What is the sixth disease?
The sixth disease, which usually affects infants and children, is caused by Herpes group viruses. The sixth disease, also called Roseola Infantum, spreads rapidly in environments such as nurseries where babies between the ages of 6 months and 2 years are collectively present. Although it is rare in older children and adults, its symptoms are mild. Therefore, it does not require hospitalization.
Sixth causes of disease
The sixth disease is caused by viruses from the Herpes virus family, which also causes cold sores. It is usually Herpes virus 6, but human Herpes virus 7 can also occur.
Sixth disease diagnostic criteria
The sixth disease is characterized by fever and rashes. If these symptoms are present, the diagnosis can be made without the need for any laboratory tests. However, in case of immunodeficiency or unusual symptoms, various tests may be ordered according to the physician’s prediction.
Sixth disease symptoms
After the sixth disease-causing virus enters the body, the incubation period must end before the first symptoms appear. Symptoms seen in babies during this process are mild and faint. Symptoms caused by the sixth disease include the following:
- Fever that develops suddenly and rises above 38 degrees Celsius
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck
- Skin rashes
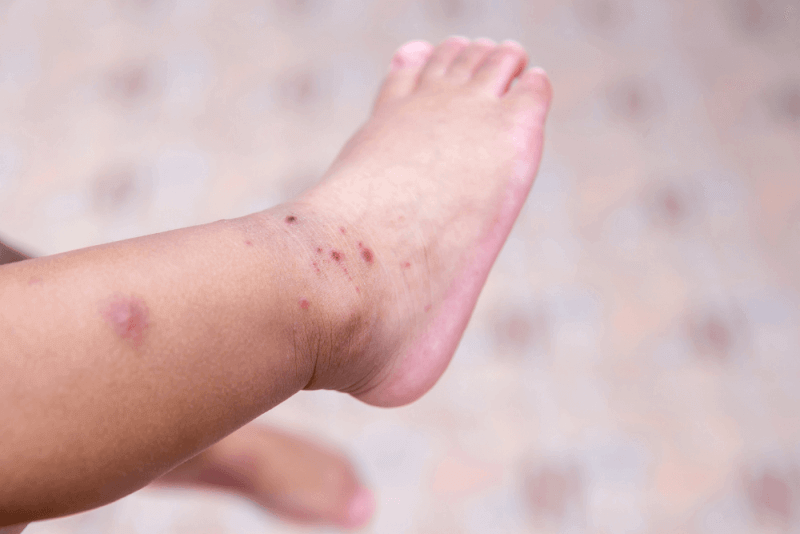
In the sixth disease, skin rashes usually appear after the fever subsides. These rashes can be pink and small, or they can appear as patches. Although most of the debris has a smooth surface, some of them may also have a rough surface. It is also possible to see white patches around the skin rashes, which usually start on the abdomen, chest and back. Later in the course of the disease, the rash may spread to the neck and arms, but is less likely to appear on the face and legs. These rashes, which do not cause itching or any discomfort in children, can be mistaken for measles or rubella. However, in the sixth disease, the rash disappears after 2 to 3 days. In addition, other symptoms that can be seen in infants and young children include the following:
- Restlessness
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Mild diarrhea
- Decreased appetite
In young children, fever can cause convulsions. For this reason, in case of signs of convulsions, the emergency room should be consulted as soon as possible and the following symptoms should be shared with the physician:
- Persistence of the rash after 3 days
- Fever lasting longer than 7 days
- The child’s temperature is higher than 39.4 degrees Celsius
What are the risk factors for the sixth disease?
Children and adults all over the world come into contact with roseola. However, the immune systems of adults and older children with strong immune systems can eliminate this virus without causing any illness. On the other hand, infants, young children and people whose immune systems are underdeveloped for any reason are not immune to the virus. In addition, babies younger than 6 months are not affected by the virus because they still have antibodies from their mother.
Sixth disease treatment methods
The sixth disease can be treated by a pediatrician or a family doctor. Since it usually has a benign course, treatment by an infectious disease specialist is rarely needed. Since the sixth disease is caused by a virus, treatment is aimed at reducing the patient’s symptoms. In addition, since it is a viral disease, antibiotics are not used in its treatment. In order for patients to recover quickly, they should pay attention to the following:
- Applications to reduce fever
- Use of air humidifiers to keep the environment moist
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Bed rest
Dressing children with fever in comfortable and thin clothes is one of the most important practices to reduce fever. In addition, the ambient temperature should not be raised too high. If necessary, patients can take a warm shower. In addition, wrapping the hands and feet with a towel soaked in warm water can also help lower the fever. Alcohol and vinegar should be avoided to reduce fever. Antipyretic medicines can also be used.
Sixth disease recovery period
In order to talk about the child’s recovery, the fever should not rise for at least 24 hours and the other symptoms should disappear. After these changes have taken place, the child can return to normal life. However, if certain conditions change, the physician should be contacted:
- Rashes lasting longer than 3 days
- The child’s temperature rises more than 39.4 degrees Celsius
- The child’s fever lasts longer than 7 days
What is the incubation period of the sixth disease?
As with other virus infections, the sixth disease is a disease with a high risk of transmission. After transmission through sneezing, coughing or talking, it enters the incubation period without any symptoms. This period lasts 14 days. Although children do not show any symptoms during the incubation period, there is a risk of transmission. For this reason, the sixth disease can spread rapidly, especially in environments where children congregate.
What are the complications of the sixth disease?
The course of the sixth disease is mild. Therefore, it usually does not cause complications. On the other hand, since the sixth disease causes fever, the most common complication is convulsions. A sudden rise in body temperature can cause children to have seizures. During a seizure, children may lose consciousness, experience temporary loss of bladder and bowel control and involuntary movements of the arms and legs. As frightening as it may be, the development of seizures due to the sixth disease is rare and short-lived. However, because it is an urgent and important medical situation, 112 should be called and emergency assistance should be requested.
In addition, people who have undergone organ transplantation or bone marrow transplantation have suppressed immune systems and the sixth disease can activate previous infections. For this reason, the sixth disease can be more severe and last longer in these patients.
How to avoid the sixth disease?
No vaccine has been developed to protect against the sixth disease. For this reason, children should avoid contact with infected patients, especially during the risk months. In addition, the sick child should not be allowed to see immunocompromised people or other young children until the fever has subsided.
Caregivers also need to be vigilant to prevent the spread of the sixth disease. For this reason, they should constantly wash their hands and clean surfaces with antibacterial cleaners.
In addition to these measures, children should be taught to use tissues when sneezing or coughing and to throw them in the trash afterwards. To reduce exposure to infection, utensils such as cups, plates or forks should also be separated.
What are the differences between the sixth disease and measles?
The rash caused by the sixth disease is similar to the rash caused by measles, a childhood infection. However, there are significant differences between the rashes of both diseases. In measles, the rash is red and brown, while the rash caused by the sixth disease is pink.
On the other hand, the rash caused by measles starts on the face and then progresses to the lower parts of the body. In addition, the rashes caused by the sixth disease start on the back and abdomen and then spread. Finally, the sixth disease has a much milder course than measles.