What is a Fungal Infection?
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, are caused by fungi that can lead to infections by yeast or mold. Fungal infections are often seen on the skin and nails. However, fungi can also cause infections in the lungs, vagina, and urinary tract. Fungi are organisms classified separately from animals and plants. They reproduce by spores. Many types of fungi can live in different parts of a healthy body, but their populations can increase significantly under certain conditions. There are estimated to be millions of different types of fungi, but only a very small portion of them cause diseases in humans.
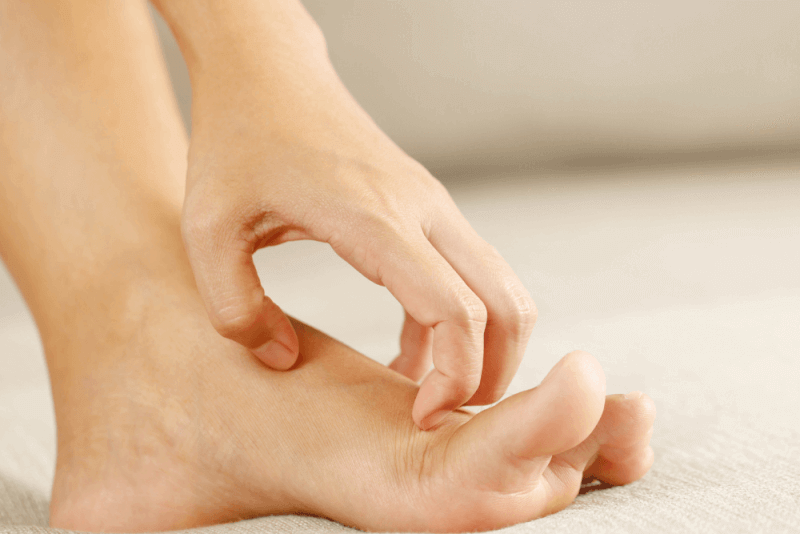
Fungal infections can appear in different ways depending on the area where they occur. For example, fungal infections on the skin appear red and swollen, while fungal infections on the nails cause discoloration. Fungal infections in the throat appear as white patches.
Fungal infections can affect anyone but are more common in areas that remain constantly moist or experience continuous friction. People with weakened circulatory or immune systems and those with diabetes are more prone to fungal infections. Fungal infections usually do not pose a serious health risk, but certain types of fungi can cause severe health problems in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Causes of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are caused by molds, fungi, and yeast. While most fungi do not cause infections, a few different types, especially opportunistic fungi, can cause infections, particularly in people with weakened immune systems. The common fungi that can cause infections include:
Dermatophytes
These fungi feed on keratin, affecting the scalp, nails, and skin, and do not infect living tissues.
Candida
Candida fungi naturally live in the body and usually do not cause any issues. However, under certain conditions, their population can increase significantly, leading to infections. These infections rarely cause severe health problems.
Environmental Fungi
These fungi, including aspergillus, histoplasma, blastomyces, and coccidioides, live in soil or water.
How Do Fungal Infections Spread?
Fungal infections typically spread through the following ways:
- Damp public areas like showers and locker rooms
- Contact with infected humans or animals in some dermatophyte infections
- Breaks or injuries in the skin
- Use of antibiotics that can lead to an overgrowth of naturally occurring fungi
- Inhalation of fungal spores
Symptoms of Fungal Infections
The symptoms of fungal infections vary depending on the type of fungus causing the infection and the area affected. Symptoms are often seen on the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. In some cases, symptoms can affect the eyes, brain, lungs, sinuses, and intestines.
Superficial or Subcutaneous Infections
Symptoms of these types of fungal infections can include:
- Painless lumps under the skin
- Itching, pain, redness, and rash in the affected area
- Pain and loss of taste while eating
- White patches in the mouth and throat
- Discolored, thick, or cracked nails
Fungal Lung Infections
Symptoms of lung fungal infections can include:
- Cough
- Coughing up blood in some cases
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Night sweats
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Joint pain
Other Symptoms of Fungal Infections
Other symptoms of fungal infections can include:
- Infections in or around the brain causing headaches, confusion, neck pain, fever, light sensitivity, nausea, and vomiting
- Eye fungal infections causing pain, blurred vision, redness, light sensitivity, discharge, and tearing
- Intestinal fungal infections causing abdominal pain, vomiting, and nausea
- Fungal infections of the sinuses causing headaches, fever, facial pain, nasal congestion, and unilateral facial swelling
Diagnosis Criteria for Fungal Infections
The diagnosis of fungal infections varies depending on the tissue affected. Therefore, culture tests can be performed on a wide range of samples. These samples include:
- Skin or other affected tissues
- Secretions
- Nails
- Urine
- Blood
- Sputum
- Fluid around the brain and spinal cord
- Vaginal discharge
If fungal infections are present in the internal organs or brain, MRI, X-ray, and CT scans can be performed to investigate the infection symptoms.
Treatment Methods for Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are usually treatable with antifungal medications. The prescribed medication varies depending on the tissue where the infection occurs. Antifungal medications can be administered in various forms, including:
- Shampoo
- Oral tablets
- Eye drops
- IV medications
- Mouthwash and lozenges
- Lotions or creams
Types of Fungi
Fungi can affect many different tissues of the body. Fungal infections are primarily divided into three subgroups based on the area they affect.
Superficial Fungal Infections
Superficial fungal infections affect the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. The types of superficial fungi include:
Ringworm Infection
Also known as tinea, this group of fungal infections affects the hair and nail cells. The areas affected by this infection include:
- Feet
- Groin
- Inner thighs
- Scalp
- Hands
- Facial hair
Onychomycosis
Various types of fungi can cause nail infections on both the hands and feet, leading to discoloration and brittle nails.
Candidiasis
Candida fungi cause an infection known as candidiasis, affecting the skin and mucous tissues. These types of fungi include:
- Oral thrush
- Diaper rash
- Vaginal yeast infections
- Esophageal candidiasis
- Candidal intertrigo
Tinea Versicolor
Also known as pityriasis versicolor, this fungal infection causes changes in skin color.
Subcutaneous Fungal Infections
Subcutaneous fungal infections occur when fungi enter the body through cuts in the skin. These infections, which cause skin rashes and ulcers, are more common in tropical and subtropical regions. Types of subcutaneous fungal infections include:
Sporotrichosis
Also known as rose gardener's disease, sporotrichosis is caused by the Sporothrix fungus and can affect the lungs and other parts of the body.
Chromoblastomycosis
Various fungi can cause chromoblastomycosis, a type of infection that leads to long-term skin infections and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
Eumycetoma
This type of infection, often affecting the feet, is caused by various fungi.
Deep Fungal Infections
Deep fungal infections affect tissues beyond the skin, such as the lungs, blood, urinary tract, and brain. Some of these infections are opportunistic, occurring in individuals with weakened immune systems. Types of deep fungal infections include:
Histoplasmosis
This type of fungal infection, caused by histoplasma, affects the lungs, brain, and other parts of the body. It is commonly found in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys.
Coccidioidomycosis
Also known as valley fever, this infection is caused by the Coccidioides fungus and typically affects the lungs, although it can also affect other tissues in rare cases.
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis, caused by the Blastomyces fungus, affects the lungs, bones, and skin, and can rarely affect the spinal cord and brain.
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis, caused by the mold Aspergillus, leads to various lung infections, including chronic pulmonary aspergillosis and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, and can also cause a fungal ball.
Candida Urinary Tract Infection
While urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria, Candida fungi can be the cause in some cases.
Invasive Candidiasis
Certain types of Candida can cause invasive candidiasis, infecting the brain, blood, heart, eyes, bones, and other tissues.
Pneumocystis Pneumonia
This type of pneumonia, caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii, affects the lungs.
Mucormycosis
Caused by a group of molds called mucormycetes, mucormycosis affects the sinuses and brain and can infect the lungs, intestines, skin, and other tissues simultaneously.
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii fungi, primarily infecting the lungs and sometimes spreading to the brain and spinal cord.