30-Second Summary
- Mammography, which involves taking an image of the breast tissue using low-dose radiation, is used to diagnose breast cancer before symptoms develop.
- Although mammography can reveal abnormal breast tissue, it does not always mean the tissue is cancerous. Therefore, additional procedures like biopsies may be required.
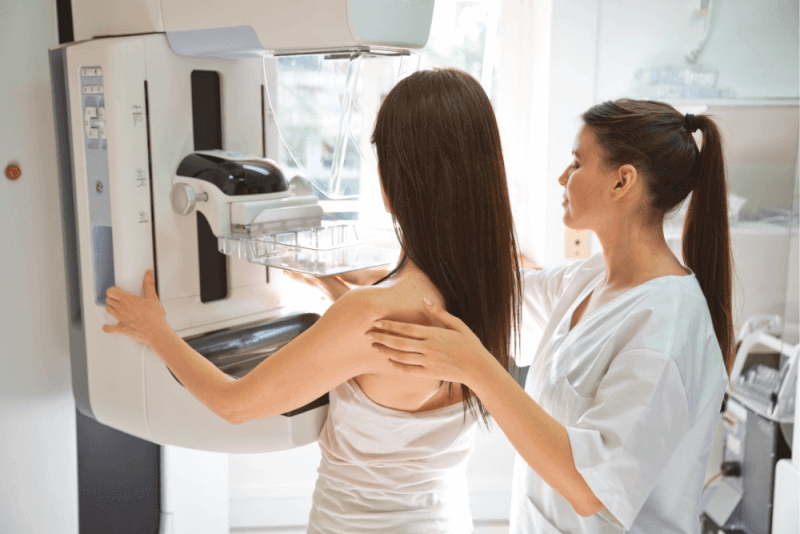
- Mammography is performed using a machine specifically designed to capture breast images.
- Women between the ages of 40 and 75 are recommended to get mammograms every two years. However, for individuals with special conditions, this frequency and the starting age for routine mammograms may vary.
What is Mammography?
Mammography, which involves taking an image of the breast tissue using low-dose radiation, is used to diagnose breast cancer before symptoms develop. It is also used to detect abnormalities in breast tissue in cases of lumps, pain, nipple discharge, or skin changes.
Types of Mammography
Mammography is divided into two subtypes. These are:
2D Mammograms
2D mammography captures two different views of both breasts, typically from above and below.
3D Mammograms
3D mammograms use a newer technology where multiple X-rays are sent over the breast as a machine moves in a circular motion. After the scans, computer images are combined to create a 3D image of the breast tissue.
Why is Mammography Done?
Mammography helps detect cancer, but it does not provide a definitive diagnosis. While abnormal tissue can be seen in mammography, it cannot always be concluded that it is cancerous, so additional procedures like biopsies may be required.
How is Mammography Performed?
Mammography is performed using a machine designed to capture breast tissue images. The machine has a special section that positions the breast and a detector that sends electrical signals to the computer to create digital images.
Mammography Preparation
Before the mammography appointment, the following points should be considered:
- If you are breastfeeding, pregnant, or suspect you might be, inform your doctor.
- During menstruation, avoid scheduling mammograms during your period or one week before, as your breasts may be more sensitive, which could cause discomfort.
- If you have breast implants or have recently been vaccinated, inform your doctor.
On the day of the mammogram:
- There is no need to alter your daily routine before the mammogram.
- Do not use deodorants, perfumes, lotions, or powders on the day of the test, as these products can affect the images.
- You will need to undress from the waist up for the imaging process.
Steps of Mammography
The mammography process includes the following steps:
- Remove all clothing and jewelry from your waist up. A hospital gown will usually be provided.
- Stand in front of the mammography machine and uncover one breast.
- The breast will be placed on a support plate.
- A plastic piece will be lowered to compress the breast. Some discomfort or pain may be felt during compression. If the pressure is unbearable, inform the technician, and adjustments will be made.
- Once compressed, the machine will take the images.
- If both breasts are to be imaged, the process will be repeated for the other breast.
- After the technician completes the imaging, the procedure is done, and you can get dressed and leave the testing room.
After the mammogram, you can return to your regular activities.
Risks of Mammography
Mammography involves the use of low-dose radiation, which may lead to radiation exposure. However, the benefits of mammography outweigh the risks of radiation exposure.
Mammography Results
Mammography results are typically available immediately. The radiologist will compare the current results with previous mammograms and provide a report with the necessary explanations. The results will also provide information on the density of the breast tissue, showing how much fibrous and glandular tissue is present compared to fatty tissue.
Normal Mammogram
A normal mammogram means no abnormal areas were found in the images. If a normal result is obtained, it is recommended to continue with regular mammograms. Regular mammograms allow for comparisons, which helps in more effective diagnoses.
Abnormal Mammogram
If one or more areas of shadowing are found in the mammogram images, it is considered an abnormal result. If an abnormal result is found, additional tests such as breast ultrasound, special mammogram images, or a biopsy may be requested.
When Should Mammography Be Done?
It is recommended for women between the ages of 40 and 75 to have a mammogram every two years. However, for those with special conditions, the frequency and age at which to start routine mammograms may vary.
Women who are at higher risk of developing breast cancer should have a mammogram before age 40 or more frequently. In such cases, additional imaging tests like breast ultrasound and MRI may also be required.
A risk assessment should be done to determine if someone is at high risk. The following risk factors require a consultation with a doctor:
- Personal history of breast cancer
- Family history of breast or ovarian cancer
- Genetic mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2
- Benign breast diseases like atypical ductal hyperplasia
- Dense breast tissue