30-Second Summary
- Oral thrush in babies is a mouth infection caused by a fungal infection called Candida albicans.
- It appears as white lesions resembling milk residue on areas such as the palate, tongue, and inner cheeks.
- Although it is commonly seen in newborns, it can occur at any time up to 12 months of age during growth. It is more frequently observed in premature (preterm) babies.
- Babies who are not breastfed are more likely to develop thrush, as breast milk strengthens the baby's immune system and helps prevent its occurrence.
What is Thrush in Babies?
Thrush in babies is an oral infection caused by a fungus called Candida albicans. Candida albicans is a type of fungus that normally resides in the human body but can appear when the immune system is weakened. In babies, it appears as white lesions resembling milk particles on areas such as the palate, tongue, and inside the cheeks.
Although it is commonly seen in newborns, it can also appear until the baby is 12 months old. It is more frequently encountered in premature babies, who are born early. When a baby has thrush, breastfeeding mothers are also treated along with their babies, and the infection is quickly resolved.
Diagnostic Criteria for Thrush in Babies
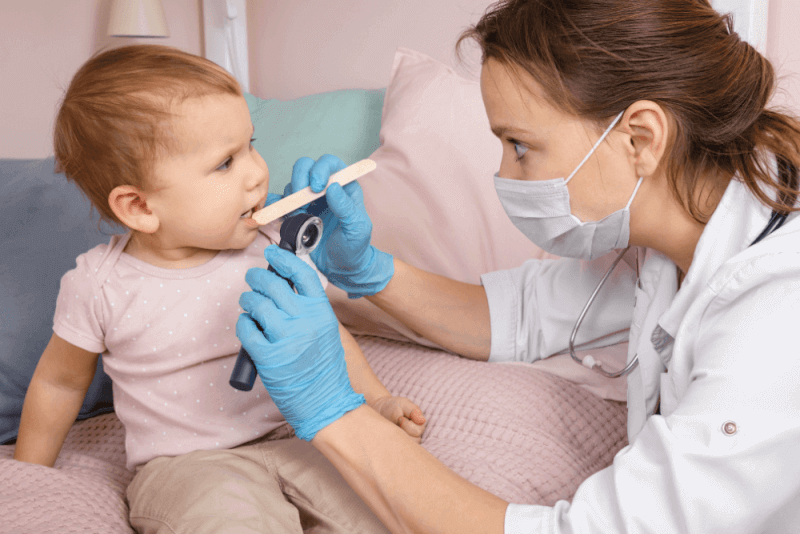
Diagnosing thrush in babies is relatively easy, as white lesions are visible inside the mouth, on the tongue, and on the inner cheeks. During a medical examination, the lesions are inspected to confirm the diagnosis. In uncertain cases, a sample is taken and sent to the laboratory. If treatment is delayed, the infection may spread to the throat, esophagus, and lungs. In advanced cases, a throat culture is taken to diagnose the condition.
Causes of Thrush in Babies
- Thrush in babies is known to be related to a weakened immune system. Especially in premature babies, the immune system is weaker, making this problem more common.
- Babies who are not breastfed are more likely to develop thrush because breast milk strengthens the baby’s immunity, helping to prevent the occurrence of thrush.
- Medication taken by the mother during pregnancy can also cause thrush. If antibiotics were used during pregnancy, thrush may appear in the baby after birth.
- Thrush can occur in babies who have deficiencies in vitamins and minerals. Low levels of important body minerals such as B12, iron, and folic acid can lead to thrush.
- An infection present in the mother can be transmitted to the baby during breastfeeding, leading to thrush.
- Failure to regularly disinfect bottles and pacifiers is one of the causes of thrush.
- Excessive sugar intake or diabetes in the mother during pregnancy can cause fungal problems, which in turn may result in thrush in the baby.
Symptoms of Thrush in Babies
- White lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, and throat
- Thick white coating inside the mouth
- Burning, itching, and pain in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Bad breath
- Restlessness
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
- Itching on the mother's breast
- Flaky skin
- If pain and discomfort are present, the infection has spread from the baby to the mother.
Treatment of Thrush in Babies
- Thrush in babies is usually treated with antifungal medications. When these medications are used, the infection subsides and disappears.
- To accelerate healing, attention should be paid to oral hygiene. The inside of the mouth can be wiped with a clean cloth moistened with water. Cleaning the white patches in the mouth helps to relieve discomfort.
- Mineral and vitamin supplements that strengthen the baby’s immune system should be used as recommended by the doctor.
- If a pacifier or bottle is used, it should be regularly disinfected.
- Mothers should use breast pads to keep the nipple from remaining moist.
Cleaning Thrush in Babies
After thrush develops in babies, cleaning the inside of the mouth can help relieve the baby. Daily cleaning of thrush helps to eliminate fungal infections. During daily care, the inside of the mouth is cleaned with gauze soaked in boiled and cooled water.
The most important step in cleaning is the use of drops prescribed by the doctor. The prescribed drops are applied to the affected area, and with regular use, thrush typically clears up within about a week. The treatment is also supported with ointments given to the mother.
How to Prevent Thrush in Babies?
- To prevent thrush in babies, it is important to maintain good hygiene of the mother’s breasts and the baby’s items such as pacifiers and bottles.
- The baby’s blood levels should be monitored to ensure they are not experiencing deficiencies in vitamins and minerals.
- During pregnancy, the mother should avoid taking medication, especially antibiotics, unless absolutely necessary.