What is a pacemaker?
Pacemakers, used to regulate the abnormal rhythm of the heart, are small medical devices usually placed just below the left collarbone. It can help alleviate the symptoms associated with abnormal heart rhythm, while at the same time allowing patients to continue their active lives.
Pacemakers implanted through a surgical procedure keep the heart beating regularly. The pacemaker, which sends electrical pulses to keep the heart beating at its normal rhythm, also ensures that the heart chambers work in synchronization to enable the heart to pump the body more efficiently. In addition, pacemakers are also used in patients with heart failure.
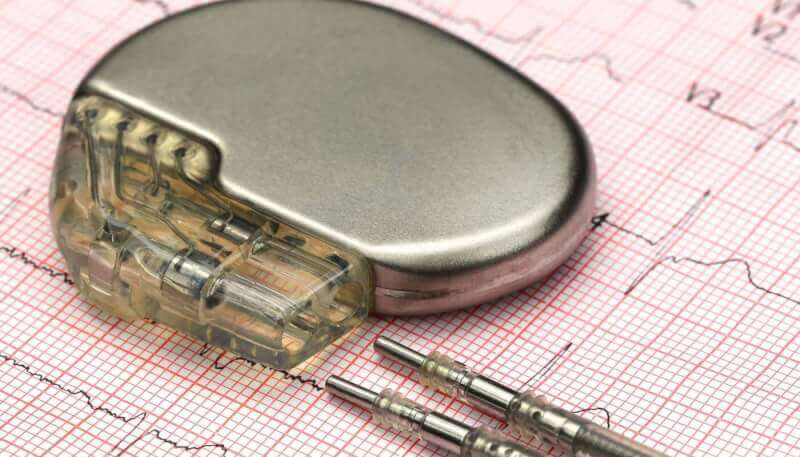
Pacemakers, which have a complex structure, are the size of a matchbox. With weights ranging from 20 to 50 g, the cables in pacemakers go to different points of the heart.
In very thin people, it is placed under the pectoral muscle because it can be noticed from the outside. However, in a significant proportion of patients, it is not possible to recognize the pacemaker from the outside. In addition, a lump is felt in the area where the pacemaker is located. Usually placed under the left collarbone, pacemakers are rarely placed under the armpit and under the chest muscle.
Types of pacemakers
Among the different types of pacemakers, the one most suitable for the patient's health condition is selected and applied. Regardless of the type of pacemaker, an additional feature called rapid responsive can be added to the pacemaker. Thanks to this feature added to the pacemaker, pacemakers give more efficient results in patients and children who have an active life. This is because pacemakers with fast responsiveness respond more quickly to changes in metabolism.
Temporary Pacemakers
Temporary pacemakers are used in emergencies or when the cause of the abnormal heart rhythm is expected to resolve in a short period of time. In some patients, it is used to stabilize the patient's condition until a permanent pacemaker is implanted.
The generators of temporary pacemakers used for tachycardia, heart attacks and after open heart surgery are quite large. They are therefore located outside the body. The pacemaker is connected to the heart by wires.
Permanent Pacemakers
Pacemakers used in permanent rhythm disorders are called permanent pacemakers. Permanent pacemakers, which are surgically implanted inside the body, are placed depending on the hand actively used by the patient.
Single Chamber Pacemaker
Single-chamber pacemakers are usually used to deliver electric current to the right ventricle of the heart.
Dual Chamber Pacemakers
Dual-chamber pacemakers are used to control the timing of contractions between the two chambers. To do this, it delivers electrical impulses to the right atrium of the heart.
Biventricular Pacemaker
It is a type of pacemaker used in patients with both heart failure and heartbeat problems. This battery allows the heart to work more efficiently. Biventricular pacemakers stimulate the lower chambers of the heart.
Transvenous Pacemakers
These pacemakers have wires that are inserted into the veins and carry the pulse to the heart. The battery has electrodes that follow the natural beating of the heart. In the event of a heart rhythm disturbance, it transmits electrical impulses, allowing the heart to return to its normal rhythm.
Wireless Pacemakers
Smaller in size than conventional pacemakers, wireless pacemakers are implanted in the chamber of the heart. This battery, which is implanted in an operation lasting approximately 1 hour, sends an electric current to the right ventricle. Wireless pacemakers have the ability to send data to the outside, enabling more efficient regulation of the heart rhythm
How a pacemaker works
Pacemakers are basically medical devices used to normalize abnormal changes in the heart's rhythm. In addition, pacemakers continuously monitor the heart's natural rhythm. In case of any problems during this follow-up, it automatically sends an electric current to the required areas and allows the heart rhythm to return to normal.
Pacemakers consist of 2 basic parts. These parts are the generator and the cable part, also called the metal sheath. A lithium battery inside the metal case powers the pacemaker. The electronic circuit next to the battery is a small computer that monitors the heart rhythm and sends an electric current when necessary. It also converts the electric current from the battery into small pulses. The cables transmit electrical impulses to the heart, while the metal sheath protects the pacemaker from external factors.
Pacemaker surgery
Permanent pacemakers are implanted in patients' bodies with different operations according to their types. Some pacemakers are placed under the collarbone, while others are placed directly on the heart. For this reason, pacemaker surgery methods vary according to the type of pacemaker used and the area where it will be placed.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery 1-2 Hours
Method of Anesthesia Local
Hospitalization Duration: 1 Day
Return to Work Period: 1-2 Weeks
How is a pacemaker implanted?
Endocardial or transvenous pacemakers are usually placed under the collarbone. First, the area to be operated on is disinfected and patients are given antibiotics against the risk of infection. A small incision is then made in the skin under the collarbone and the blood vessels are accessed with thin cables. These cables are then delivered to the heart. X-rays are taken to confirm the position of the tips.
Once the leads are where they should be, the pacemaker box is connected. After checking that the pacemaker is working, the physician makes the necessary adjustments. The box is then placed under the collarbone. Finally, the procedure ends when the incision is closed with sutures.
How is an epicardial pacemaker implanted?
Epicardial pacemakers are implanted directly on the heart. For this reason, surgeons first make an incision between the ribs or in the armpit through which the pacemaker is inserted under the skin of the abdomen. It is especially applied as a precautionary measure in open heart surgeries.
Recovery after pacemaker implantation
It takes 7 to 10 days for the incision for the pacemaker to heal. However, patients need between 6 and 8 weeks to fully recover. After the surgery, the physician's recommendations should be followed and regular dressings should be done if recommended.
Who gets a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is usually a treatment for patients with heart rhythm disorders. A pacemaker can also be implanted in patients with the following problems.
- Those with electrical conduction problems in the heart
- Patients with a shorter than normal pulse
- Patients with a rapid pulse
- Patients with a slow pulse
- If the heart has difficulty pumping blood
- Bradycardia
- Heart block
- Arrhythmia
- Heart failure
- Cardiac fibrillation
- Elimination of side effects caused by certain medications
- Acute trauma to the heart muscle
- Heart attacks
- Drug poisoning
- Tachycardia
Life after a pacemaker
After the pacemaker is implanted, you can return to your normal life when your doctor gives it to you. Many patients with a pacemaker can participate in many strenuous activities, such as playing tennis or taking long walks. However, patients with special conditions should avoid strenuous activities. For this reason, it is important that you do not participate in activities other than those authorized by your physician. Especially sports with hard falls and hard physical contact should be avoided. If you place the stock of the rifle on the side of your pacemaker while hunting, then you will also be banned from hunting. In short, you will need to avoid activities that can put pressure on your pacemaker.
Things to consider after a pacemaker:
- After pacemaker implantation, patients receive a card with information about the pacemaker used. Patients should keep this card with them at all times. Patients should also learn the make and model of the pacemaker they are using.
- Household appliances are thought to affect the pacemaker, but this has not yet been proven. For this reason, you should get information from your doctor about this issue.
- Metal detectors used in areas such as airports and courthouses cause activation of the pacemaker. For this reason, in areas with metal detectors, the patient is asked to show his/her card and be searched manually.
- X-rays do not affect the pacemaker.
- Cell phones rarely cause pacemaker activation. For this reason, they should be at least 15 cm away from the pacemaker, even if it is turned off. When making a phone call, it should be held in the ear on the side without the pacemaker.
- MRI imaging significantly affects the pacemaker and should not be used unless absolutely necessary.
- Patients should stay away from strong magnetic fields. These areas include high-voltage power lines, junkyards with strong magnets, amusement parks and poorly protected car engines.
- Pacemaker users should not come into contact with running car engines.
- Care must also be taken when using radio computer equipment. It is important to ensure that this equipment is at least 15 cm away from the pacemaker.
- Patients should also avoid large speakers with magnets and hydroelectric power plants.
- Finally, patients should not use chainsaws and welding machines.
Lifespan of pacemaker patients
There is no change in the life expectancy of patients using a pacemaker. However, pacemakers have a certain lifespan. At the end of these periods, they must be replaced with new ones.