What is Polyneuropathy?
Polyneuropathy refers to the damage of multiple peripheral nerves. It involves the nerves responsible for transmitting information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body, and it is also known as peripheral neuropathy. Since multiple nerves are affected simultaneously in polyneuropathy, the nerves responsible for movement and sensation are also impacted. Polyneuropathy typically results from conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases.
Types of Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy is classified into three types based on the rate of development.
Acute Polyneuropathy
Acute polyneuropathy, which is rare, progresses rapidly. It usually occurs due to autoimmune diseases or infections. These conditions can be treated in a short time. Acute polyneuropathy is often seen in individuals with Guillain-Barre syndrome, a fatal autoimmune disease.
Chronic Polyneuropathy
This type of polyneuropathy is caused by diseases such as kidney disease or diabetes. The symptoms develop slowly over time. Additionally, many factors can contribute to chronic polyneuropathy, making it challenging to identify the underlying cause.
Multiple Polyneuropathy
In this type of polyneuropathy, at least two peripheral nerve regions are damaged. Diseases that can cause this type include inflammation of blood vessels, sarcoidosis, and certain types of cancer.
Symptoms of Polyneuropathy
- Dizziness
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty eating and swallowing
- Breathing difficulties
- Abnormalities in blood pressure and pulse
- Digestive system problems
- Bladder problems
- Excessive sweating
- Inability to tolerate heat
- Leg and foot ulcers
- Skin and nail infections
- Falling attacks
- Lack of coordination
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle twitching
- Difficulty sensing temperature changes
- Burning or stabbing pain
- Freezing-type pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Sleep problems due to night pain
- Difficulty using arms, legs, hands, and feet
- Numbness
- Feeling pain
- Tingling and pricking sensations
Causes of Polyneuropathy
The primary cause of polyneuropathy is damage to the peripheral nerves. The factors that contribute to peripheral nerve damage include:
Diabetes
The inability to control blood sugar levels with insulin can lead to polyneuropathy. It is particularly seen in one out of every five patients with type 2 diabetes.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Peripheral nerve damage is seen not only due to excessive alcohol consumption but also due to poor nutrition.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases such as Sjögren's syndrome, lupus, Guillain-Barre syndrome, celiac disease, and rheumatoid arthritis can cause damage to the peripheral nerves.
Bacterial and Viral Infections
In addition to diseases such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Lyme disease, and shingles, some viral and bacterial infections are among the most common causes of neuropathy.
Bone Marrow Disorders
Some bone marrow cancers can lead to neuropathy by causing abnormal increases in protein levels in the blood.
Hereditary Disorders
Certain hereditary disorders, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, can contribute to the development of neuropathy in individuals.
Medications
Certain medications used in chemotherapy and HIV treatment can cause neuropathy.
Liver and Kidney Diseases
Research shows that approximately half of kidney patients develop neuropathy. Neuropathy is also a common condition in individuals with liver disease.
Poor Nutrition
Nerve damage can occur when the body is not adequately nourished with vitamins E and especially B1, B6, and B12. This can lead to the development of neuropathy.
Injuries and Trauma
Peripheral nerve damage can occur due to repetitive movements, such as writing, or injuries following trauma.
Toxins
Exposure to chemicals like arsenic and mercury, as well as the misuse of drugs and chemicals, are also among the causes of polyneuropathy.
Hypothyroidism
Although rare, an underactive thyroid gland can lead to damage in the peripheral nervous system.
How is Polyneuropathy Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of polyneuropathy begins with taking the patient's medical history. A detailed physical and neurological examination is also conducted. Certain tests are used to check muscle strength, reflexes, coordination, and posture.
MRI and CT Scans
These imaging methods are used to identify factors such as tumors or hernias that may cause nerve damage.
Electrodiagnostic Tests
These tests measure the electrical activities in muscles and nerves. Electromyography is used to measure nerve conduction velocity, helping detect nerve damage.
Biopsies
Samples of nerve or skin may be taken to detect abnormalities in nerves or nerve endings.
Treatment of Polyneuropathy
To treat polyneuropathy, the underlying condition must first be addressed. Additionally, vitamin and mineral deficiencies in the body due to poor nutrition are corrected.
Medication Therapy
The medications used in the treatment of neuropathy vary depending on the underlying cause. Medication therapy is also used to alleviate the symptoms of polyneuropathy. The groups of medications used in treatment include:
- Pain relievers
- Insulin-containing medications if due to hypothyroidism
- TCA antidepressants and duloxetine
- SNRI drugs
- Certain anti-seizure medications
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
In this treatment method, a gentle electric current is sent into the skin to alleviate the pain experienced by patients.
Plasma Exchange
This method is used in cases of polyneuropathy caused by autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. The patient's blood is removed from the body, cleared of antibodies and proteins, and then returned to the body.
Immunoglobulin Therapy
This treatment method is used to control antibody and high protein levels and to regulate the immune system.
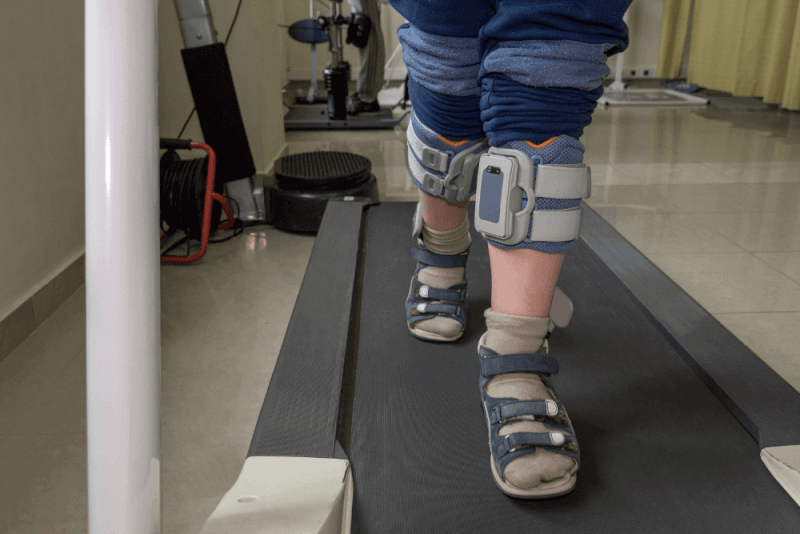
Physical Therapy for Polyneuropathy
Physical therapy methods are used to address muscle weakness and coordination problems. As a result, patients experience a reduction in these symptoms.
Polyneuropathy Exercises
There are three types of exercises considered ideal for polyneuropathy. The first is aerobic exercise, which involves large muscle groups and helps patients take deep breaths. The second is balance exercises, which increase the flexibility of muscles and joints while reducing the risk of falls. Lastly, stretching exercises are also recommended.
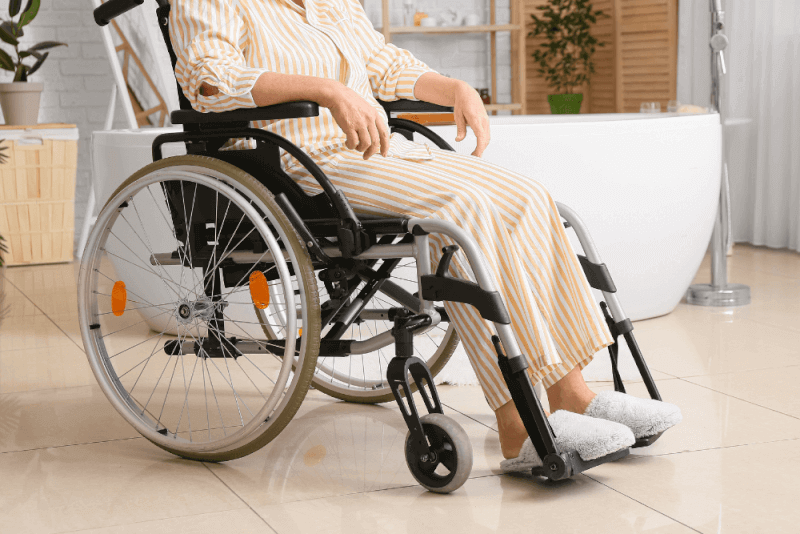
Treatment with Orthotics and Devices
Certain medical devices, such as splints, wheelchairs, or braces, are used to provide relief for the legs, arms, and hands.
Complementary Therapies
Methods such as meditation, acupuncture, and massage can help relieve pain in patients.
Tips for Polyneuropathy Patients
- Caffeine consumption should be limited.
- A stressful lifestyle should be avoided.
- Activities such as daily walks, yoga, and meditation help relax both muscles and patients.
- Issues such as anxiety or depression should be treated as soon as possible.
- Consuming foods rich in elements such as iron, calcium, folic acid, and magnesium strengthens the muscles.
- If following a vegetarian or vegan diet, B12 supplements should be used.
- A diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential.
- A balanced diet should be maintained to strengthen the immune system.
- Alcohol and smoking should be avoided.
- Physical therapy sessions should be followed regularly, and exercises should not be neglected.