What is pleurisy (blistering of the lung)?
There are 2 membranes that completely surround the lungs and fill the chest cavity. These membranes are called pleura, and between them is a fluid that allows the lung to move freely. This fluid secreted by the membranes is approximately 20 ml and has a slippery texture. This fluid secreted by the pleura is absorbed by the lungs. This keeps the amount of fluid between the two membranes constant.
However, if the membranes secrete more fluid than normal or if the lungs do not absorb enough fluid, fluid increases between the membranes. This condition is called pleurisy. Pleurisy, which is popularly referred to as blistering of the lungs, is also known as pleural effusion in medicine. These changes in the lungs or membranes can be caused by many different health problems.
Diagnostic methods for pleurisy (lung blisters)
Pleurisy is diagnosed by pulmonologists. For diagnosis, the patient's history is first taken and then a detailed physical examination is performed. During the examination, the patient is asked to continue breathing normally. The absence of breath sounds at this time indicates the presence of pleurisy.
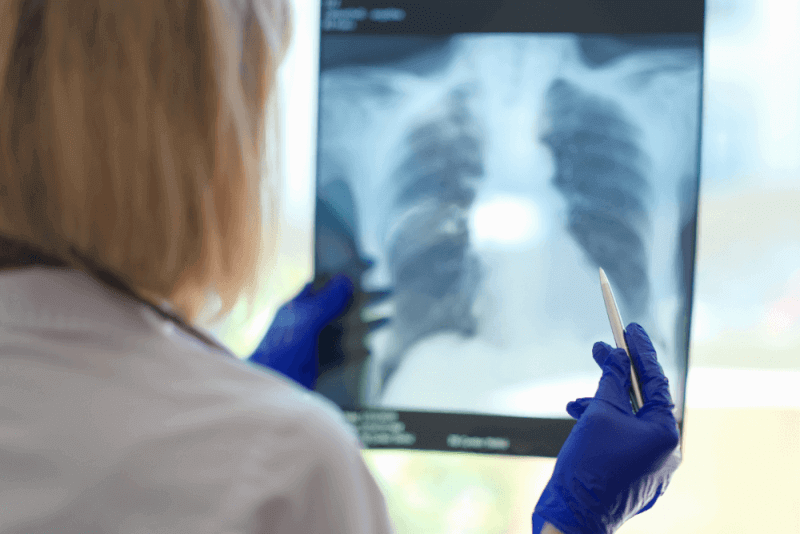
If deemed necessary by the physician, patients are asked for a chest X-ray. Fluid accumulation in the lung can often be seen on X-rays. However, in some cases, computed tomography images may also be necessary. With these imaging methods, not only the presence of pleurisy can be detected, but also the health problem that is causing it.
Once the presence of fluid has been diagnosed, an ultrasound scan may also be ordered to get detailed information about the location and amount of fluid. In addition to these diagnostic methods, other tests that may be requested from patients include the following.
Thoracentesis
In the thoracentesis test, a sample is taken from the water accumulated in the lung with a syringe. Thoracentesis is one of the methods used in the diagnosis of pleurisy, as well as relieving the complaint of shortness of breath due to a small amount of water accumulation. For this reason, thoracentesis is both diagnostic and therapeutic. In some cases, the color of the sample obtained by thoracentesis can provide information about the health problem causing the fluid accumulation. The fluid sample is sent to the laboratory for bacterial examination.
Biopsy
A biopsy is a method used to diagnose the health problem causing pleurisy. It is applied when other diagnostic methods cannot explain water retention in the lung. Biopsy is performed with two different methods, open and closed, and open biopsy is rarely performed.
Causes of pleurisy (lung blisters)
Pleurisy is seen due to many different health problems. In countries where tuberculosis is prevalent, tuberculosis is the primary cause of pleurisy. In addition, health problems that can cause pleurisy are as follows.
- Side effects of some medicines
- Familial Mediterranean fever
- Pancreatitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Traumas
- Thyroid diseases
- Systemic lupus
- Cirrhosis
- Esophageal cancer
- Lymph cancer
- Fungal infections
- Complications after heart surgery
- Some autoimmune diseases
- Rib fracture
- Kidney diseases
- Liver diseases
- Increased pressure in the artery to the lung
- Heart failure
- Part of the lung does not swell during breathing
- Presence of pulmonary edema
- Viral and bacterial infections
- Lung cancer
- Pleural cancer
- Lung abscess
- Sarcoidosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
Symptoms of pleurisy (lung blisters)
The symptoms of pleurisy, one of the lung diseases, are similar to those of other lung diseases. For this reason, the symptoms of pleurisy include the following:
- Cough
- Severe or moderate chest pain
- Stinging sensation in the chest
- Having trouble breathing due to pain
- Shortness of breath
- Inability to sleep on your back
- Fire
- Tremor
- Sweating
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- A squeaking sound from both lungs during deep breathing in the early stages
- Pain in the shoulder and abdomen
- Severe and dry cough
Pleurisy (lung blister) treatment methods
Treatment of pleurisy is planned depending on the underlying health problem. Curing the disease that causes pleurisy will also eliminate pleurisy.
Infections
With the exception of tuberculosis, all infections of the lung are treated in the same way. Water accumulation in the lung due to infection is called parapneumonic effusion. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used to treat infections in the lungs. The important thing in the treatment of pleurisy caused by infection is to choose the right antibiotic. It is also necessary to determine whether pleural fluid drainage is necessary.
Pleural drainage provides relief to patients in a shorter period of time. Drainage is applied in two different ways. The first of these is therapeutic thoracentesis. In addition, a chest tube is inserted in patients with excessive water accumulation to drain the fluid.
Tuberculosis
Treatment of tuberculous pleurisy is similar to treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. For this reason, tuberculous pleurisy medicines are used for 6 months on a schedule.
Malignant pleural fluids
Malignant pleural fluid is usually an indication that the underlying disease is terminal. When it comes to the treatment of malignant pleural fluid, a multidisciplinary approach, especially oncology, is required. Treatment options for malignant pleural fluid include chemotherapy, thoracentesis, radiotherapy, tube drainage, thin catheter, pleurodesis and continuous fluid drainage.
Pleurisy surgery
In some cases where pleurisy is caused by cancer, surgical treatment is necessary. In these procedures, the part where the pleura meets the chest wall is removed. This section was removed because it is responsible for fluid production. With this surgical intervention, patients are prevented from accumulating water in their lungs in the future.
Another reason for resorting to surgical methods in pleurisy is that procedures such as drainage applied to lung cancer patients cause thickening of the lung membrane over time. Cancer cells are also likely to spread to the membrane and cause thickening. In these cases, the thickening of the membrane is removed by surgery and the two membranes are glued together to prevent fluid collection.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery 45 Minutes - 1 Hour
Anesthesia Method: Local or General anesthesia
Hospitalization Duration: 1-2 days
Return to Work Period: 1-2 Weeks