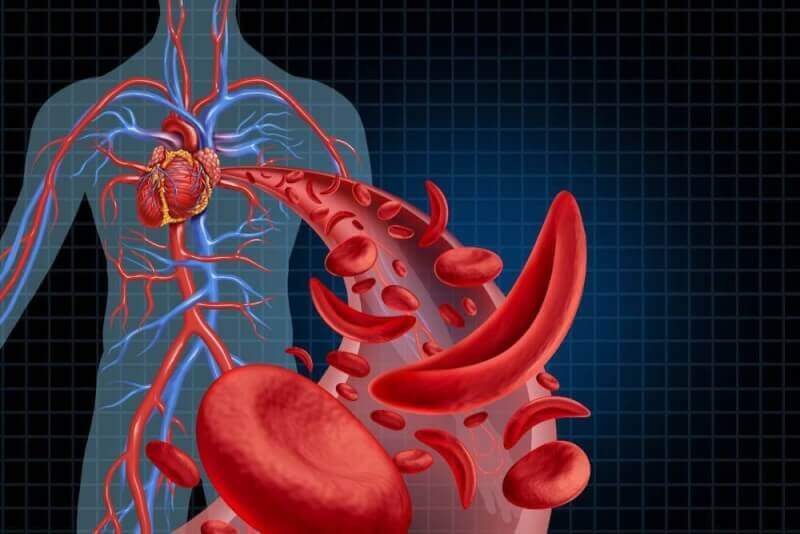
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
Sickle cell anemia, commonly seen in the Adana, Mersin, and Antakya regions of our country, is the inability of red blood cells in the blood to perform their function due to structural deterioration. The deformation of red blood cells, also known as hemoglobin, causes their numbers to decrease over time. Sickle cell anemia, a genetic disease, leads to insufficient oxygen delivery to tissues and makes the body more susceptible to infections. The change in shape from round to sickle of the red blood cells can also block small blood vessels.
Causes of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is a disease caused by genetic transmission. It arises due to a mutation at the 6th position of the beta chain of hemoglobin. This mutation causes the amino acid valine to replace glutamine, which is normally found in red blood cells. Although this change may seem simple, it causes red blood cells to take on an S shape.
How is Sickle Cell Anemia Diagnosed? (Tests)
To diagnose sickle cell anemia, first, the patient's medical history is taken and a detailed physical examination is performed. Subsequently, various tests are applied.
Complete Blood Count
A complete blood count measures the number of blood cells in the blood. It can detect not only anemia but also infections.
Peripheral Smear
In the peripheral smear test, blood cells are examined under a microscope. This allows the shapes of the cells to be determined.
Sickling Test
In this test, certain chemicals are applied to red blood cells. These chemicals are used to observe if the red blood cells sickle in reaction.
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
Due to the characteristics of red blood cells in sickle cell anemia patients, they differ from normal blood cells. The electrophoresis test can reveal these differences.
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia, a congenital disease, typically shows its first symptoms in infants around the 6th month. At this age, a type of hemoglobin called fetal hemoglobin rises in the blood and this usually causes hand-foot syndrome. A majority of patients visit the doctor with these complaints. The symptoms of sickle cell anemia can be divided into sudden onset and long-term side effects.
Sudden Onset Symptoms
The most important and characteristic symptom of sickle cell anemia is pain crises. These pains, which especially affect the bones, also impact internal organs in some patients. These severe pain crises can occur 1-2 times a year.
Another symptom of sickle cell anemia is hematological symptoms. Due to the nature of the disease, the destruction of blood cells occurs. However, in hematological crises, this destruction happens more rapidly. Factors such as dehydration, infection, cold, or heat significantly increase the destruction of red blood cells. Complaints in these crises include jaundice, severe anemia, and darkened urine.
In addition to hematological crises, patients can also experience aplastic crises. In aplastic crises, the bone marrow stops or significantly reduces blood cell production. Not only the production of red blood cells but also white blood cells slows down in aplastic crises. Platelets may also not be produced. Aplastic crises are generally thought to be caused by viral infections.
Another symptom in sickle cell anemia patients is megaloblastic crises. In megaloblastic crises, due to the deficiency of B12 and folic acid, an additional anemia is observed along with sickle cell anemia.
Acute chest syndrome is also one of the symptoms of sickle cell anemia. Symptoms of acute chest syndrome include severe lung infection, phlegm, fever, infiltration in the lungs, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can lead to a severe medical condition and can be fatal.
Priapism, an involuntary painful erection, is caused by sickle cell anemia. If not treated, it can lead to infertility.
One of the severe symptoms of sickle cell anemia in childhood is spleen sequestration. The continuous damage caused by the disease to the spleen leads to its shrinkage over time, making patients more susceptible to infections. In some patients, the opposite occurs, with the spleen becoming excessively large and prone to bleeding. This is a very serious clinical condition requiring close monitoring.
Chronic Stage Symptoms
Sickle cell anemia patients are born at normal weight and height. However, their growth is affected during the growth period, with weight gain being more affected than height. Therefore, in adulthood, patients' height is usually normal or near normal. Additionally, the onset of menstruation in patients is delayed by 2-3 years compared to the general population, and some patients may have hormonal deficiencies.
In sickle cell anemia, the overproduction of erythrocytes causes the inner part of the bone to expand and the outer part to thin. This is especially noticeable in the skull. Additionally, the lower and upper parts of the vertebral bodies collapse inward, known as fish-mouth vertebrae.
Small blockages in the bones of patients occur within the first 4 years. This condition, called hand-foot syndrome, causes swelling of the hands, feet, and face and pain in patients. It is believed that hand-foot syndrome is responsible for deformities observed in patients during adulthood.
One of the most severe symptoms of the disease is stroke. In children who experience strokes, there is a decrease in language learning, difficulty in problem-solving, and mental retardation. Additionally, silent vascular occlusions are observed in 17% of children aged 6 to 14 who experience strokes.
Among the chronic stage symptoms of sickle cell anemia are those affecting the cardiovascular system. These include excessive iron accumulation in the heart muscles and blockage of small pulmonary vessels. Additionally, the heart working harder and faster to pump insufficient blood leads to heart enlargement. Especially right ventricular enlargement can cause heart failure. The iron accumulated in the heart muscles due to frequent blood transfusions can lead to heart failure resistant to treatment and various arrhythmias.
The lungs are also affected by sickle cell anemia. Therefore, moderate lung failure can be seen in patients due to recurring blockages and infections.
Liver enlargement in patients appears after the age of 1. This moderate enlargement lasts throughout the patients' lives. Additionally, gallstones are frequently seen in sickle cell anemia patients, with an increase in the number of stones as age increases.
One of the most characteristic features of sickle cell anemia is the disruption of urine concentration. Therefore, approximately half of the patients have blood cells in their urine.
Another organ affected by the disease is the eyes. In addition to retinal vascular occlusions, new vessel formation affects the eyes, causing scarring, bleeding, blindness, and retinal detachment.
Treatment of Sickle Cell Anemia
Although there is no definitive treatment for sickle cell anemia, the disease can be controlled. Treatments aimed at controlling symptoms are divided into preventive and complication treatments.
Preventive Measures
The most important measure to be taken is to prevent crises that increase cell death. Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids, avoid dehydration, stay away from extreme cold, and take care of their health to avoid infections. Additionally, pain medications, water-soluble vitamins (B and C), and folic acid should be taken regularly to prevent crises.
Complication Treatment
The treatment method is determined by the patient's age and the severity of the disease. If the patient is severely affected by the disease and has frequent complications, blood transfusions, medications, and bone marrow transplants can be used as part of the treatment.