30-Second Summary
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a painless test that provides detailed images of the organs inside the body.
- Since MRI does not use radiation, it is frequently used for the diagnosis and treatment of brain diseases.
- Patients may find it uncomfortable to stay still for 30 minutes or more, and the narrow and enclosed MRI machine can cause anxiety.
- The duration of an MRI scan varies depending on the area being imaged. Generally, it lasts between 15 and 90 minutes.
What is MRI?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a painless test that provides detailed images of the organs inside the body. MRI uses a large magnet, radio waves, and a computer to create images. However, it does not use X-rays. Since MRI does not involve radiation, it is particularly useful for diagnosing and treating brain diseases.
Open MRI
The term "Open MRI" refers to the difference in the machine design. Open MRI machines have flat magnets that extend both above and below the patient, allowing for an open experience on both sides. This significantly reduces the claustrophobia that patients might feel.
However, Open MRI machines offer lower-quality imaging compared to closed MRI machines because the surrounding magnets in closed MRI machines help capture better images.
Contrast MRI
In some MRI exams, a contrast agent is injected. Gadolinium, a rare earth element, is used as the contrast agent. When this substance is in the body, it alters the magnetic properties of nearby water molecules, enhancing the quality of the images.
Difference Between MRI and CT Scan
MRI uses magnetic fields, while CT scans use radiation. For this reason, experts tend to use MRI to look at soft tissues or non-bony areas of the body. Additionally, MRI is generally considered a safer option than CT scans.
MRI provides better images of the spinal cord, brain, muscles, nerves, ligaments, and tendons compared to CT scans.
However, MRI is not suitable for everyone because the strong magnetic field can cause metal implants in the body to shift. Additionally, devices like pacemakers and insulin pumps may be affected by MRI.
Why is MRI Used?
MRI can be used to image various organs and tissues in the body, including the following:
- Brain
- Soft tissue around the brain
- Heart
- Liver
- Bile ducts
- Kidneys
- Spleen
- Intestines
- Pancreas
- Adrenal glands
- Breast tissue
- Spine
- Spinal cord
- Bladder
- Reproductive organs
- Blood vessels
- Lymph nodes
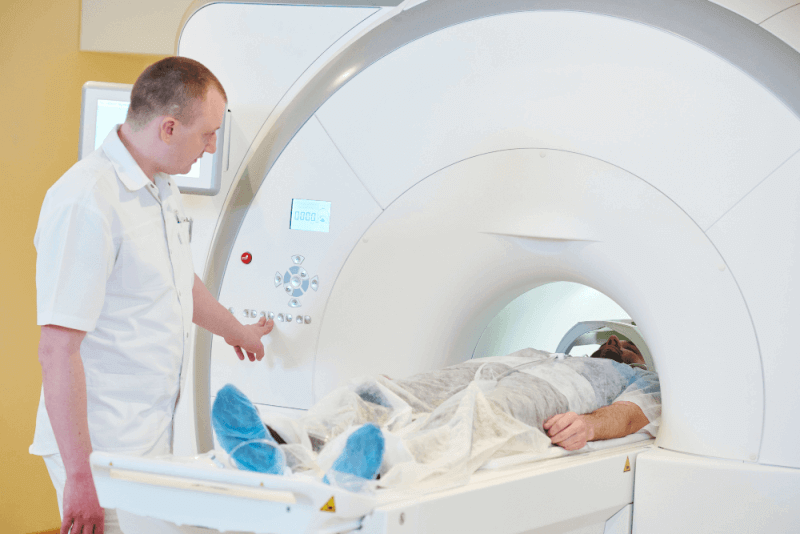
How is MRI Done?
MRI is a painless imaging technique. However, patients may find it uncomfortable to remain still for 30 minutes or more. Additionally, the narrow and enclosed MRI machine can cause anxiety. The steps of an MRI procedure are as follows:
- The patient needs to wear a hospital gown for the scan.
- During the scan, the patient typically lies on their back, and the bed slides into the machine.
- When the scan begins, rhythmic thumping and clicking sounds can be heard. Each sound sequence lasts a few minutes. Earplugs can be provided for those who find these sounds bothersome.
- The patient must remain still during the scan.
- It is normal to feel warmth in the area being imaged. If discomfort occurs, the technician should be notified.
- A system allows communication between the patient and the technician. There is also an emergency button that can be used to report any sudden changes in the patient's condition.
What Diseases Can MRI Diagnose?
MRI is used by experts for diagnosing and monitoring the treatment of many diseases. Different types of MRI are used depending on the area to be imaged.
Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nervous System Diseases
Brain and spinal cord MRIs are used for evaluating and diagnosing the following conditions:
- Brain aneurysms
- Brain and spinal cord tumors
- Trauma-related brain and spinal injuries
- Compression and inflammation of the spinal cord and nerves
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Spinal cord disorders
- Spinal anatomy and alignment
- Paralysis
Heart Diseases
MRI is also used for cardiac purposes, including evaluating the following conditions:
- Evaluating the anatomy and function of the heart chambers and valves, the size of large vessels, and blood flow
- Diagnosing cardiovascular conditions such as tumors, infections, and inflammation
- Evaluating the effects of a heart attack such as reduced blood flow to the heart muscle and scar tissue formation
- Evaluating the anatomy and function of the heart and blood vessels in individuals with congenital heart disease
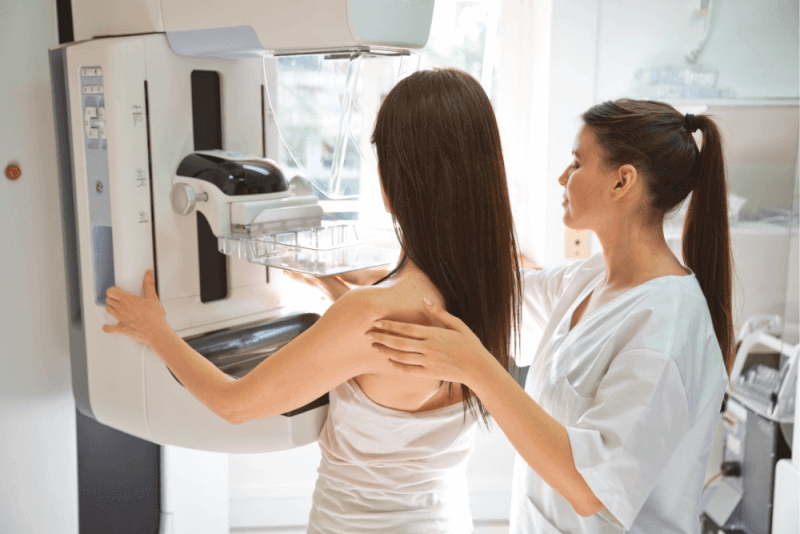
Breast Diseases
MRI is used for diagnosing breast cancer. It is often combined with mammography to increase diagnostic reliability. MRI is especially used in regular screenings for individuals at high risk of breast cancer due to dense breast tissue.
Musculoskeletal System Diseases
Bone and joint MRIs help assess the following conditions:
- Bone infections
- Bone tumors
- Spinal disc abnormalities
- Joint problems resulting from injuries
Liver and Other Internal Organ Diseases
MRI can evaluate various structures and diagnose conditions such as:
- Tumors in the chest, abdomen, and pelvis
- Liver diseases such as cirrhosis
- Problems with the bile ducts and pancreas
- Inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
- Vascular disorders and vascular inflammation
- Development of the fetus in the uterus
Types of MRI
Different types of MRI are used depending on the area of the body being imaged.
Standard MRI
Standard MRI machines are general imaging machines that provide high-quality images, although they may not meet the requirements for certain diseases.
Functional MRI
Functional MRI is used to measure small changes in blood flow associated with brain activity. It helps examine the critical functions of different brain regions, assess the effects of stroke or other diseases, or guide brain treatments.
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac MRI is used to examine the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the heart. It can be customized to different diagnostic protocols but is generally less effective than cardiac CT scans.
Breast MRI
Breast MRI is used to diagnose breast cancer. It is often used alongside mammography for higher diagnostic reliability, particularly for those at higher risk of breast cancer due to dense tissue.
Neurological MRI
Peripheral nerve MRI, also known as neurography, is used to diagnose abnormalities in the spinal canal and beyond. It is particularly used to examine plexus, lumbosacral plexus, thoracic outlet syndrome, and sciatic nerve abnormalities.
Musculoskeletal MRI
Musculoskeletal MRI is used for evaluating conditions in bones and joints, including injuries and diseases of ligaments, tendons, and joints.
Angiographic MRI
Angiographic MRI is used for evaluating blood vessels, and contrast agents are sometimes used in the procedure.
Diffusion MRI
Diffusion MRI measures the random Brownian motion of water molecules in tissues and is especially useful in characterizing cancer and evaluating cerebral ischemia.
Spectroscopic MRI
Spectroscopic MRI is used to measure metabolites in brain lesions and identify biochemical changes, helping in the diagnosis and differentiation of brain lesions.
Why is MRI Done at Night?
MRI scans are usually done at night to obtain better images due to reduced light and noise. The lack of external disturbances ensures that the images are more detailed.
How Long Does MRI Take?
The duration of an MRI scan varies depending on the area being imaged. Generally, it takes between 15 and 90 minutes. Here are examples of the duration for other types of MRI:
- Spectroscopy MRI takes 30 to 60 minutes
- Brain MRI takes 15 minutes to 1.5 hours
- Open MRI takes 5 to 45 minutes
How Long Does It Take to Get MRI Results?
The results of MRI scans usually take 1 to 3 days, depending on the area imaged. This duration can vary depending on the urgency of the case and the lab's workload.