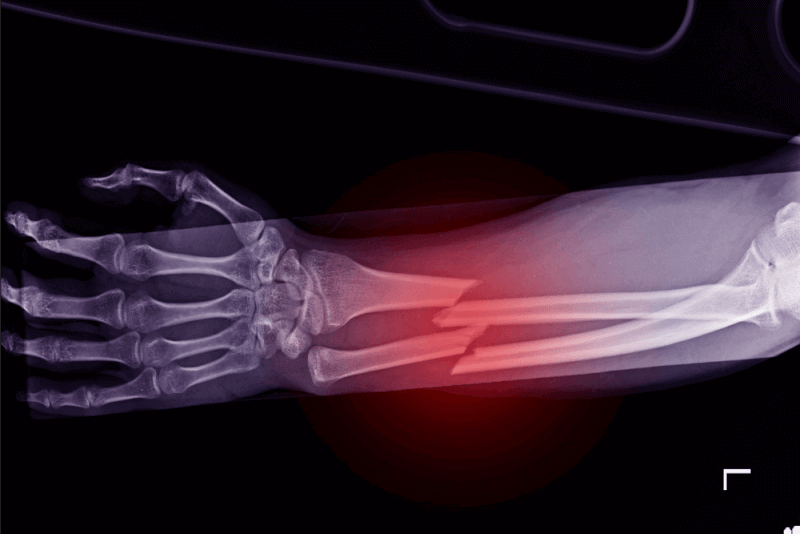
What is a Scaphoid Fracture?
A scaphoid fracture is a type of wrist fracture that occurs in a small bone near the base of the thumb. This bone is one of the carpal bones, which make up the wrist.
Scaphoid fractures almost always occur as a result of trying to slow a fall by extending the arms. They can also occur due to car accidents and other traumas. Surgery may be required to repair the bone. In most cases, it takes about 3 months for scaphoid fractures to heal.
The scaphoid bone is divided into three parts, which are:
- The distal pole, the end of the scaphoid closest to the hands and fingers
- The waist of the scaphoid, which is the middle part of the bone
- The proximal pole, the end of the scaphoid closest to the forearm
These terms describe the location of the fracture and provide specific details about it.
What Causes a Scaphoid Fracture?
Any impact to the wrist can cause a scaphoid fracture. The most common causes include:
- Falls
- Sports injuries
- Car accidents
Symptoms of a Scaphoid Fracture
The symptoms of a scaphoid fracture may include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Inability to move the wrist
- Bruising
- Discoloration
- Deformity or swelling in the wrist that was not present before
Diagnosis Criteria for a Scaphoid Fracture
Scaphoid fractures are diagnosed through physical examination and imaging tests. X-rays can confirm the presence of a scaphoid or other fractures and reveal the extent of the bone damage.
An MRI can provide a detailed understanding of the damage to the bones and surrounding area, including whether muscles or ligaments have been injured.
A CT scan is especially used for patients who require surgery, as it allows surgeons to see both the bones and surrounding tissues in detail.
Fractures that are not visible on an X-ray are called occult scaphoid fractures. In such cases, an MRI or CT scan may be required. If pain or tenderness is present over the scaphoid bone and does not subside after a few days, an occult fracture may be suspected.
Treatment Methods for a Scaphoid Fracture
The treatment methods for scaphoid fractures vary depending on the severity of the fracture. The primary goal is to bring the fractured bones together. The treatment options include:
Immobilization
If the fracture is mild or the scaphoid has not moved much out of place, a splint or cast may be sufficient for the bones to heal. Splints are typically used for 3 to 5 weeks, while casts are generally required for 6 to 8 weeks. Follow-up X-rays are necessary to determine if the bones have fused.
Closed Reduction
In more severe fractures, closed reduction may be required to realign the bones. In this non-surgical procedure, the doctor physically manipulates the fracture from outside the body to realign the bone. To prevent pain during the procedure, one of the following may be used:
- Local anesthesia to numb the area around the fracture
- Sedatives to relax the whole body
- General anesthesia to put the patient to sleep during the procedure
After a closed reduction, a cast or splint is applied.
Scaphoid Fracture Surgery
In cases where the scaphoid fracture is severe, surgery may be performed to bring the bones together and realign them.
Surgical Methods for a Scaphoid Fracture
There are two different techniques that can be used to treat scaphoid fractures, depending on the severity of the fracture:
Internal Fixation
This surgery is applied to the most severe fractures. In this method, the fractured bones are first realigned and then fixed in place to allow them to fuse. The following methods can be used for fixation:
- Plates and screws
- Pins and wires (these small parts help hold very small bone fragments together)
In some patients, these implants remain in place for the rest of their lives. In others, follow-up surgeries may be required to remove the pins or screws.
Bone Graft
Bone grafting is applied when the scaphoid fracture is severely displaced or does not heal properly. The bone graft is used to reposition the fractured bone, allowing it to fuse. Internal fixation is usually required to hold the pieces together as the bone grows.
Benefits of Scaphoid Fracture Surgery
Scaphoid fracture surgery brings together fractures that cannot align or fuse on their own, allowing for complete healing and eliminating the risk of complications associated with the fracture.
Complications of Scaphoid Fracture Surgery
The complication rate in surgeries for scaphoid fractures is very low but can still occur. Potential complications include:
- Infection
- Nerve injury
- Stiffness
- Hardware problems
- Non-union (failure of the bone to heal)
Precautions for a Scaphoid Fracture
Whether surgical methods are used or not, it can take up to 6 months for a scaphoid fracture to heal. Unlike other fractures, scaphoid fractures tend to heal slowly. During this time, it is essential to avoid the following activities unless the doctor permits:
- Lifting or pushing objects heavier than 2 kilograms
- Throwing
- Participating in contact sports
- Climbing stairs or trees
- Engaging in activities that carry a risk of falling on the hand
- Using heavy machinery or vibrating devices
- Smoking
Some patients may experience stiffness after a fracture, especially those who have been in a cast for a long time or undergone surgery. Therefore, it is essential to keep the fingers moving throughout the healing process.
Risks of a Scaphoid Fracture
If a scaphoid fracture is left untreated, potential complications may include:
Acute Compartment Syndrome (ACS)
Increased pressure in the muscles can block blood flow to the tissue, leading to permanent muscle and nerve damage.
Malunion
This occurs when fractured bones do not align properly during healing.
Non-union
The bones may not fully or correctly fuse.
Avascular Necrosis
A painful bone disease that worsens over time and affects mobility. It occurs when blood flow to the bone is blocked for any reason.
Arthritis
Non-union and avascular necrosis can lead to arthritis in the hand and wrist, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and deformity.
Scaphoid Fracture Recovery Process
During recovery, symptoms may persist for several weeks. Depending on the type of surgery performed, the wrist may begin to move again within a few weeks. If pain is severe or does not subside, a doctor should be consulted.