What is Cataract?
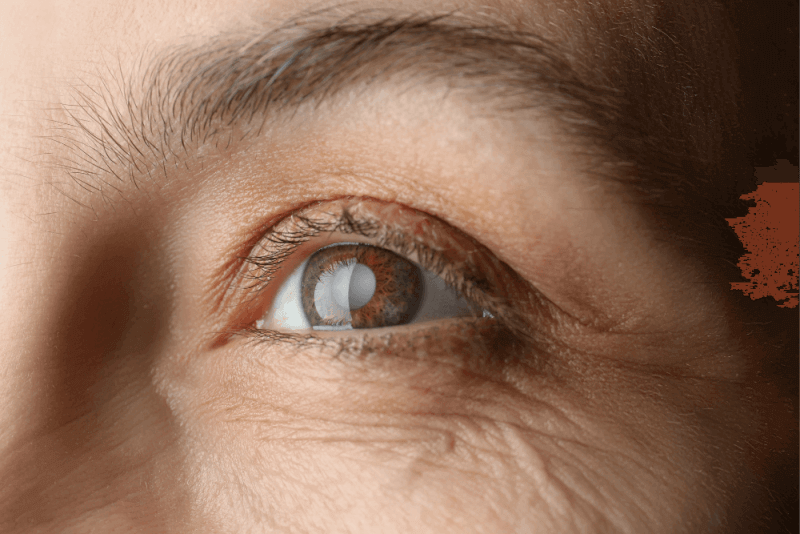
The condition of the lens of the eye becoming cloudy is called a cataract. For this reason, cataract patients have a frosted or foggy vision. This vision can cause difficulties in driving or recognizing faces. Cataracts usually develop slowly.
Therefore, it does not impair vision in the early stages. However, if left untreated over time, vision gradually becomes affected. In the early stages of the disease, stronger lighting and glasses can help cope with cataracts. However, cataract surgery is necessary if vision impairment affects activities.
Cataract Diagnosis Criteria
To determine if there is a cataract, medical history and symptoms should first be reviewed. In addition, an eye examination is performed. Various tests, including the following, are used for the diagnosis of cataracts.
- Vision test
- Eye structure examination
- Retina examination
- Fluid pressure test
Cataract Symptoms
Cataract symptoms include the following.
- Cloudy, blurry, or dim vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing halos around lights
- Frequent changes in prescription glasses or contact lenses
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in a single eye
The cloudiness caused by cataracts may initially affect only a small part of the eye's lens and may not be noticed. However, as the cataract grows, more of the lens becomes cloudy, changing the light passing through the lens. This leads to more symptoms.
Causes of Cataracts
Most cases of cataracts develop due to aging or injury that changes the tissue that makes up the eye's lens. The proteins and fibers in the lens begin to break down. This causes vision to become cloudy or blurry.
In addition to these causes, other health problems inherited from parents also increase the risk of cataracts. Moreover, past eye surgeries for other eye diseases or medical conditions such as diabetes can cause cataracts. Lastly, long-term use of steroid medications is effective in cataract development.
Cataract Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of cataracts include the following.
- Advancing age
- Diabetes
- Excessive exposure to sunlight
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Family history of cataracts
- Eye injury or inflammation
- Past eye surgeries
- Long-term use of corticosteroid medications
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Cataract Treatment Methods
When the use of prescription glasses does not improve vision, surgery is the only effective treatment for cataracts. The eye doctor's opinion is important in determining if surgery is suitable for patients. It is generally recommended if cataracts affect the quality of life.
This includes not being able to perform daily activities such as reading or driving at night. For most cataract cases, there is no need to rush for surgery. Cataracts do not harm the eyes. However, for some individuals with certain discomforts, rapid deterioration of cataracts necessitates early surgery.
Waiting for cataract surgery usually does not affect how well vision recovers. However, it is important to discuss the benefits and risks of surgery with the doctor and to have periodic follow-up examinations during the waiting period.
Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens. The artificial lens, called an intraocular lens, is placed in the same position as the natural lens and remains a permanent part of the eye.
In some individuals, the use of an artificial lens is not necessary. In these cases, vision is corrected using glasses or contact lenses after removing the cataract. Cataract surgery is typically an outpatient procedure.
As a result, patients do not need to stay in the hospital after the surgery. Various medications are used to numb the area around the eye during the surgery, and the patient usually remains awake during the procedure. Although cataract surgeries are generally safe, they carry the risk of infection and bleeding. Additionally, cataract surgery increases the risk of retinal detachment.
Patients may experience some pain for a few days after the procedure, and recovery usually occurs within a few weeks. If cataract surgery is needed for both eyes, the doctor will schedule the second eye surgery after the first one has healed.
Risks of Cataract Surgery
Complications are rare after cataract surgery, and most can be successfully treated. Risks of cataract surgery include the following.
- Swelling
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Drooping eyelid
- Dislocation of the artificial lens
- Movement of the lens
- Glaucoma
- Secondary cataract
- Vision loss
If the patient has a secondary health condition, the likelihood of complications after cataract surgery is higher. Moreover, vision impairments caused by damage from other diseases cannot be improved.
Pre-surgery Tests for Cataract Surgery
Before cataract surgery, patients undergo a comprehensive eye examination. In addition to the tests performed in this examination, some tests are conducted to determine the general condition of the patient. The pre-surgery tests for cataract surgery include the following.
Test for Current Eyeglass Prescription
This test, conducted by an eye doctor, is performed to determine the patient's current refractive error. It is done to understand whether the patient has myopia or hyperopia and to determine the degree of any vision defect.
A special machine called an automatic refractor is used in this test. Knowing the current eyeglass prescription is useful for correcting this error after cataract surgery in cases of high refractive error.
Complete Eye Examination
A complete eye examination includes the following.
- Investigating the anatomy and inflammation of the eyelid to determine if there are conditions that could increase the risk of infection after cataract surgery.
- Evaluating the status of the tear film to identify dry eye changes. Dry eyes are one of the factors that make surgery more difficult.
- Investigating abnormalities in the cornea that could make it difficult to visualize the cataract during surgery. Additional steps may be necessary to protect the corneal endothelial cells during cataract surgery. This test allows for necessary planning.
- Measuring the depth of the anterior chamber of the eye to make various plans. If the depth is insufficient, accessing the capsule may be more difficult.
- Measuring the dilation of the iris with the drops used. If the drops do not sufficiently dilate the iris, extra steps such as iris retraction may be required during surgery.
- Diagnosing the type of cataract to determine the surgical procedure to be applied. Soft cataracts are aspirated while hard cataracts require more ultrasound energy for fragmentation and removal. In white cataracts, trypan blue staining may be necessary to visualize the capsule.
- Measuring intraocular pressure to exclude glaucoma. In patients with glaucoma, the use of additional eye drops to temporarily lower intraocular pressure allows for optimal control of eye pressure during surgery.
- Investigating accompanying retinal conditions such as age-related macular degeneration or macular holes as part of the general examination.
Biometry Tests
Simple pre-surgery biometry measurements ensure the correct calculation of the power of the artificial lens to be implanted. These lenses are implanted after the cataract is removed. The axial length, or the length of the eyeball, is measured.
Next, the curvature of the cornea at two meridians at the front of the eye is measured. These measurements are known as keratometry readings. These figures obtained in biometry measurements are unique to each patient and can be automatically measured with a modified camera.
The figures are entered into a specific formula, and the biometry device calculates the lens power by deriving various refractive results. The lens power used for most patients is aimed at emmetropia. This test also helps determine if the patient has astigmatism.
If the patient has astigmatism, it can be corrected, and the opening's position on the eye is adjusted. In rare cases, standard machines may not provide accurate measurements in patients with dense cataracts, requiring different methods to measure the axial length of the eyes.
In these methods, a small painless ultrasound probe placed on the eyelids takes measurements in a few minutes. Patients wearing lenses should stop wearing them before the test to obtain accurate results.
This is because contact lenses can slightly change the shape of the cornea. Individuals using soft daily lenses should stop wearing lenses 48 hours before the measurement.
Corneal Topography
This test is performed to map the curvature of the cornea in more detail. If there are larger than normal differences in biometry readings and keratometry readings, this extra test is ordered. Corneal topography is used to diagnose keratoconus and irregular astigmatism. The results of this test can change the surgical treatment of patients.
Optical Coherence Tomography
This test provides a detailed image of the macula. It is recommended
if there is suspicion of macular changes that could prevent visual improvement after cataract surgery. This test takes sectional photographs of the retina.
If patients have conditions such as age-related degeneration or macular holes, it can be diagnosed that their vision may not improve as expected after cataract surgery.
Blood Pressure Measurements
Knowing the blood pressure measurements before cataract surgery is extremely important. Although the risk of bleeding at the back of the eye during surgery is very low, this risk significantly increases in patients with uncontrolled blood pressure.
Therefore, it is expected that the safe upper limit blood pressure measurements before cataract surgery should be systolic 200 mmHg and diastolic 100 mmHg. To treat high blood pressure and avoid the high risk of bleeding at the back of the eye, cataract surgery may be postponed.
Blood Sugar Measurements in Diabetic Patients
Before cataract surgery, diabetic patients should routinely measure their blood sugar, and surgery may be postponed if the blood sugar level is above 20 mmol/L. The reason for postponing the surgery is that high blood sugar significantly increases the risk of infection.
Post-Cataract Surgery Care
Recovery after cataract surgery usually takes 2 to 4 weeks. It is important for patients to take great care of their eyes after cataract surgery. Therefore, experts provide different recommendations for the hours, days, and weeks after the surgery. General tips for post-cataract surgery care include the following.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercises for a few weeks
- Avoid bending over for a few days after the surgery
- Avoid swimming for a few weeks after the surgery
- Protect the eyes from irritants
- Avoid rubbing the eyes
Post-Cataract Surgery Recovery Process
Complete recovery after cataract surgery can take up to 4 weeks. The recovery process for patients during this period includes the following.
Immediately After Surgery
Immediately after surgery, patients may experience the following conditions.
- Watery eyes
- Foreign body sensation in the eye
- Blurry or double vision
- Redness in the eyes
During this period, patients should adhere to the following points.
- Avoid driving
- Wear sunglasses
- Use prescribed eye drops regularly
- Protect the eyes with a sleep shield while sleeping
A Few Days After Surgery
A few days after surgery, discomfort begins to subside. However, patients may still need to wear glasses. During this recovery period, patients should pay attention to the following points.
- Avoid direct contact with soap and water on the face.
- Avoid using hair products, perfume, face wash products, lotions, and makeup
- Avoid strenuous activities
- Attend follow-up appointments.
Weeks After Surgery
During the 2 to 4 weeks following surgery, patients' vision continues to improve. If cataract surgery is needed for both eyes, the second eye surgery is performed during these weeks. During this period, patients should pay attention to the following points.
- Attend the follow-up appointment approximately 1 month after the surgery
Post-Cataract Surgery Infection
Although rare, infection after cataract surgery is a serious complication. It can have devastating effects on the patient's vision. In some patients, total loss of light perception may occur.
The primary source of intraocular infection is thought to be bacteria from the patient's ocular surface or adnexa. The most frequently isolated bacteria, accounting for seventy percent of culture-positive cases, are Staphylococcus epidermis.
Factors that increase the risk of infection after cataract surgery include the following.
- Blepharitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Canaliculitis
- Lacrimal duct obstruction
- Contact lens wear
- Other orbital ocular prostheses
- Eyelid abnormalities
How to Recognize Lens Displacement After Cataract Surgery?
The lens should not move after cataract surgery. However, lens displacement may occur. This condition can cause blurred vision, eye and headache, as well as double vision.
In such cases, patients should urgently consult a doctor as it can cause serious problems such as eye inflammation and corneal edema. If lens displacement occurs, a new operation is needed to replace the lens.
How is Eye Cataract Surgery Performed?
Patients should stop eating and drinking 12 hours before cataract surgery. In addition, it is recommended to stop taking medications that can increase the risk of bleeding during surgery. Medications used for prostate issues should be reported to the doctor.
This is because some medications can interfere with cataract surgery. If antibiotic eye drops are prescribed to be used one or two days before the surgery, they should be used regularly. Cataract surgery, usually an outpatient procedure, takes 1 hour or less to perform.
Before starting the surgery, drops are applied to dilate the pupil. Additionally, medications are used to numb the area. Sedatives are also administered to help patients relax, allowing them to remain awake but dazed during the surgery.
During cataract surgery, the cloudy lens is removed, and a clear artificial lens is usually implanted. However, in some cases, the cataract can be removed without implanting an artificial lens. The surgical methods used to remove the cataract include the following.
Phacoemulsification
In this method, an ultrasound probe is used to remove the lens. During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the front part of the eye called the cornea. Then, a needle-thin probe is inserted into the lens where the cataract has formed.
In the next step, probes that transmit ultrasound waves are used to break up the cataract and suction out the pieces. The back part of the lens capsule, called the lens capsule, is left intact to allow the artificial lens to be placed. Stitches may be used to close the small incision in the cornea once the procedure is completed.
Cataract Extraction
The process of removing the lens in one piece through an incision in the eye is called cataract extraction. This method is rarely used because it requires a larger incision. Through this larger incision, the surgeon uses various tools to remove the lens capsule and the cloudy lenses.
The back capsule of the lens is left in place to support the artificial lens. This procedure is preferred in cases of certain eye complications. Because the incisions are larger, stitches are required.
Types of Cataracts
The types of cataracts include the following.
Congenital Cataract
A cataract that is present from birth is called a congenital cataract. Some people are born with cataracts or develop cataracts during childhood. In these cases, cataracts can be inherited from parents. Additionally, infections or trauma occurring in the womb can cause cataracts.
Congenital cataracts can also be caused by certain diseases. These diseases include myotonic dystrophy, galactosemia, neurofibromatosis type 2, or rubella. This type of cataract does not always affect vision.
Senile Nuclear Cataract
Senile nuclear cataract refers to a type of cataract that affects the center of the lens. In this type, distant objects initially become blurry, but nearby objects appear clear.
Nuclear cataracts may even temporarily improve reading vision. However, over time, the lens slowly turns more yellow or brown, and vision worsens. Over time, it becomes more difficult for these individuals to distinguish colors.
Cortical Cataract
A cataract that affects the edges of the lens is called a cortical cataract. In this type, white wedge-shaped spots and streaks appear on the outer edges of the lens cortex. As the cataract slowly grows, these streaks extend to the center, affecting the light passing through the lens.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract
A cataract that affects the back of the lens is called a posterior subcapsular cataract. This type usually starts as a small area near the back of the lens. It often affects reading vision and reduces vision in bright light, causing halos around lights at night. This type of cataract tends to grow faster than others.
Posterior Polar Cataract
In posterior polar cataracts, part of the cataract is attached to the back capsule. As a result, posterior capsule rupture is usually seen during surgery.
Corticonuclear Cataract
In the corticonuclear cataract type, both the lens nucleus and the cortex develop cataracts.
Hypermature Cataract
In this type of cataract, the entire lens develops cataracts.
Morgagnian Cataract
Morgagnian cataracts occur when the cataract treatment is delayed, and the cortex becomes liquefied, causing the nucleus to sink down.
Cataracta Nigra
In cataracta nigra, the cataract becomes very hard, resulting in a brown and black appearance.
Brands of Lenses Used in Cataract Surgery
The brands and quality of lenses used in cataract surgery are extremely important for the outcomes of the surgery and the person's quality of vision. Choosing low-quality lenses can lead to issues such as reduced vision and color loss, so it is essential to select the most suitable and highest quality lens for the patient before surgery.
Alcon
Produced in America, this brand is used not only in cataract surgeries but also in lens replacement surgeries performed to eliminate high eye degrees.
While Alcon lenses are not smart lenses, they are not standard lenses either. The feature in the central part of these lenses provides patients with enhanced depth perception. This ensures very good vision levels at both distant and medium distances.
Johnson & Johnson
The lenses from the American brand Accuvue, produced by Johnson & Johnson, are also available for daily use in addition to cataract lenses.
VSY
VSY lenses used in cataract surgery offer significant changes in distant, intermediate, and near vision. This brand, which has a hydrophobic surface and UV protection, is also effective in reducing halo effects around lights. Thanks to these features, VSY lenses significantly reduce the need for glasses after cataract surgery.
Rayner
Produced in England, this brand pioneers ophthalmic innovation. Having designed the world's first intraocular lens, the brand also produces lenses with various features. These features include monofocal and hydrophobic types. Rayner lenses, which allow for easy placement by surgeons, do not contain suspicious substances.
Tecnis
This brand of lenses offers patients the freedom to see ideally at both night and day distances. They provide the ability to see distant and near objects with high contrast even in low-light conditions.
German Zeiss
Founded in Germany, the Zeiss brand, which belongs to a company producing optical instruments, medical devices, and industrial measurements, offers not only permanent lenses but also daily lenses.