What is Spasticity?
Spasticity, one of the pathological health problems, is a health problem that occurs due to severe contraction of any muscle group. Spasticity, which occurs as a result of damage to the brain, can be seen in certain muscle groups or in all muscles in the body.
These involuntary, violent contractions limit mobility because the muscles are constantly tense, stiff and rigid. Depending on the muscles affected, patients may be able to walk, talk, As their ability to eat and move is restricted, there is a serious decrease in the quality of life of patients.
Besides all these, spasticity is not a single disease. It is a condition caused by deformations of the brain or spinal cord. It is especially common after brain trauma, cerebral palsy, stroke and multiple sclerosis. The general cause of spasticity in children is oxygen deprivation in the brain.
Spasticity can be seen in patients in different dimensions and is a progressive condition. Spasticity that occurs in one muscle group may then start to be seen in other muscle groups. Preventing its progression requires appropriate treatment and careful attention to the first symptoms by the person caring for the patient.
Factors that trigger the progression of spasticity are;
- Ingrown toenail
- Urinary tract infection,
- It's too cold,
- It's too hot,
- Constipation
- Vascular occlusion,
- Broken,
- Dislocation,
- Gallbladder diseases,
- Gum problems,
- Menstrual bleeding
- Hemorrhoids,
- Infections occur.
Symptoms of Spasticity
Symptoms of spasticity in adults are as follows:
- Increased muscle tone,
- Rapid muscle contractions,
- Exaggerated deep tendon reflexes,
- Muscle spasms
- Involuntary crossing of the legs,
- Fixed joints,
- Constant muscle stiffness,
- Involuntary contractions,
- Pain or discomfort,
- Ability to perform fewer functions,
- Inability to fulfill personal care,
- Abnormal posture,
- Bone and joint deformities,
- Severe pain
Symptoms of spasticity in children are as follows:
- Growth problems,
- Painful and deformed joints,
Causes of Spasticity
The most common cause of spasticity in our country, which occurs due to problems in the motor nerves and spinal cord, is due to oxygen deprivation during birth. Other causes of spasticity include the following diseases:
- Krabbe disease
- Phenylketonuria
- Adrenoleukodystrophy,
- Hereditary spastic paraplegia,
- ALS,
- Traumatic brain injuries,
- Paralysis
- MS,
- Cerebral Palsy
How is Spasticity Diagnosed?
Spasticity in both children and adults can be diagnosed by neurological examination. Patient history, physical examination and neurological imaging methods are the methods used in the diagnosis of the disease.
Spasticity Treatment
Spasticity treatment is planned individually for the patient. Because each patient's affected muscle group and degree differ. In order to recommend treatment for spasticity, there must be reasons such as the impact on patients' quality of life, difficulty sleeping and pain. When preparing the treatment plan, it is planned according to the patient's condition and goals. It is important to implement treatment to improve patients' independence and well-being. Otherwise, spasticity causes problems such as chronic constipation, pain, permanent joint deformities, urinary tract infections and pressure sores.
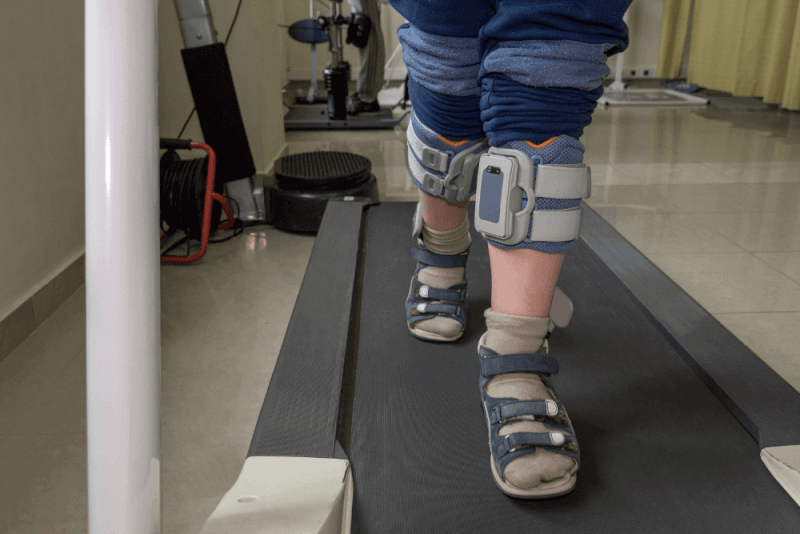
Spasticity Treatment in Children
When planning the treatment of children, the main goal is to relax the muscles as much as possible, promote optimal height growth, relieve pain and stiffness, and improve walking and independence. Specialists involved in the treatment of children include doctors, physician assistants, nurses, therapists and child specialists. Many techniques and treatment methods are applied together with a multidisciplinary approach.
Physical therapy is used to expand children's range of motion, increase muscle flexibility, improve coordination and maximize their strength. Extremely successful results are obtained with regular and correct continuation of physical therapy. There are also some methods used in addition to physical therapy for children. These are:
- Temporary plaster casts,
- Braces
- Therapeutic hot and cold applications,
- Electrical stimulation,
- Biofeedback therapy is happening.
Medicines are also used to treat spasticity in children. In some patients, medicines can be used in combination.
In addition, some patients are also helped by surgical procedures. These procedures are applied to fulfill the function of casts and splints used to apply force against the muscles.
Spasticity Treatment in Adults
The treatment of spasticity in adults is similar to the treatment of children. In some patients it is necessary to start treatment immediately, while in others it may be safer to wait. This decision is made by experts after the necessary evaluations are made.
Physical therapy is also an important part of treatment in adult patients. In particular, regular stretching movements prevent permanent contractions in the future.
The drugs to be used for spasticity are muscle relaxants. These drugs are preferred in patients with several muscle clusters affected. Muscle relaxants can be used orally or injected into the spinal fluid. For isolated spasticity, chemodenervation agents are used to weaken or paralyze overactive muscles. In cases of severe spasticity that do not respond to medication or physical therapy, surgery can be used to destroy some overactive nerves in the spine.
Botulinum Toxin Treatment
Botulinum toxin, a type of protein isolated in the laboratory from a specific bacterium, prevents the interruption of signals to the muscles. For this reason, it is one of the methods used in the treatment of spasticity.
Botulinum toxin is injected only into the muscle groups that cause the most significant problems. The injection sites and amount are determined according to the size of the muscles. For small muscle groups, it is sufficient to do it from 1 to 2 places, and for large muscle groups from 3 to 4 places. Since the toxin does not spread far from the injection site and clusters at the injection site, the surrounding muscles are not affected.
The effect of botulinum toxin starts to be seen in small muscle groups within 24 hours and in large muscle groups within 3 to 4 days. It takes up to 2 weeks for the muscles to fully benefit from the injection. The effects of the application continue for 3 to 4 months. However, if an intensive physical therapy program is applied, the effects of the injection can last up to 6 to 12 months. After the effects wear off, the muscles are restored.
Physical therapy for spasticity
In the treatment of neuroplasticity and therapeutic spasticity, physical therapy is one of the keys to reversing spasticity permanently. With physical therapy, the brain is re-taught movements with neuroplasticity. This allows more nerve cells to be separated to control the affected limbs.
Physical therapy movements need to be repeated many times to ensure learning. For this reason, exercises should be practiced as much as possible in order to get the expected results from spasticity treatment.