What is Bradycardia?
Bradicardia is a slower than normal heart rate. In adults who are sitting still and are not in a situation that triggers the heart to speed up, the normal heart rate should be between 60 and 100 beats per minute. When a person has bradycardia, the pulse rate is below 60. In some individuals, this condition does not cause any problems, but sometimes it can cause serious problems.
Heart rate varies according to individuals' age, physical activity and health status. Someone who exercises a lot may have a faster heart rate because the heart needs to carry more oxygen and nutrients to the body in response to the increased demand on the heart. Bradycardia can also be seen in old age due to the slowing of movement.
Bradicardia Treatment
In cases of prolonged bradycardia, an underlying cause should be investigated. If the person is taking medication that may cause bradycardia, the medication may be stopped or the dose adjusted. Conditions such as heart diseases, other conditions or lifestyle that may cause a drop in heart rate are evaluated and regulated by the doctor.
In some cases, a pacemaker is needed to treat bradycardia that is not caused by medication or a temporary cause. A pacemaker is inserted to regulate the rhythm of the heart and normalize the heart rate.
Bradicardia Diagnosis
- To diagnose bradycardia, the doctor will first ask about your medical history and medications you are taking.
- Listening to the heart determines the beating of the heart and the depth of the beat.
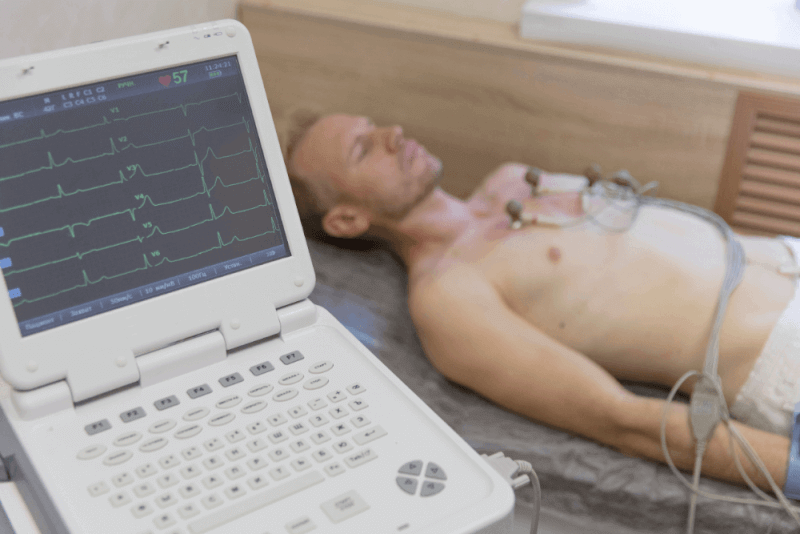
- EKG examines the conduction in the heart in detail.
- Blood tests check blood values that affect the functioning of the heart.
- A holter is installed to monitor the heart for 24 hours. After all these tests, bradycardia is diagnosed.
Symptoms of Bradycardia
A slower heartbeat per minute than normal means that the brain and many organs do not receive enough oxygen. In later stages, this can negatively affect the functioning of organs and cause damage. Some symptoms of bradycardia are as follows;
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Theft
- Fainting
- Memory problems
- Fatigue quickly during physical activity
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the chest area
- Heart palpitations
- Cardiac arrest