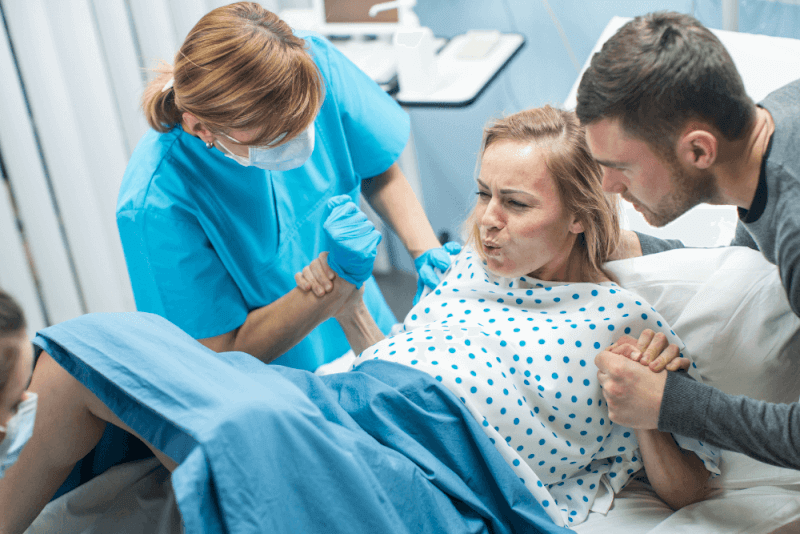
What is natural childbirth?
Natural childbirth refers to the process of delivering a baby through the vagina. In this most common method of childbirth, the uterus contracts and the cervix thins and dilates, allowing the baby to be pushed out through the birth canal.
Experts generally agree that vaginal delivery is the safest method for both the fetus and the mother. Natural childbirth typically occurs between 37 and 42 weeks of pregnancy.
Types of natural childbirth
There are different types of natural childbirth, including spontaneous, assisted, and induced vaginal delivery.
Spontaneous natural childbirth
Spontaneous vaginal delivery occurs when labor begins on its own without the use of drugs.
Induced vaginal delivery
Labor is started with medication or other techniques, preparing the cervix for delivery. This type of natural childbirth is also known as labor induction.
Assisted natural childbirth
In assisted vaginal delivery, instruments such as forceps or a vacuum device are used to help deliver the baby. It can be used in both spontaneous and induced vaginal deliveries.
Signs of natural childbirth
The onset of natural childbirth is called the latent phase, where the cervix becomes soft and thin, and begins to dilate in preparation for birth. This phase can last for hours or even days, and during this time, it is generally recommended that women stay at home. Signs that labor has begun include:
- Contractions begin.
- Back pain occurs.
- Increased urge to use the bathroom due to the baby pressing on the bowels.
- The mucus plug is discharged, sometimes with a slight bloody show.
- Amniotic fluid leaks (water breaks).
You should go to the hospital if any of the following occur:
- Water breaks.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- The baby moves less than usual.
- More than three contractions occur within 10 minutes.
- Signs of labor occur before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Stages of natural childbirth
Natural childbirth occurs in three stages. These stages and the events that occur during each include:
Stage 1
In the first stage of labor, the uterus begins to contract and the cervix dilates to 10 centimeters. The following events are typical during this stage:
- Contractions start to occur every 8 to 10 minutes.
- The mucus plug is discharged with a slight amount of blood.
- As the cervix dilates to 6-7 centimeters, the baby's head applies pressure on the birth canal, causing the amniotic sac to rupture.
- After the water breaks, the pressure decreases and contractions may lessen temporarily but then intensify again.
About 85% of natural deliveries occur in the first stage, so it is important for the mother-to-be to avoid exhausting herself during this phase.
During the first stage of labor, activities to help relax the mother-to-be include:
- Practicing breathing techniques taught in childbirth classes.
- Taking a warm shower.
- Taking a light walk.
- Changing positions.
- Listening to calming music.
During the first stage, healthcare providers will monitor the baby's heartbeat and frequently check the dilation of the cervix.
Stage 2
In the second stage, also known as the delivery stage, the birth begins. The following events are typical during this stage:
- This is the stage where contractions are felt most intensely.
- Contractions occur every 2-3 minutes.
- Each contraction lasts about 60 to 70 seconds.
- An involuntary urge to push begins.
- The delivery stage lasts about one hour for first-time mothers.
- For mothers giving birth to their second or third child, this stage lasts about half an hour.
To ensure a smooth delivery, it is important to follow the instructions of healthcare providers. Typically, pushing should occur with each contraction. Strong pushing helps the baby move more quickly through the birth canal. After the baby's head is visible, one or two more pushes will be enough for the baby to be born.
Stage 3
In the third stage, the baby has been born, but the delivery is not complete because the placenta has not yet been delivered. During this stage, the baby is given to the mother while healthcare providers monitor for signs of placental separation. The placenta is then delivered by gently massaging the uterus through the abdomen.
The delivery of the placenta usually takes about half an hour, during which time breastfeeding can begin. After the placenta is delivered, the uterus and cervix are checked to ensure that the placenta has been delivered in one piece. If there are any tears in the cervix or vagina, stitches are applied.
Risks of natural childbirth
Among all childbirth options, vaginal deliveries carry the least risk. Common complications of natural childbirth include:
Failure to progress
Labor may slow down, stop, or the cervix may fail to dilate. In such cases, oxytocin is administered to stimulate contractions and progress labor.
Irregular fetal heartbeat
The baby's heart rate may become irregular due to the head or umbilical cord being compressed.
Hemorrhage
One of the most serious complications of natural childbirth is excessive or life-threatening bleeding during or after delivery. In some cases, bleeding may not occur until a few hours after delivery.
Vaginal tears
Tears may occur in the tissues around the vagina or uterus during delivery.
Deep vein thrombosis
Blood clots may form in the legs or pelvis shortly after delivery.
Postpartum preeclampsia
Extremely high blood pressure after childbirth is known as postpartum preeclampsia.
Benefits of natural childbirth
Natural childbirth offers various benefits for both the mother and the fetus. The benefits of natural childbirth for the mother include:
- Faster recovery.
- Earlier start to breastfeeding.
- Lower risk of complications in future pregnancies.
The benefits of natural childbirth for the baby include:
- Lower risk of respiratory problems.
- Enhanced immune system function.
- Increased likelihood of breastfeeding.
When natural childbirth is not recommended
While natural childbirth is usually preferred, it can be dangerous in certain situations. In such cases, a cesarean section is recommended. Situations where a cesarean may be advised include:
- Breech position of the baby.
- Placenta previa or other placental issues.
- Untreated infection with the herpes simplex virus.
- Presence of open genital lesions.
- Chronic health conditions.
Side effects that may occur after vaginal delivery
After childbirth, women may experience some physical and emotional changes. Common changes include:
- Constipation.
- Lack of breast milk production.
- Pain and tenderness in the vagina if there were tears.
- Mood swings.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Hemorrhoids
- Headaches, hot flashes, or sweating due to hormonal changes.
- Cramps.
- Lochia, a type of vaginal discharge.
- Postpartum depression.