What is a Stye?
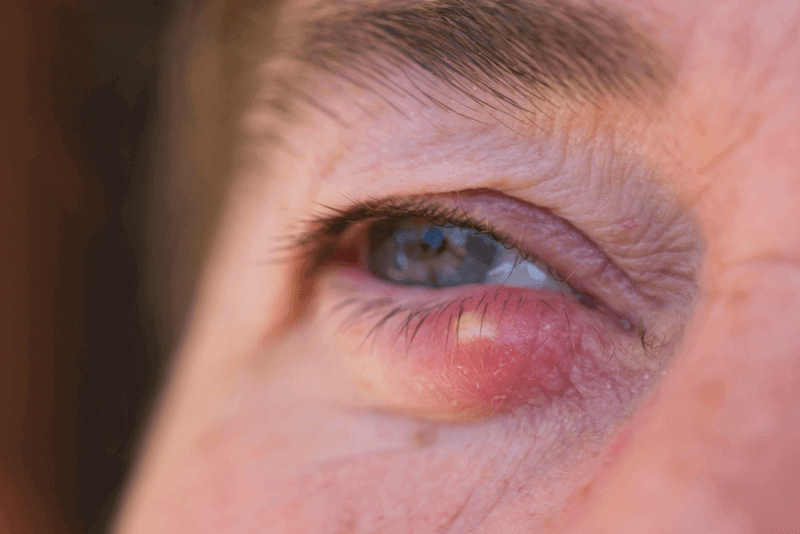
Stye, an inflammatory skin disease that occurs on the eyelids, causes extreme discomfort to people, although it is easily treated. Stye, which is quite common in the society, is referred to as hordeolum in medical language. Due to the blockage of the sebaceous glands located on the outer part of the eyelids close to the eyelashes, inflammation occurs due to the bacteria remaining in the glands. If the stye, which is a small redness in the initial stage, progresses, the eye may close. It usually occurs when body resistance is low, and its appearance resembles a pimple or boil.
Types of Stye
The stye is divided into two different groups according to its location.
Internal Shallot
It forms on the inside of the eyelid. It is characterized by swelling of the eyelid in addition to other symptoms of stye.
Outer Shallot
It is a type of stye that forms at the base of the eyelashes. It develops due to Zeiss and moll glands. The type of bacteria that is effective in its formation is staphylococcus.
Stye Symptoms
In the initial stage, the stye takes the form of a painful spot. Itching and stinging sensation in the eye is also seen. 1 to 2 days after the onset of these symptoms, the spot swells enough to be visible. Redness increases. A sac filled with pus forms. An internal stye is usually seen after the eyelid is turned upside down. If the meibomian sebaceous gland is blocked, it causes swelling of the eyelid. If the pain sensation increases, tearing also starts.
Causes of Stye
The sebaceous glands in the eyelids prevent the secreted tears from drying out. This makes it easier for the eyelids to move and prevents irritation of the eyes. However, bacteria that settle in the eyelash follicles, usually as a result of manual handling, are effective in the formation of stye. It occurs especially when people are tired and sleep deprived and when their body resistance is low. The factors that cause the bacteria that cause stye to settle are the following:
- Touching the eye with dirty hands,
- Not removing make-up,
- The eye is prone to infection,
- Eating a diet rich in fat,
How is a Stye Diagnosed?
A simple physical examination is sufficient to diagnose a stye. No imaging or laboratory tests are used for diagnosis.
Stye Treatment
The most important step in the treatment of styes is for patients to pay attention to their personal hygiene and maintain eye hygiene.
Medication Therapy
Pomades and drops are also used in the treatment of stye, which heals in approximately 1 week. These medicines shorten the healing time and at the same time reduce the symptoms.
Surgical Intervention
If the stye does not heal or hardens for 2 to 3 weeks despite treatment, surgical intervention is used. In the surgery, a small incision is made on the inside of the eyelid to drain the inflammation completely.
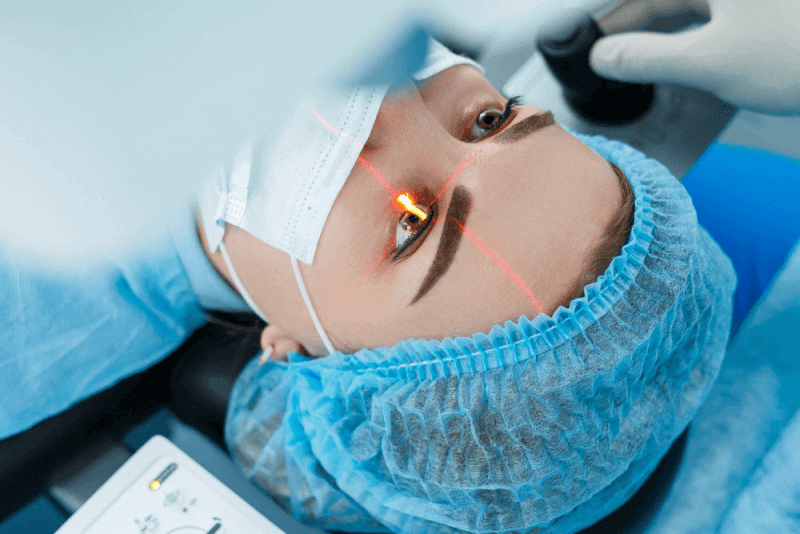
Stye Surgery
If the stye causes cyst formation, the method known as stye surgery is applied. In this surgery, the eyelids and surrounding tissues are numbed with local anesthesia. The inflammation is then removed by making an incision through the eyelid. After the removal of the fatty tissues that cause cystic formation, the eye is closed with a bandage. This surgery, which takes approximately 15 minutes, is extremely simple. Since the incision is made through the eyelid, no stitches and no wound care is required. The bandage is removed the next day and antibiotic eye drops are applied for a week.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery 15-30 Minutes
Method of Anesthesia Local
Length of Hospitalization: No Hospitalization Required
Return to Work Period: 1-3 Days
Things to Consider in Stye
- Textile products should not be shared with other people until the stye has healed.
- Hands should always be washed with soap before contact with eyes.
- Makeup should not be applied until the stye is completely healed.
- The eye should not be bandaged until the stye has healed.
- Do not try to drain the pus from the stye.