30 Second Summary
- Although the liver has the ability to regenerate itself, if there is too much scar tissue, the liver cannot function properly and cirrhosis occurs.
- The most common causes of cirrhosis are alcohol consumption, hepatitis B and C, obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- In the early stages of cirrhosis, there are usually no symptoms. In advanced stages, symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, jaundice, itching, fluid accumulation in the abdomen, bleeding, and impaired brain function are observed.
- Treatment of cirrhosis aims to eliminate the factors that cause cirrhosis and control complications.
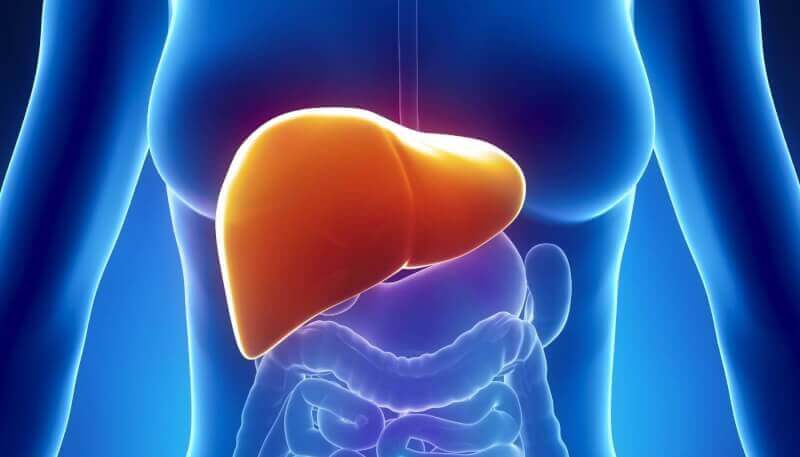
In addition to being the only organ in the body that has the ability to self-renew, the liver is approximately 1.5 to 2 kg. The liver has many important functions in the body. These tasks include producing enzymes that digest food, cleaning toxins in the blood and ensuring blood clotting. Because it has undertaken so many important tasks in the body, any problem in the liver causes major problems.
However, scar tissues formed in the liver can heal easily due to the special properties of the organ. On the other hand, if there is too much scar tissue, healing does not take place fast enough and the liver cannot function properly. Over time, the injured tissue begins to replace healthy liver tissue. When injured tissues do this, it is called cirrhosis.
There are many factors that contribute to the development of cirrhosis. These factors often include infectious diseases and alcohol abuse. However, it is not clear why some patients develop cirrhosis.
In short, cirrhosis is caused by irreversible damage to the liver tissue by many different factors, resulting in the liver not being able to fulfill its function.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
Patients with cirrhosis may not see symptoms in the early stages of the disease. Usually, the first symptoms appear with an increase in damaged tissues in the liver. Symptoms of cirrhosis include the following:
- Fatigue
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss,
- The body bruises easily and bleeding occurs,
- Jaundice
- Swelling of the legs,
- Swelling in the abdomen,
- Intense itching,
- Rashes on the palms of the hands,
- Whitening of the nails,
- Too many visible blood vessels in the skin,
- Hafiz problems,
- Difficulties concentrating,
- Irregular menstrual periods,
- Loss of sex drive in men,
- Enlargement of breasts in men,
- Shrinking of the testicles,
- Coughing up blood,
- Edema formation in the abdomen,
- Severe muscle cramps,
- Coffee-colored urine,
- Fire,
- Enlarged spleen
- Bone disease
- Easy fracture of bones.
What are the tests for cirrhosis? (How is the diagnosis made?)
Since cirrhosis is a disease that can progress without any symptoms in its early stages, diagnoses in this period are usually recognized by chance as a result of a general examination.
If cirrhosis is suspected, the doctor will first ask about the patients' alcohol consumption. The patient's history should also be examined in detail.
In order to detect cirrhosis, some blood tests and imaging methods should be used in addition to clinical examination. Patients are asked to take blood tests to determine whether the liver is functioning properly. These tests include abnormal blood counts, liver enzyme levels, virus infection, low protein levels in the blood, antibodies.
Imaging tests include MRI and ultrasound. Doctors may also order a liver biopsy to see how much damage has been done to the liver.
As a result of these tests, doctors can easily determine the stage of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis Treatment Methods
The treatment of cirrhosis has good main goals. The first is to eliminate the cause of cirrhosis. The second stage is the elimination of complications caused by cirrhosis. The treatment of each patient is planned individually. However, first of all, patients should avoid the factors that cause cirrhosis. These factors include the following.
- Cutting alcohol consumption,
- Weight loss,
- Treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis C,
- The use of medicines to relieve symptoms such as pain and fatigue.
The second stage, complications, needs to be treated. Many methods are used for this.
Low Sodium Diet
Especially if there is a lot of water retention in patients, then patients should follow a low-sodium diet. Patients may also be helped by medication to reduce water retention.
Blood Pressure Drugs
Blood pressure-lowering drugs are used to reduce the swelling and bursting of blood vessels seen in cirrhosis.
Antibiotics and Vaccines
Since cirrhosis can be caused by diseases, antibiotics may be required. Medications can be used to reduce the accumulation of toxins in the liver. In addition, if there is inflammation in the liver, then steroids are used.
It is also necessary to monitor the occurrence of liver cancer. For this, patients should have regular tests.
Thanks to the liver's ability to regenerate itself, patients can continue their lives despite having lost ⅔ of their liver.
Liver Transplant Surgery
If cirrhosis is advanced, patients may need a liver transplant. For this purpose, liver transplantation can be performed from a deceased organ donor or a part of the liver can be taken from living donors.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery: 6-12 hours
Anesthesia Method: General
Length of Hospitalization: 7-21 days
Return to Work Time: 3-6 Months
Stages of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis consists of two stages. Simply put, the first stage is mild cases, while the second stage is more severe.
Compensated Cirrhosis
In this stage, called compensated cirrhosis, the liver can repair itself without serious problems in the body.
Decompensated Cirrhosis
The stage that occurs after the exacerbation of cirrhosis is called decompensated cirrhosis. In patients at this stage, liver cells begin to fail to perform their functions. In the decompensated stage of cirrhosis, water retention in the abdomen, varicose veins in the esophagus or stomach and edema in the legs are seen. In addition, patients in these stages may also experience brain damage or coma due to the inability to remove toxins in their blood.
Signs of death in cirrhosis patients
Advanced liver disease is a term used to indicate that the disease has reached an irreversible stage. Advanced liver disease is also referred to as end-stage liver disease and decompensated cirrhosis. At this stage, the hepatic architecture of the liver is disrupted and regenerative.
Patients who have not yet developed major complications are referred to as compensated cirrhosis. In decompensated cirrhosis patients, complications such as hepatopulmonary syndrome, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, ascites and variceal bleeding are possible. Unlike other fatal diseases, irreversible liver disease is curable and definitive with liver transplantation. Complications seen in end-stage liver disease include the following.
Jaundice
Jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and eyes due to bile accumulation. Bilirubin, a yellow pigment, causes skin and gene discoloration. This change also indicates that bile is not being delivered to the intestines. The accumulation of bile in the body causes itching. Medicines may be prescribed to manage itching. In addition, an external tube is applied to the liver to drain the bile.
Blood clotting
In the final stage, structural defects in the liver render it unable to produce proteins for blood clotting. This increases the risk of bruising and bleeding in patients. In particular, dilation of the veins in the lower part of the esophagus and changes in the veins in the gastrointestinal tract occur. These changes in the blood vessels can cause them to rupture. This increases the risk of bleeding. Therefore, the risk of bleeding must be taken into account in patient care.
Fluid accumulation in the abdomen
Another complication of end-stage liver disease is fluid accumulation in the abdomen. This accumulated fluid causes serious discomfort to patients. The biggest reason for this is that it puts pressure on the diaphragm. This pressure on the diaphragm causes patients to experience shortness of breath. Other problems caused by fluid accumulation in the abdomen include the following:
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Back pain
- Infection
Fluid accumulated in the abdomen can be drained to relieve patients. However, the fluid will soon accumulate again. Diuretics may be prescribed to slow fluid retention. Opioids are also prescribed to help patients breathe easier.
Decreased brain function
Another complication seen in end-stage liver disease patients is reduced brain function. This is because toxic substances in the blood accumulate and cause confusion in patients. Other changes that can be seen in patients include irritability and personality disorder. Decreased brain function causes patients to become more sleepy. This can even cause patients to fall into a coma. Other symptoms caused by reduced brain function include
- Depression
- Decreased appetite
- Fatigue
- Difficulty sleeping at night
- Muscle cramps
Is cirrhosis contagious?
Cirrhosis is a general term used to refer to liver diseases. There are therefore many causes that can lead to cirrhosis. These include factors such as alcohol and obesity, as well as hepatitis diseases.
Hepatitis is caused by a virus that can be transmitted between people. Cirrhosis caused by hepatitis can therefore be transmitted from the patient to other people. However, there is no risk of transmission in cirrhosis caused by other causes.
Does cirrhosis kill?
Cirrhosis is one of the chronic diseases. For this reason, it is a disease that progresses in stages. In the early stages of cirrhosis, which progresses slowly, it is not life-threatening. However, in its later stages, it causes liver failure. This is why cirrhosis can be life-threatening if left untreated. However, even in end-stage cirrhosis, liver transplantation removes the threat to life.
Types of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a disease that can occur for many different reasons. For this reason, it is divided into different types depending on the cause.
Alcoholic cirrhosis
In alcoholic cirrhosis, which is an extremely serious disease, there is fat in the liver due to alcohol. This adiposity leads to an increase in non-functioning tissue in the liver. Genetic predisposition also plays a role in the development of alcoholic cirrhosis. It also causes long-term inflammation and loss of wound function.
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a cirrhosis caused by an immune system disorder that affects the bile ducts and liver. In addition to being one of the autoimmune diseases, it is especially seen in older women. The symptoms of primary biliary cirrhosis are markedly different from other types of cirrhosis.
Secondary biliary cirrhosis
Secondary biliary cirrhosis, a rare type of cirrhosis, is caused by injuries to the bile ducts. Over time, wound cells are replaced by healthy bile duct cells. This leads to an increase in non-functioning liver tissue.
Cirrhosis due to hepatitis C
This type of cirrhosis, which causes the liver to enlarge or swell, affects approximately 25% of patients. Hepatitis C is especially common in people who consume alcohol.
Cardiac cirrhosis
It is one of the rare types of cirrhosis. Cardiac cirrhosis occurs because abnormalities in the cardiological system affect the liver over a long period of time.
Cryptogenic cirrhosis
Cryptogenic cirrhosis can be briefly defined as cirrhosis of undetermined cause. The cause of cirrhosis is usually determined by liver biopsy. However, the cause of some cirrhosis cannot be determined despite a biopsy.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Bile fluid, which digests fats, is produced in the liver and then sent to the small intestine through the bile duct. If the bile duct is inflamed, bile fluid cannot flow sufficiently. Bile fluid accumulating in the liver causes damage to the tissues in the liver and cirrhosis develops.
Cirrhosis due to genetic diseases
Some cirrhosis is due to the accumulation of elements in the body. For example, Wilson's disease causes cirrhosis through copper accumulation.