30 Second Summary
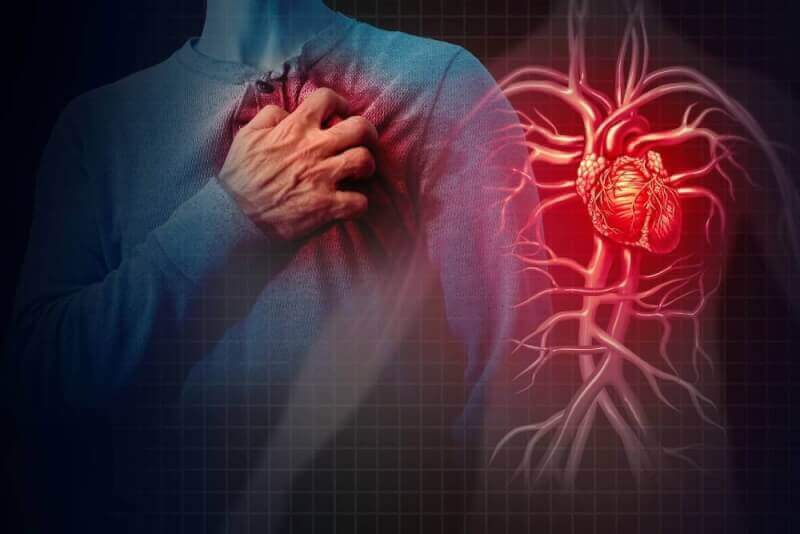
- A heart attack is a blockage of the blood vessels supplying the heart, which deprives the heart of oxygen.
- The most common symptom is chest pain.
- Symptoms include shortness of breath, nausea, palpitations and fainting.
- A heart attack is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated early.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack, also called myocardial infarction, is defined as a blockage in the arteries supplying the heart, resulting in a lack of oxygenation and nutrition to the heart. Because of this blockage in the coronary arteries, the vessel is deprived of blood supply and every second the heart is deprived of blood, the heart tissues die.
The accumulation of fatty structures called cholesterol in the vessels that provide blood flow to the heart is called plaque. Over time, these plaques become thicker and thicker and cracks appear on them. Sometimes clots form in these cracks and sometimes some of the plaque breaks off, causing blockage of already narrowed blood vessels and suddenly blocking blood flow to the heart.
If a heart attack is not treated early and correctly, it can cause permanent damage to heart tissue. In addition, these untreated blockages prevent the heart from pumping enough blood, leading to heart failure.
Heart attack symptoms
The most characteristic symptom of a heart attack is pain in the heart, also known as chest pain. Along with this pain, patients also feel pressure and heaviness. Chest pain, which is a dull ache, can also radiate to the left arm, neck, jaw and back. These pains usually last between 5 and 15 minutes and are relieved by rest or the use of coronary artery dilating drugs. Other common symptoms of a heart attack include nausea, dizziness, fatigue and heart rhythm disturbances.
The symptoms of a heart attack vary depending on the location of the blocked vessel. This condition is more common in women. Other symptoms of a heart attack include the following.
Sweating that does not occur during exercise or activity and is more common than normal is also one of the symptoms of a heart attack. Some patients experience cold sweating in particular.
The intense stress experienced by patients during a heart attack can make them weak. Fatigue and shortness of breath are the most common symptoms of heart attack in women. Another heart attack symptom that occurs in female patients is dizziness. Patients should seek medical attention as soon as possible, especially if the dizziness is accompanied by lightheadedness.
Another symptom of a heart attack is palpitations. Patients may feel palpitations not only in the chest but also in the neck. The palpitations experienced by patients can also be felt as intense anxiety.
Symptoms of a silent (hidden) heart attack
Digestive problems, also called hidden heart attack symptoms, are also among the symptoms of a heart attack. Digestive problems such as burning in the chest and indigestion are also among the symptoms of a heart attack.
Men are generally more prone to heart disease. On the other hand, men have heart attacks at an earlier age than women. Symptoms of a heart attack vary from patient to patient, but the symptoms seen in men consist of more classic symptoms. Symptoms of heart attack in women differ. Heart attacks in women are characterized by symptoms such as prolonged fatigue, sleep problems and upper back pain.
Causes of Heart Attack
One of the most common causes of heart attacks is the formation of fatty plaques on the walls of the vessels that feed the heart. Clots or ruptures in blood vessels can also result in a heart attack. However, there are factors that cause these problems in the blood vessels. These are also factors that increase the risk of heart attack.
- The most important factor that increases the risk of heart attack is smoking. The likelihood of a heart attack increases 3-fold in smokers.
- Another factor that increases the risk of heart attack is the high LDL ratio in the blood, which is defined as bad cholesterol. In order to reduce this value, foods with high cholesterol content such as delicatessen products, red meat, shellfish, full-fat dairy products and butter should be avoided.
- Another important factor that increases the risk of heart disease is diabetes. A significant proportion of diabetics die from heart attacks. The reason for this is that the blood clotting level of diabetics increases as a result of the loss of elasticity of the vessel walls.
- One of the most important factors that increase the risk of heart attack is increased pressure in the blood vessels.
- With age, the risk of heart attack increases as vascular structures deteriorate and vessels become more damaged.
- Menopause is one of the most important causes of heart attacks in women. The rate of heart attacks seen in the postmenopausal period is higher.
- Obesity increases the risk of heart attack as it causes many comorbidities.
- A family history of heart attack is also one of the reasons that increase the risk of heart attack.
How is a heart attack treated?
A heart attack is a medical emergency. The vast majority of deaths from heart attacks occur within a few hours of the heart attack. For this reason, it is very important for patients to consult a full-fledged health institution at the first sign of symptoms and receive a diagnosis immediately.
Patients admitted to hospital with a heart attack are first administered blood thinners and necessary emergency treatments. Patients are then referred to a cardiologist. If the cardiologist deems it appropriate, angiography can be performed to check the patient's blood vessels. Depending on the results of the angiography, patients may undergo surgery or medication.
The main treatment options for heart attacks include stents, angioplasty and bypass surgery. In bypass surgery, blood vessels taken from another part of the patient's body are replaced with damaged blood vessels in the heart.
Pre-heart attack symptoms
There are some symptoms even before a heart attack occurs. Being careful about these symptoms, which differ from patient to patient, and consulting a specialist helps to prevent a heart attack before it occurs. Symptoms before a heart attack are as follows.
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
- Heart rhythm disorders.
- Powerlessness
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Bloating
- Sudden weight gain,
- Loss of appetite
- Restlessness,
- Fear of death
- Fatigue
- Cold sweating
- Nausea
- Palpitations