30-Second Summary
- This test, which allows the measurement of the heart's electrical activity, is extremely quick and painless.
- There is no need for special preparation before an ECG test. However, it is recommended to wear comfortable clothes on the day of the procedure.
- The ECG procedure has no side effects. Since it does not use radiation or electricity, it is an extremely low-risk test. However, some patients may develop sensitivity to the adhesive used for the electrodes.
- If the pulse is weak or the heartbeat is irregular and cannot be counted, an ECG is used.
What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
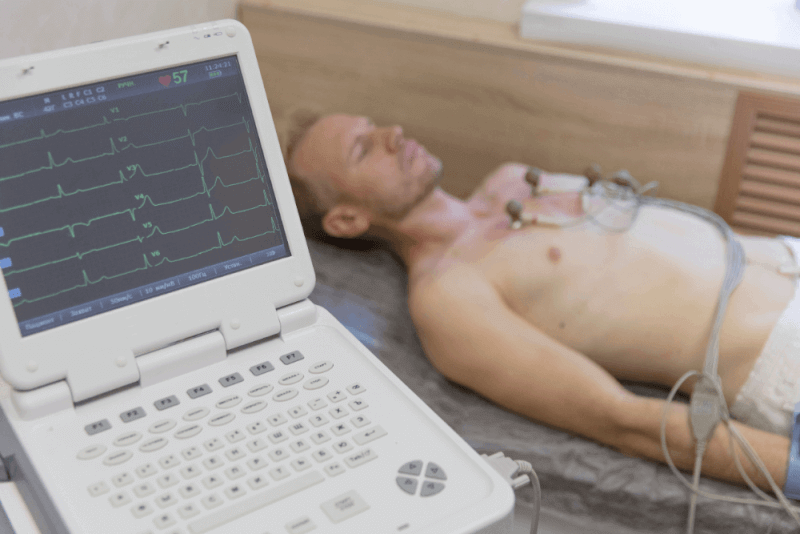
The electrocardiogram, used for diagnostic purposes, is commonly referred to as ECG. This test, which allows the measurement of the heart's electrical activity, is extremely quick and painless. To monitor the heart's electrical activity with an ECG device, electrodes are attached to the patient's chest and limbs. The information from the electrodes is converted into a wave pattern via a computer. This allows healthcare professionals to easily understand the heart rhythm. The ECG can be applied during rest or as part of a stress test.
Types of Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Classic ECG devices may be insufficient to detect occasional electrical activities. Therefore, different ECG devices are used. These device types include the following:
Holter Monitor
The Holter monitor remains on patients for 24 or 48 hours. During this period, the heart's electrical activity is continuously recorded. This allows occasional electrical changes to be detected.
Event Monitor
Event monitors are worn for a week or longer. However, since this device does not have an automatic recording feature, the patient must press a button when symptoms are felt.
Why is an Electrocardiogram (ECG) Used?
Uses of the ECG include the following:
- To check whether the heart rhythm is normal or if an arrhythmia is present
- To determine if there is poor blood flow to the heart muscle due to coronary artery disease
- To diagnose a heart attack
- To diagnose heart abnormalities such as enlargement of heart chambers or abnormal electrical conduction
- To detect heart damage or heart failure
- To determine if the heart is ready for surgery before an operation
Additionally, there are some situations where checking how the heart is functioning is necessary. These include:
- Use of a pacemaker
- Initiation of medication for heart disease
- Having had a heart attack
Symptoms for which specialists recommend an ECG include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Heart palpitations
- Skipped heartbeats
- Rapid heartbeat
- Lightheadedness
- Confusion
- Reduced ability to exercise
How is an Electrocardiogram (ECG) Performed?
There is no special preparation required before an ECG test. However, it is recommended to wear comfortable clothing on the day of the procedure. Additionally, the following points should be considered before the test:
- Do not use body lotion on the day of the test.
- Since electrodes will also be placed on the legs, do not wear pantyhose.
- Choose front-buttoned clothing to allow easy access to the chest area for electrode placement.
The steps of the ECG test are as follows:
- To perform the test, the patient lies on a stretcher and relaxes.
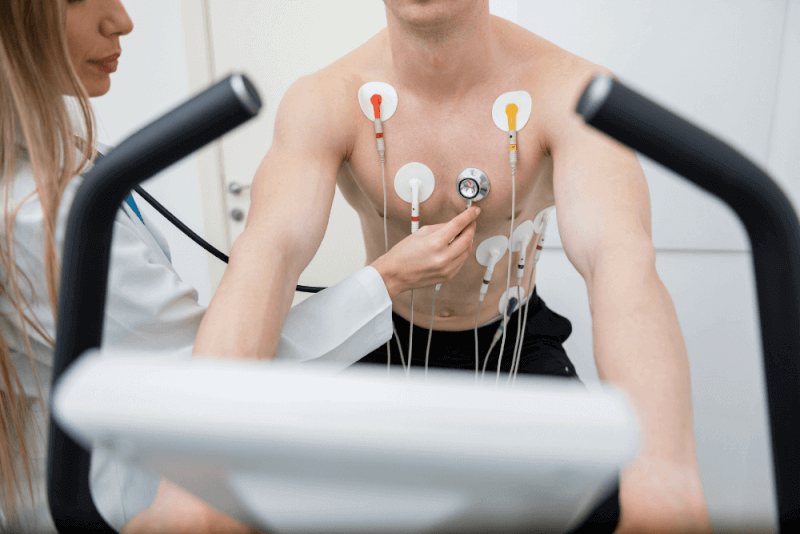
- The healthcare professional attaches 12 electrodes to various areas of the chest. To improve the connection, chest hair may be shaved.
- Clamp-shaped electrodes are placed on the wrists and ankles.
- The electrodes are not removed until the test is complete.
The procedure usually takes about 10 minutes, although the actual recording time is 1–2 minutes. Patients do not feel anything during the test. In stress tests, electrodes are attached before getting on the treadmill. After the procedure, patients can return to their normal activities.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Side Effects
The ECG procedure has no side effects. Since radiation or electricity is not used, it is considered a very low-risk test. However, some patients may develop sensitivity to the adhesive used for attaching the electrodes.
How is an Electrocardiogram (ECG) Read?
Healthcare professionals look at how much electrical activity is in the heart, how strong it is, and how much time passes between the different waves or peaks that represent electrical signals. The information contained in the ECG output includes the following:
- The upper heart chambers, where the heartbeat begins, form the first wave or P wave.
- The lower heart chambers form the next wave called the QRS complex.
- The third wave is called the T wave. It shows the resting state of the heart or the recovery process after beating.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Results
Specialist doctors look for heart signal patterns in ECG results. This way, the following information can be obtained:
Heart Rate
The number of heartbeats per minute is called the heart rate. It is also possible to determine the heart rate by checking the pulse. However, when the pulse is weak or the heartbeats are irregular and cannot be counted, ECG is used. With ECG results, tachycardia or bradycardia can be diagnosed.
Heart Rhythm
The time between each heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. Additionally, the signal pattern between each beat is also referred to as heart rhythm. ECG can be used to diagnose arrhythmia.
Heart Attack
It is possible to diagnose past heart attacks with ECG. Additionally, the patterns in the results show which parts of the heart were damaged due to a heart attack.
Blood and Oxygen Supply to the Heart
ECG performed on patients with chest pain helps determine whether there is a decrease in the blood flow to the heart.
Heart Structure Change
ECG results can provide clues about an enlarged heart, congenital heart defects, and other heart conditions.