30-Second Summary
- Hip avascular necrosis occurs when any condition prevents blood flow to the bone tissue.
- It may take weeks or even months to diagnose hip avascular necrosis.
- During the physical examination for hip avascular necrosis, the specialist applies pressure around the hip joint to check for tenderness and moves the joint into different positions to assess range of motion.
- The goal of treatment for hip avascular necrosis is to prevent further loss of bone tissue and relieve the symptoms caused by the condition.
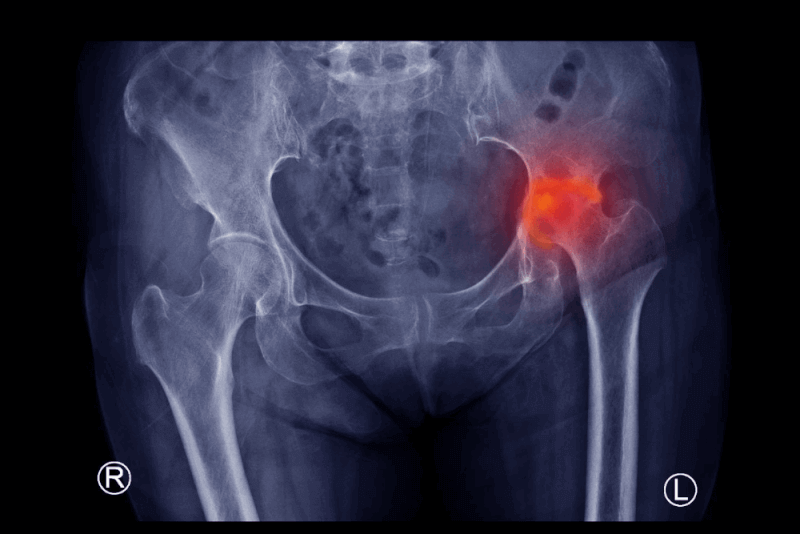
What is Hip Avascular Necrosis?
Hip avascular necrosis occurs when blood flow to the bone tissue is disrupted by any condition. The skeletal system constantly regenerates as old and damaged bone tissue is broken down and replaced with new bone tissue.
This cycle keeps the bones strong and healthy. Blood supplies the necessary nutrients and oxygen to maintain healthy bones. Without adequate blood flow, new bone tissue cannot be produced fast enough. As a result, the dead bone begins to break down and eventually collapses.
Causes of Hip Avascular Necrosis
Hip avascular necrosis develops when the blood supply to the hip bones is blocked for any reason. Causes that prevent blood from reaching the hip bone include the following:
Joint and Bone Trauma
Injuries such as joint dislocation can damage nearby blood vessels, disrupting proper blood flow. Radiation treatments can also weaken the bone and damage blood vessels. The likelihood of avascular necrosis increases in cases of hip fractures or dislocations.
Fat Deposits in Blood Vessels
Fat deposits in the blood vessels, known as lipids, can particularly block small blood vessels. This contributes to reduced blood flow to the bones.
Certain Diseases
Diseases such as sickle cell anemia and Gaucher’s disease can disrupt the blood supply to the bones. Other diseases that may cause avascular necrosis include:
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes
- HIV
- Lupus and organ transplants
In addition, the causes of non-traumatic hip avascular necrosis are not fully understood. Genetics, alcohol use, certain medications, and other diseases are thought to play a role.
Symptoms of Hip Avascular Necrosis
It may take weeks or even months to detect hip avascular necrosis. The symptoms that gradually appear over time include:
- Pain that appears and eases when pressure is applied and lifted from the bone
- Increasing pain and joint stiffness
- Limited range of motion
- Limping
- Difficulty climbing stairs, standing, or walking
- Groin pain
- Thigh pain
Diagnosis Criteria for Hip Avascular Necrosis
During the physical examination for suspected hip avascular necrosis, the specialist presses around the hip joint to check for tenderness. They also move the joint into various positions to assess any reduction in range of motion. Diagnostic tests may also include the following:
X-ray
X-rays help identify bone changes that occur in the advanced stages of avascular necrosis. In the early stages, X-rays may not reveal any abnormalities.
MRI and CT Scans
These tests help visualize early changes in the bone that may indicate avascular necrosis.
Bone Scan
In a bone scan, a small amount of radioactive material is injected into the patient. This tracer travels to injured or healing parts of the bone, which appear as bright spots on the imaging plate.
Treatment Methods for Hip Avascular Necrosis
The aim of treating hip avascular necrosis is to prevent further loss of bone tissue. Additionally, the treatment helps to relieve symptoms caused by avascular necrosis.
Medication
In the early stages of hip avascular necrosis, certain medications can help relieve symptoms. Commonly prescribed medications include:
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium can relieve pain caused by the condition. Stronger alternatives may require a prescription.
Osteoporosis Medications
Medications used in osteoporosis treatment may help slow the bone loss associated with avascular necrosis.
Cholesterol-lowering Drugs
Reducing the amount of cholesterol and fat in the blood may help prevent vessel blockages that could lead to avascular necrosis.
Vasodilators
These drugs aim to increase blood flow to the affected bone, though further research is needed.
Blood Thinners
Used for clotting disorders, these medications may prevent clots from forming in vessels that supply the bones.
Therapy
Doctors may also recommend the following therapy options:
Rest
Limiting physical activity or using crutches for a few months to avoid putting weight on the joint can help slow down bone damage.
Exercises
Physical therapists may suggest exercises to prevent or improve restricted joint movement.
Electrical Stimulation
Electrical currents may promote new bone growth to replace damaged bone. This can be done during surgery or non-invasively with electrodes placed on the skin.
Hip Avascular Necrosis Surgery
In most people, symptoms of hip avascular necrosis do not appear until the disease has progressed, making surgical treatment necessary to repair the damage.
Surgical Methods for Hip Avascular Necrosis
Hip avascular necrosis surgeries can be performed using various techniques, including:
Core Decompression
This procedure involves removing a portion of the inner layer of the bone. It helps relieve pain and stimulates the production of healthy bone tissue and new blood vessels by creating space inside the bone.
Bone Graft
This technique helps strengthen the bone area affected by avascular necrosis using healthy bone grafted from another part of the body.
Osteotomy (Bone Reshaping)
This procedure involves removing a wedge of bone above or below the weight-bearing joint to relieve pressure from the damaged area. Bone reshaping may help delay joint replacement.
Joint Replacement
If the affected bone collapses or other treatments are ineffective, the damaged part of the joint is removed and replaced with plastic or metal components.
Regenerative Medicine Therapy
Bone marrow aspiration and concentration is a newer procedure that may help with early-stage avascular necrosis of the hip. During surgery, a sample is taken from the dead bone, and stem cells from bone marrow are placed into the area to promote new bone growth. Further studies are needed on this technique.
Benefits of Hip Avascular Necrosis Surgery
Surgical procedures used in the treatment of hip avascular necrosis help relieve symptoms such as pain and also prevent further bone loss. Some procedures additionally promote the formation of new bone tissue in the affected area, allowing the bone to return to a healthier state.
Complications of Hip Avascular Necrosis Surgery
Potential complications that may occur after hip avascular necrosis surgery include the following:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Infection of implants
- Hardware malfunctions
Recovery Process of Hip Avascular Necrosis
The only method that ensures the healing of hip avascular necrosis is surgical intervention. Other treatment options aim to slow the progression of the disease and delay the need for surgery.
Risks of Hip Avascular Necrosis
If left untreated, hip avascular necrosis progressively worsens and eventually leads to the collapse of the bone. Additionally, the loss of the bone’s smooth shape creates a condition that paves the way for arthritis to develop.