a few months.
Chemotherapy Treatment for Lung Cancer
Chemotherapy is a procedure that uses anticancer drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs circulate throughout the body via the bloodstream, killing cancer cells.
Chemotherapy Treatment for Small Cell Lung Cancer
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for small cell lung cancer. It is one of the cancers that respond best to chemotherapy, although it often tends to spread outside the lungs during treatment. Chemotherapy drugs circulate in the bloodstream, allowing them to fight cancer cells that have spread from the lung tumor to other parts of the body. In the treatment of small cell lung cancer, chemotherapy can be used in the following ways:
- Chemotherapy can be used alone to treat cancer.
- Chemotherapy can be administered before or after radiotherapy, or during radiotherapy.
- Chemotherapy can be used before and after surgery.
- In cases where the disease has spread, chemotherapy can be combined with immunotherapy.
Chemotherapy Treatment for Large Cell Lung Cancer
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for large cell lung cancer in its early stages. The following are situations where chemotherapy is used:
- Chemotherapy is administered before surgery to shrink the tumor.
- Chemotherapy can be administered before, after, or in combination with radical radiotherapy, especially in physically fit patients.
- Chemotherapy is also administered to patients with metastatic lung cancer.
Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer
Radiation therapy for lung cancer is a procedure that uses powerful, high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing. The most commonly used radiation therapy for lung cancer is external radiation. The following types of radiation therapy are also used:
- In external beam radiation, radiation doses are directed at the lung or surrounding areas.
- In intensity-modulated radiation therapy, radiation beams are shaped to match the tumor. The intensity of the treatment can be adjusted during the session.
- In brachytherapy, sealed radioactive material is placed directly into or near the tumor.
- In stereotactic body radiation therapy, very high doses of radiation are delivered to the tumor in the lung or other organs, while limiting radiation exposure to surrounding organs.
- In stereotactic radiosurgery, very high doses of radiation are delivered directly to lung cancer tumors that have spread to the central nervous system.
Possible side effects of radiation include:
- Mild skin reactions
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Pain during swallowing
- Cough
Recovery Process of Lung Cancer
Recovery after lung cancer surgery can take weeks. Part of the recovery process takes place in the hospital, while part is spent resting at home. Most patients stay in the intensive care unit for a few days after surgery, where they are constantly monitored. After a few days, patients are moved to a regular room. In addition, the following situations may occur during the recovery process after surgery:
Wound Care
A dressing is applied to the surgical site. The dressing is changed, and the wounds are cleaned a few days after surgery. The size and number of surgical wounds vary depending on the type of surgery. Minimally invasive surgeries typically result in three small wounds, while open surgeries leave a long incision.
Dissolvable stitches are usually used to close the wound after surgery. If dissolvable stitches are not used, the stitches will need to be removed 10 days later.
Drains
During surgery, various drains are inserted for different reasons. These drains serve the following purposes:
- IV lines are inserted into veins in the neck and arm to administer blood transfusions and fluids.
- A chest drain is used to remove air and fluid around the surgical wound and help re-expand the lungs.
- A bladder catheter is used to measure urine output.
- A small tube is attached to the artery to monitor blood pressure.
In addition, patients may have an oxygen mask after surgery. Pain medications controlled by electronic pumps may also be administered.
Pain
Pain during the first week after surgery is expected. Various painkillers are prescribed for this purpose. Patients should inform their doctor if they experience any pain so that the most suitable type and dosage of painkiller can be adjusted. Regular use of painkillers ensures the best results. One or more of the following methods may be used to control pain after surgery:
- Patient-controlled analgesia allows patients to receive painkillers continuously through an IV line as needed.
- Paravertebral catheters allow painkillers to be administered directly to the area around the lungs.
- Painkillers administered through a pump-controlled IV line provide continuous pain relief to the patient.
Patients may continue to experience pain even after being discharged. The doctor will prescribe various painkillers for this purpose. If the pain worsens, patients should consult a specialist.
Eating and Drinking
Patients can start eating as soon as they are fully awake and feel ready after surgery. However, patients often experience a loss of appetite after surgery. This is expected, and patients should not force themselves to eat.
Getting Out of Bed
Patients should start moving as soon as possible after surgery. Nurses and physical therapists will assist patients in this process. Performing breathing and leg exercises before getting out of bed helps with recovery. Patients are expected to sit upright in a chair within 12 hours after surgery. The day after surgery, patients are expected to walk around the bed, and within a few days, they should be walking in the hospital corridors.
Risk Factors for Lung Cancer
The following factors can increase the risk of lung cancer:
- Exposure to radon
- Exposure to asbestos
- Radiotherapy
- Smoking
- Passive smoking
- Age
- Air pollution
- Family history of lung cancer
- Occupational exposure
- Radiation
- HIV infection
- Exposure to arsenic
- Exposure to chemicals
- Dietary habits
- Familial risk factors
- Inflammation and other benign lung diseases
Signs of Death in Lung Cancer
The following signs may be observed in patients requiring palliative care in the final stages of lung cancer:
- Shortness of breath
- Pain
- Cough
- Difficulty concentrating
- Confusion
- Extreme weakness and fatigue
- Loss of interest in eating and drinking
- Restlessness
- Wheezing in the throat and chest during breathing
- Rapid breathing or pauses between breaths
- Severe weight loss
- If the cancer spreads to the brain, headaches, seizures, and other neurological problems may occur
Emotional Changes
Emotional changes are observed in lung cancer patients in the final stages of their lives. These changes include:
- Some patients withdraw from social settings in their final days.
- As a result, they become less open to family and friend visits.
- For some patients, activities that previously excited them are no longer of interest.
- Irritability
Spiritual Changes
Spiritual changes observed in patients during their final days include the following:
- Talking about seeing heaven
- Talking about seeing deceased loved ones
- Realizing that death is near
Physical Changes
The following physical changes may be observed in lung cancer patients in the final stages:
- Fluid accumulation around the lungs
- Blockage or bleeding in the major airways
Lung Cancer and Nutrition
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet helps lung cancer patients experience fewer side effects from treatment, such as loss of appetite, fatigue, and nausea. Basic guidelines include avoiding added sugars and saturated fats.
Foods That Lung Cancer Patients Should Avoid
The following foods commonly trigger side effects during lung cancer treatment:
- Fatty, fried, or overly spicy foods
- Very hot foods and beverages
- Dairy products
- High amounts of caffeine
Chemotherapy and other lung cancer treatments can damage white blood cells, which fight infections. Therefore, it is common for bacteria in certain foods to enter the body and cause infections. To prevent this, lung cancer patients should avoid the following foods:
- Deli meats
- Undercooked eggs
- Salad dressings containing raw eggs
- Unpasteurized milk or dairy products
- Melted ice cream
- Custards and pastries containing milk
- Raw vegetable sprouts, such as alfalfa, broccoli, or radish
- Leafy greens that have not been thoroughly cleaned
- Sushi
- Smoked fish
- Raw or undercooked shellfish, such as oysters
- Raw nut butter
- Unpasteurized fruit juices
Key Points to Consider in the Diet of Lung Cancer Patients
To cope with the effects of lung cancer and its treatment, the body needs a lot of energy. Therefore, regular and calorie-rich meals will help fight the disease more easily. The following points should be considered:
Minimizing Weight Loss
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in lung cancer. To do this, it is necessary to consume a high amount of energy. Choosing foods rich in carbohydrates and fats will help maintain a healthy weight. Extra fat can be added to meals, and carbohydrate-rich vegetables like potatoes can be included.
In addition, patients should not wait until they are hungry to eat. Instead, frequent meals are important. Patients often tend to eat more in the morning, so breakfast should be given more importance.
Consuming Enough Protein
Protein is the most important macronutrient for the body's healing process. Protein supports the growth of new and healthy cells, repairs damaged tissues, and maintains a strong immune system. To achieve this, patients should consume plenty of protein-rich foods such as fish, poultry, red meat, eggs, full-fat milk, yogurt, cheese, nuts, and nut butter, beans, peas, lentils, soy, and gelatin.
Water Consumption
In addition to helping the body stay healthy, drinking plenty of water helps manage side effects such as vomiting and diarrhea and removes harmful byproducts of medications from the body. It is recommended to drink 8 to 12 glasses of water a day, along with beverages like milk and fruit juice. Patients should also avoid tea, coffee, and carbonated drinks.
Managing Your Taste Preferences
Taste changes during treatment are common. As a result, patients may no longer tolerate many foods they previously enjoyed. Instead, foods they rarely ate before can be introduced. If patients become sensitive to the smell of food, cold or room temperature foods can be preferred. Brushing teeth and using dental floss is also recommended to remove unpleasant tastes from the mouth. Gargling with a baking soda solution before and after meals is also helpful.
Coughing Up Blood in Lung Cancer
Coughing up blood is known as hemoptysis. Although this may be a symptom of lung cancer, it can also indicate other health problems. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor.
This is especially common in people over the age of 40 who smoke. Between 30% and 60% of lung cancer patients experience this problem. The cause is often that lung cancer disrupts blood flow in the lungs. Tumor growth can irritate blood vessels in the lungs or actively invade blood vessels, causing this issue.
What Should Lung Cancer Patients Pay Attention to?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help lung cancer patients feel better during and after treatment. Good nutrition and exercise improve the quality of life during treatment. In addition to good nutrition and exercise, controlling stress and quitting bad habits like smoking can significantly benefit patients during treatment.