What is Cross Linking (corneal cross-linking)?
Keratoconus is a procedure used to treat a condition called keratoconus. The purpose of cross-linking is to strengthen the tissues in the cornea. Keratoconus is a condition where the cornea thins and weakens over time. This leads to impaired vision and difficulty in seeing. The thinning of the cornea causes it to deform and become cone-shaped.
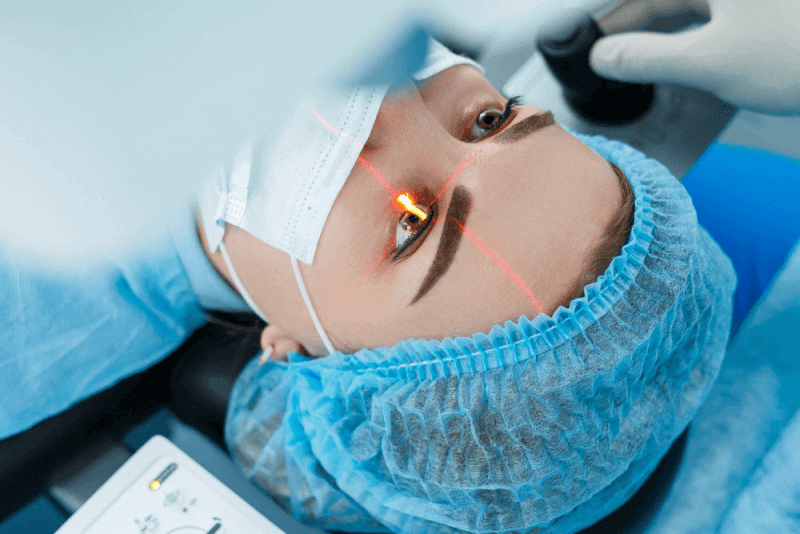
In corneal cross-linking procedures, eye drops and ultraviolet light from a special machine are used to strengthen the tissues. This prevents the cornea from becoming conical due to the disease. The reason this procedure is called cross-linking is that it adds bonds between the collagen fibers in the eye. These bonds, which act like supportive beams, help keep the cornea stable.
Corneal cross-linking is the only treatment method that can prevent the worsening of progressive keratoconus and helps avoid a larger surgery like corneal transplantation.
In which diseases is Cross Linking (corneal cross-linking) used?
Corneal cross-linking surgery is used to treat a disease called keratoconus. While the procedure does not reverse the existing corneal changes, it prevents the condition from worsening. The progression slows down after the surgery.
How is Cross Linking (corneal cross-linking) performed?
Corneal cross-linking is a procedure that can be performed during a doctor's examination. Before the procedure, the eyes are numbed with anesthetic drops. If necessary, a sedative is also given to the patient.
Then, the doctor applies specially formulated vitamin B2 eye drops that help the cornea absorb light better. It takes about 30 minutes for the drops to penetrate the cornea.
In the next step of the procedure, patients look at a special light. The entire treatment takes 60 to 90 minutes, and since it is performed under anesthesia, patients do not feel any pain or discomfort.
Post-procedure care for patients after corneal cross-linking
After the procedure, patients need to pay attention to the following points for eye care:
- Patients may feel discomfort for a few days after the operation. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe medication to alleviate the discomfort.
- To ensure quick healing, contact lenses are applied. If the lens falls out, it should be reported to the doctor and should not be attempted to reapply by the patient.
- It is important not to rub the eyes for 5 days after the surgery.
- Sensitivity to light may occur after the surgery. Wearing sunglasses can help with this.
- Some patients may feel a foreign body sensation in the eye after the operation.
- In case of severe pain or a sudden deterioration in vision, a doctor should be consulted.
Risks of corneal cross-linking
The potential risks of corneal cross-linking include:
- Eye infection
- Eye pain
- Swelling in the eye
- Damage to the cornea or epithelium
- Blurred vision
- Hazy vision
- Other vision problems