What are infectious diseases?
Infection is a health problem caused by pathogens such as parasites, bacteria, fungi and viruses. They can develop acutely or spread over time. The field of medicine that deals with life-threatening infections is called infectious diseases.
The infectious diseases unit does not deal with a specific organ. Instead, it deals with infections that occur throughout the body. It can therefore deal with a disease of the lungs, such as pneumonia, as well as infections of the urinary tract or the brain, such as encephalitis.
What are the conditions associated with infectious diseases?
Infectious diseases unit is the unit authorized in the diagnosis and treatment of infections that occur in all tissues of the body and are caused by various pathogens. Conditions related to infectious diseases include various infectious diseases such as sexually transmitted diseases, types of jaundice, influenza and other respiratory infections, diabetic foot infections, soft tissue infections and gastrointestinal infections.
What are the diseases that infectious diseases doctors deal with?
The diseases that infectious diseases specialists are interested in are generally grouped under the following headings.
Pathogen-borne infections
Pathogens are divided into four categories: bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. These pathogens can be transmitted from humans to humans, from animals to humans or from soil to humans. There are various routes of transmission of pathogens such as blood, respiration and body fluids. Although medication is used in the treatment of the majority of pathogen-induced infections, surgical methods are used in some infections. Characteristic symptoms of pathogen-borne diseases include diarrhea, fever, coughing, muscle aches and fatigue.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Another group of diseases that infectious disease specialists are interested in are sexually transmitted diseases. The most common of these diseases are gonorrhea, hepatitis B, AIDS and HIV. Although there are many other sexually transmitted diseases, the most risky groups are the patient groups with these diseases.
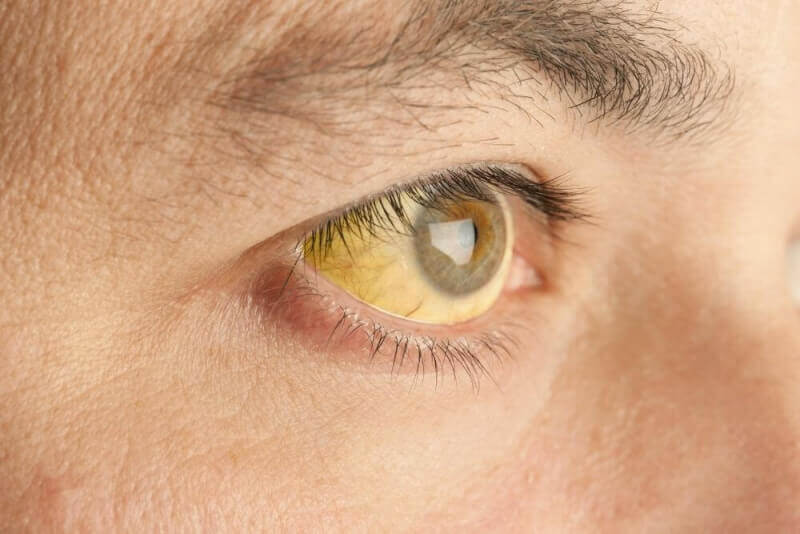
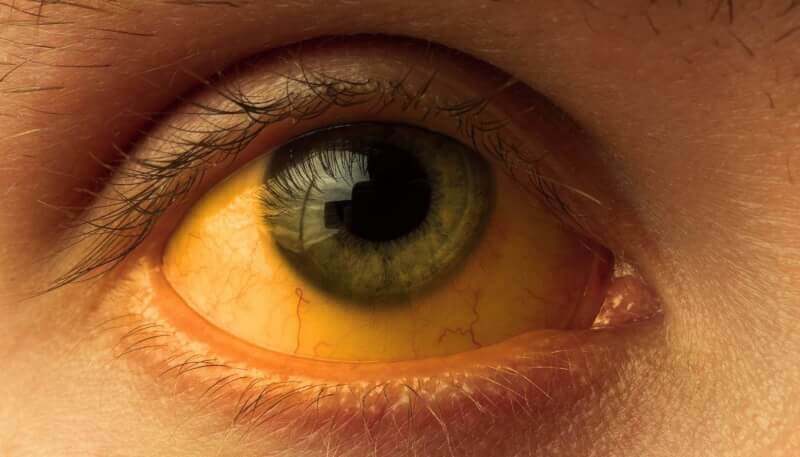
Types of hepatitis
The types of hepatitis characterized by yellow skin and eye discoloration are also within the areas of responsibility of infectious disease specialists. Jaundice occurs as a complication of many different diseases. Measurement of bilirubin levels is usually sufficient to diagnose the disease. In the treatment, methods aimed at lowering the bilirubin rate are applied.
Typhoid, tuberculosis, brucellosis and similar diseases
In this group of diseases, pathogens are transmitted from animals to humans. This disease group, which can be transmitted by consuming infected animal products, can also be transmitted by contact with sick animals. Characteristic symptoms include loss of appetite, body aches, fever and prolonged weight loss. Antibiotics are usually used for treatment.
Urinary tract infections
Normally there are no bacteria in the urinary tract, so if bacteria are found in the urine or urinary tract, a urinary tract infection occurs. The main cause of urinary tract infections is bacteria from outside the body reaching the urinary tract and causing infection. Urinary tract infections can occur in the urinary tract as well as in the kidneys, urethra and bladder. Characteristic symptoms of urinary tract infections include burning during emptying, frequent urination, fever and fatigue. Antibiotics are used to treat early urinary tract infections.
Diarrhea
In order to talk about diarrhea, people must have more than 3 liquid stools during the day. In breastfed babies, although there is no specific number, diarrhea can be mentioned if they defecate more than normal. The transmission routes of diarrhea include contact with feces by hand or mouth. For this reason, pathogens, especially in drinking water, often cause diarrhea. In addition to diarrhea, patients may also experience symptoms such as dizziness, vomiting or headache. It is important to consume plenty of fluids in the treatment.
Influenza and other respiratory infections
The characteristic symptoms of influenza and other respiratory infections during seasonal transitions include headache, fever and difficulty breathing. Respiratory tract infections include diseases such as sinusitis, colds, tonsillitis and upper respiratory tract infections.
Brain and spinal cord infections
Cerebrospinal infections are caused by inflammation of the meninges, the brain or both at the same time. The most common causes of brain and spinal cord infections include parasites, viruses, fungi and bacteria. Antibiotics are usually used in the treatment of brain and spinal cord infections, but surgical methods are used in some cases.
Soft tissue infections
Soft tissue infections, one of the most common types of infection, are infections characterized by fever and pain. Although it is sufficient to apply blood tests in the diagnosis of soft tissue infections, antibiotics are usually used in the treatment.
Diabetic foot infections
Diabetic foot infections, which are frequently seen in diabetic patients whose blood sugar is not controlled for a long time, are one of the infectious diseases that should be treated in the hospital. While antibiotic treatment is sufficient in the early period, limb loss may occur if the clinical condition worsens. Diabetic foot infections are a health problem that often occurs in men, people who are overweight and people with long-standing diabetes.
Other infections
Other infectious diseases that infectious disease specialists are interested in include the following.
- Tick-borne infections
- Prevention and treatment of travel-associated infections
- Blood and catheter-borne infections
- Bone and joint infections
- Investigation of fever of unknown cause
- Viral diseases
- Pneumonia
- Food poisoning
- Chickenpox and shingles
In which cases should the infectious diseases department be consulted?
Characteristic symptoms caused by infectious diseases include the following.
- Fatigue
- Fire
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Tremor
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Muscle aches
If one or more of these symptoms are observed, an infectious disease specialist should be consulted.