What is Rett Syndrome?
Rett syndrome is a neurological developmental disorder that occurs due to a mutation in the MECP2 gene located on the X chromosome, and it is typically seen in girls. In Rett syndrome, autistic problems are prominent, and verbal skills are often absent. It is a genetic disorder that hinders brain development, and it does not show itself in the first six months. Symptoms can be observed during the development process.
Diagnosis of Rett Syndrome
For the diagnosis of Rett syndrome, it is crucial for parents to notice the symptoms during infancy. A doctor suspecting Rett syndrome will perform a genetic test to check for the presence of the MECP2 gene mutation. The genetic screening is done through a blood test and does not require any additional procedure.
Causes of Rett Syndrome
Rett syndrome is a genetic disorder. It occurs due to a mutation in the MECP2 gene located on the X chromosome. Typically, normal development is observed for 6-12 months after birth. After this period, problems such as regression in language and motor functions, difficulties in using hands, and slowed head growth occur in children.
Although Rett syndrome is mostly seen in girls, it can also occur in boys. The syndrome can progress up to the age of twelve, and the progression of the disease can vary from person to person.
Symptoms of Rett Syndrome
There are many different symptoms in Rett syndrome. The general symptoms of Rett syndrome are as follows:
- Difficulty using hands
- Bringing hands to the mouth
- Slow growth
- Tremors or contractions in hands and feet
- Delayed language development
- Microcephaly
- Constant crying
- Avoiding eye contact
- Screaming fits
- Lack of interest
- Not speaking
- Lack of balance
- Teeth grinding
- Irregular breathing
- Spinal curvature
- Swallowing problems
- Behavior changes
- Epilepsy or seizures
- Aggressiveness
Treatment Methods for Rett Syndrome
There is no definitive cure for Rett syndrome, but the goal is to reduce symptoms and potential complications caused by the symptoms.
- Medications to control muscle weakness and epileptic seizures
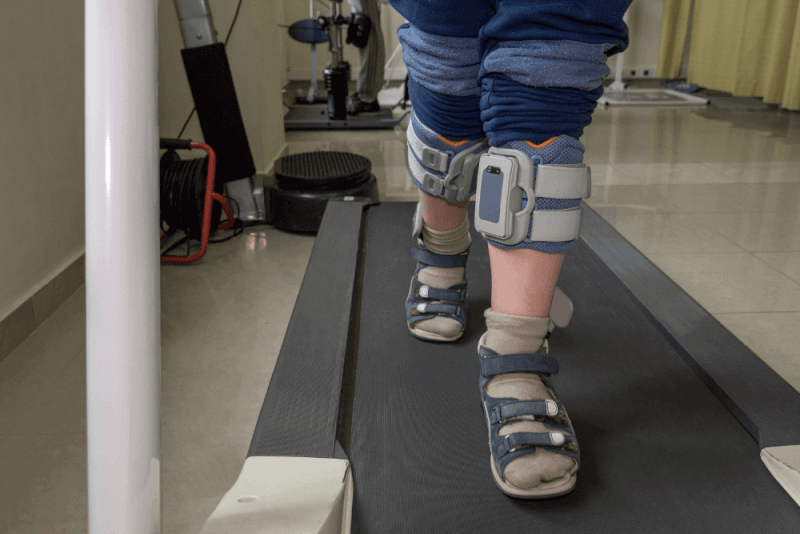
- Physical therapy
- Speech therapy
- Psychological support
- Activities to support social interactions
- Nutritional supplements
- A diet plan to prevent constipation
- Creating a reassuring and relaxing environment for the patient is important.
Rett Syndrome and Autism
Like autism, Rett syndrome is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is often not noticed at birth and can be detected as child development progresses. Rett syndrome and autism can coexist in the same individual, but they are different diagnoses. Rett syndrome is often mistaken for autism, and a person with Rett syndrome may exhibit autistic features.
Symptoms such as difficulty making eye contact, inability to socialize, regression in motor skills, and repetitive hand movements are seen in both disorders. There are fundamental differences between Rett syndrome and autism. Rett syndrome is mostly seen only in girls, while autism can be seen in both girls and boys. Individuals with autism have an irregular walking style, but children with Rett syndrome may completely lose the ability to walk.
Stages of Rett Syndrome
In Rett syndrome, there are different stages depending on the symptoms and the age at which they appear.
Stage 1
Stage 1 is the early onset stage and can start between 6 to 18 months, but it is often not noticed.
Stage 1 symptoms
- Decreased interest in toys
- Reduced eye contact
- Slowed head growth
- Hand sweating
- Delay in motor skills like crawling and sitting
Stage 2
- Stage 2 involves cognitive and motor regression and begins between ages 1-4, lasting for months. It can progress gradually or rapidly.
Stage 2 symptoms
- Loss of speech
- Loss of hand movements
- Repetitive hand movements (bringing hands to the mouth, clapping, grasping, etc.)
- Communication difficulties
- Breathing irregularities
- Marked slowing of head growth
- Unsteady walking
- Difficulty initiating motor movements
Stage 3
- Stage 3 is the plateau stage and can start between ages 2 to 10. Many girls remain in this stage for most of their lives.
Stage 3 symptoms
- Difficulty with motor skills
- Feeding difficulties
- Involuntary movements
- Constipation
- Seizures
- Difficulty performing learned movements or speech
Stage 4
- In stage 4, cognitive status stabilizes or shows slight decline. There are significant musculoskeletal issues, and girls under 15 often become wheelchair-dependent due to reduced movement.
Stage 4 symptoms
- Spinal curvature
- Complete loss of walking ability
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle rigidity
- Increased eye contact
- Increased muscle tone in arms and legs
Characteristics of Rett Syndrome
Rett syndrome is a condition that arises from a genetic mutation. It is generally not noticeable until around 12 months of age, after which it presents itself through developmental issues in the child.
It is mostly seen in girls but can also occur in boys, although rarely. Since it is a disorder that progresses with developmental issues, it significantly reduces the individual's quality of life and can lead to a wheelchair-dependent life in advanced stages.