What is Jaundice?
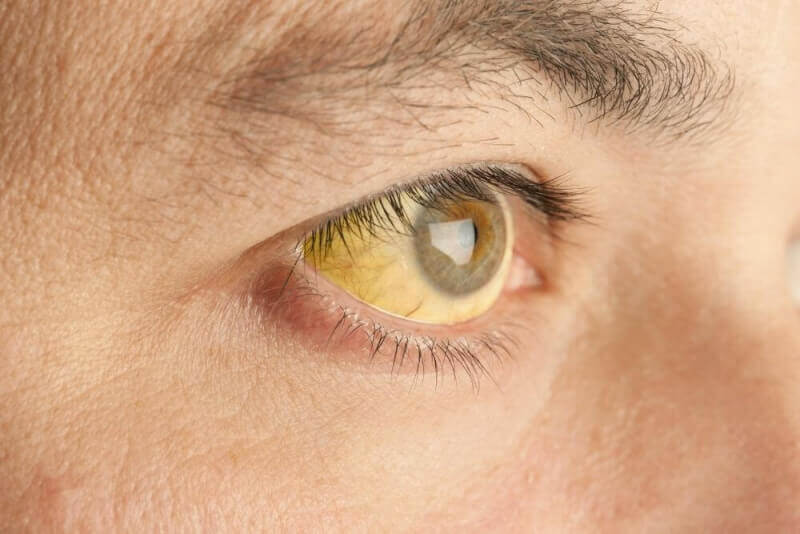
When red blood cells die, bilirubin, a yellow-orange pigment, remains in the blood. This waste is filtered from the bloodstream by the liver to be excreted in the stool. If there is too much bilirubin in the system or if the liver is overloaded, it leads to an accumulation known as hyperbilirubinemia. This condition causes the skin and the whites of the eyes to appear yellow.
Stages of Jaundice Development
Under normal conditions, the body regularly breaks down old red blood cells and produces new ones. The natural waste product of this breakdown process is bilirubin.
Bilirubin is processed in the liver and becomes part of bile, which helps digest food. The liver then releases bile into the digestive system.
Jaundice occurs if the liver does not filter bilirubin from the body or has trouble releasing it. Excess bilirubin in the blood seeps into the surrounding tissues, causing the skin and eyes to turn yellow, which is the most common symptom of jaundice.
Jaundice in Babies
Approximately 60% of newborns develop jaundice within the first few days after birth. Neonatal jaundice is the yellowing of a newborn baby's skin and eyes caused by high levels of bilirubin in the blood.
It is particularly common in babies born before 38 weeks of gestation and those breastfed, often due to the immaturity of the baby's liver. However, underlying health issues can also cause neonatal jaundice in some babies.
Babies born between 35 and 40 weeks of gestation usually do not require treatment for jaundice. Rarely, an unusually high bilirubin level in the blood, especially in the presence of certain risk factors for severe jaundice, can pose a risk of brain damage in a newborn.
Diagnostic Methods for Jaundice
To diagnose jaundice, it is necessary to measure the bilirubin level in the blood. It is also important to investigate whether the elevated bilirubin level is related to the breakdown of red blood cells or liver damage. Checking for signs of other liver diseases, including the following, is crucial for diagnosis:
- Bruising
- Abnormal accumulation of blood vessels close to the skin surface
- Redness of the palms and fingertips
Doctors also perform a physical examination to understand the size and sensitivity of the liver. An MRI scan or liver biopsy may be conducted to determine the cause of liver damage.
In newborns and infants with jaundice, the baby's appearance is first assessed. Blood tests may be done to measure bilirubin levels. The bilirubin level is crucial for determining the treatment for the baby. If jaundice is suspected to be caused by an underlying disorder, blood and urine tests may be requested.
Causes of Jaundice
There are three phases of bilirubin processing. Jaundice occurs when there is an issue in any of these phases. These issues include:
- Excessive breakdown of red blood cells before the liver processes bilirubin, overwhelming the liver's filtering capacity
- The liver's inability to adequately remove bilirubin from the blood
- A blockage in the bile duct preventing bile from being excreted into the digestive system, known as obstructive jaundice
Causes of Jaundice in Babies
The primary cause of jaundice is the presence of high levels of bilirubin in the blood. Newborns produce and break down red blood cells more rapidly in the first few days of life. This results in higher bilirubin levels in the blood compared to adults.
Additionally, the immature liver of a newborn is often not capable of filtering out high bilirubin levels in the blood effectively. This type of jaundice in babies is known as physiological jaundice and typically occurs in the first week of life.
Other Causes
Jaundice in babies can also be caused by underlying physiological problems. In such cases, jaundice may occur before or after the typical period for physiological jaundice. Conditions that may cause jaundice in babies include:
- Internal bleeding
- Abnormalities causing rapid breakdown of red blood cells
- Blood infections
- Enzyme deficiencies
- Incompatibility between the mother's and baby's blood types
- Blocked or damaged bile ducts
- Liver problems
Factors that increase the risk of jaundice and complications in babies include:
- Babies born before 38 weeks of gestation cannot process bilirubin as quickly as full-term babies. Premature babies also feed less and have fewer bowel movements, leading to less bilirubin excretion through stool.
- Some babies may bruise during birth, leading to an increase in bilirubin levels due to the breakdown of additional red blood cells.
- Incompatibility between the mother's and baby's blood types can lead to the rapid breakdown of red blood cells due to the development of antibodies.
- Breastfeeding, especially if the baby is not getting enough nutrition, can increase the risk of jaundice. Dehydration or low calorie intake can contribute to the onset of jaundice.
- Studies show that babies of East Asian descent are at higher risk of developing jaundice.
Symptoms of Jaundice
The skin color changes caused by jaundice may not always be noticeable. In some cases, doctors may discover jaundice incidentally while looking for something else. The severity of symptoms depends on the cause of jaundice and how quickly the condition develops. Symptoms associated with jaundice include:
- Yellowish skin and eyes
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Itching
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Chills
- Confusion
- Flu-like symptoms
- Pale stools
- Dark urine
Symptoms of Jaundice in Babies
In cases of physiological jaundice in babies, the following symptoms are observed:
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin
- Symptoms appearing between the 2nd and 4th days
- Yellow skin when pressing the nose or forehead
If the following symptoms are observed, it is crucial to contact a doctor as soon as possible:
- Increased yellowing of the skin
- High-pitched crying
- Jaundice appearing on the arms, legs, or abdomen
- Failure to gain weight
- Poor feeding
- Lethargy
- Difficulty waking up
Jaundice in the Eyes
The most common cause of yellowing of the sclera (the white part of the eye) is jaundice. However, yellowing of the eyes can also occur for other reasons, including:
Hepatitis
Hepatitis, which causes inflammation of the liver, is usually caused by a virus that infects liver cells, such as hepatitis A, B, or C. The infection can be short-term or long-term. Hepatitis infections can damage the liver and prevent it from filtering bilirubin from the blood, leading to jaundice. In some cases, medications or autoimmune diseases can also cause hepatitis.
Gallstones
These small, hard stones develop in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. Gallstones are the most common cause of bile duct blockage. The bile ducts carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and then to the small intestine. When the bile ducts are blocked by stones, bilirubin accumulates in the blood.
Alcohol Consumption
Consuming excessive alcohol for at least 8 to 10 years can cause serious liver damage. In some people, it can lead to inflammation that destroys liver cells. Over time, scar tissue can replace healthy liver tissue, making it difficult for the liver to function. Alcoholism can lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
Certain Medications
Medications associated with yellowing of the eyes include:
- Acetaminophen when used excessively
- Penicillin
- Birth control pills
- Chlorpromazine, used to treat certain mental and mood disorders
- Steroids
Liver Infection
Liver infections can occur from sources other than hepatitis viruses. The most common cause of liver infection is parasites, often acquired from raw or undercooked fish or infected plants. These parasites can enter the bile ducts and cause blockages.
Reaction to Blood Transfusion
If a blood transfusion is done with the wrong blood type, the body quickly breaks down the transfused blood, leading to an excess of bilirubin in the blood. Although rare, this situation requires immediate medical attention.
Types of Jaundice
There are four main types of jaundice, categorized based on where bilirubin accumulates in the body. A blood test can determine the type of jaundice.
Hemolytic Jaundice
Hemolytic jaundice occurs when red blood cells in the bloodstream break down more quickly than usual. The rapid increase in bilirubin levels in the blood overwhelms the liver's filtering capacity. This condition, also known as hemolysis, can be fatal. It is commonly seen in patients with malaria because the parasite that causes malaria attacks red blood cells, causing them to break down rapidly.
Hemolytic jaundice is also referred to as prehepatic jaundice because the jaundice begins before the blood reaches the liver. There are two main causes of this condition. The first is the breakdown of a large hematoma in the body, with the pieces being absorbed by the bloodstream. The second cause is hemolytic anemia, which occurs when blood cells are destroyed and removed from the bloodstream before their normal lifespan ends.
Hepatic Jaundice
Hepatic jaundice refers to jaundice occurring in the liver. Also known as hepatocellular jaundice, it is usually caused by liver damage. Damage to healthy liver cells significantly reduces liver function, preventing the removal of bilirubin from the body. Factors that can cause hepatic jaundice include:
- Infections from hepatitis viruses
- Hepatitis caused by alcohol
- Autoimmune disorders
- Genetic metabolic disorders
- Use of certain medications
Posthepatic Jaundice
When bilirubin levels rise after the blood has been filtered by the liver, it is known as posthepatic jaundice. In this case, the body cannot clear bilirubin quickly enough. Causes of posthepatic jaundice include:
- Gallstones
- Pancreatic tumors
- Gallbladder inflammation
- Gallbladder cancer
Obstructive Jaundice
This type of jaundice, also known as obstructive jaundice, occurs when bile or pancreatic ducts are blocked or narrowed, preventing bile from flowing into the intestines. Many different diseases that cause blockage or narrowing of the ducts can cause obstructive jaundice. The presence of stones in the bile duct or swollen lymph nodes can often lead to obstructions or narrowing. Due to the high mortality rate of this type of jaundice, it is crucial to diagnose and treat it early.
Complications of Jaundice in Babies
If untreated, high levels of bilirubin causing severe jaundice can lead to serious complications in babies. These complications include:
Acute Bilirubin Encephalopathy
Bilirubin is toxic to brain cells. Severe jaundice in a baby can lead to a condition called acute bilirubin encephalopathy, where there is a risk of bilirubin passing into the brain. Rapid treatment can prevent permanent damage. Symptoms of acute bilirubin encephalopathy in jaundiced babies include:
- Lethargy
- Fever
- Difficulty waking up
- Arching of the neck and body backward
- High-pitched crying
Kernicterus
Kernicterus is a syndrome resulting from permanent damage to the brain caused by acute bilirubin encephalopathy. This condition can result in:
- Improper development of tooth enamel
- Involuntary and uncontrolled movements
- Hearing loss
- Persistent upward gaze
How to Prevent Jaundice?
Preventing jaundice is challenging due to its many causes. However, some general tips include:
- Getting vaccinated
- Practicing safe sex
- Maintaining personal hygiene
- Consuming alcohol within recommended limits
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding natural and herbal supplements
- Managing cholesterol levels
What Should Jaundice Levels Be?
The normal bilirubin level in a healthy person's blood ranges from 0 to 0.3 mg/dL. To diagnose jaundice, the level should be between 0.3 and 1.2 mg/dL.
| Condition | Bilirubin Level (mg/dL) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Individual | 0 - 0.3 | Normal range of bilirubin levels. |
| Jaundice | 0.3 - 1.2 | Range of bilirubin levels for diagnosing jaundice. |