In a healthy person, the number of heart beats in a minute varies between 60 and 100. The reason for this change is according to the needs of the body at times of the day. It is normal for the heart rate to accelerate during exercise or trauma, while it should slow down during rest.
What is Tachycardia?
If the heart rate of a person at rest is above 90, this is considered the most important sign of the presence of tachycardia. Tachycardia is defined as more than 100 beats per minute. However, it is important that this pulse rate develops independently of stress.
In some patients, tachycardia may progress without any symptoms. For this reason, untreated tachycardia can lead to impaired heart function in the future. This can lead to stroke, heart failure and sudden cardiac arrest.
Tachycardia, also known as palpitations, is caused by altered electrical currents due to abnormalities in the heart tissue.
Types of Tachycardia
Tachycardia is divided into different types according to the location of the electric current problem. The types of tachycardia are as follows.
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, the most common type of tachycardia, is caused by incorrect electrical currents in the upper chambers of the heart. The irregular electrical signals that occur in these chambers cause the atria to contract both rapidly and weakly. Hypertension, hyperthyroidism, valvular heart disease and heavy alcohol consumption are not among the factors that trigger this tachycardia.
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is simply the rapid but regular beating of the atria of the heart. However, this speed causes the heart valves to contract weakly, resulting in tachycardia.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Very fast heartbeats that start at any point above the lower chambers of the heart are called SVT. It is especially seen in people who smoke and drink alcohol.
Ventricular Tachycardia
A rapid heartbeat is caused by abnormal electrical currents in the lower chambers of the heart. However, in this form of tachycardia, the ventricles are unable to pump enough blood for the body. Ventricular tachycardia episodes usually last a few seconds and do not cause any damage. On the other hand, if the attacks last longer, they cause damage that can lead to an emergency situation.
Ventricular Fibrillation
The chaotic, rapid, electrical impulses in the heart cause the lower chambers to vibrate instead of the heart pumping blood. This type of tachycardia can be fatal if the heart is not shocked within a short period of time. Ventricular fibrillation, especially before or after a heart attack, can be caused by serious heart disease or lightning strikes.
Causes of Tachycardia
In some cases, the cause of tachycardia was not clear, but some conditions were found to cause tachycardia. We can list these situations as follows.
- Some lung diseases,
- Overactive thyroid gland,
- Hypertension
- Heart valve disease,
- Heart infections
- Heart tumors
- Coronary artery insufficiency,
- Heart muscle disease,
- Heart failure
- Electrolyte imbalance,
- Smoking,
- Coronary artery disease,
- Drug use,
- Excessive alcohol consumption,
- Some anomalies of the heart,
- Heavy exercise,
- Anemia,
- Side effects of some medicines,
- Use of certain medications,
Symptoms of Tachycardia
Although the symptoms of tachycardia vary according to the patients, the symptoms usually seen in patients include the following.
- Low blood pressure, dizziness,
- Feeling dizzy,
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden weakness,
- Chest pain
- Heart palpitations
- Heart attack
- Becoming unconscious
How is Tachycardia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of tachycardia requires a detailed medical history and a thorough physical examination. Other diagnostic methods are then used to determine the exact diagnosis and type of tachycardia.
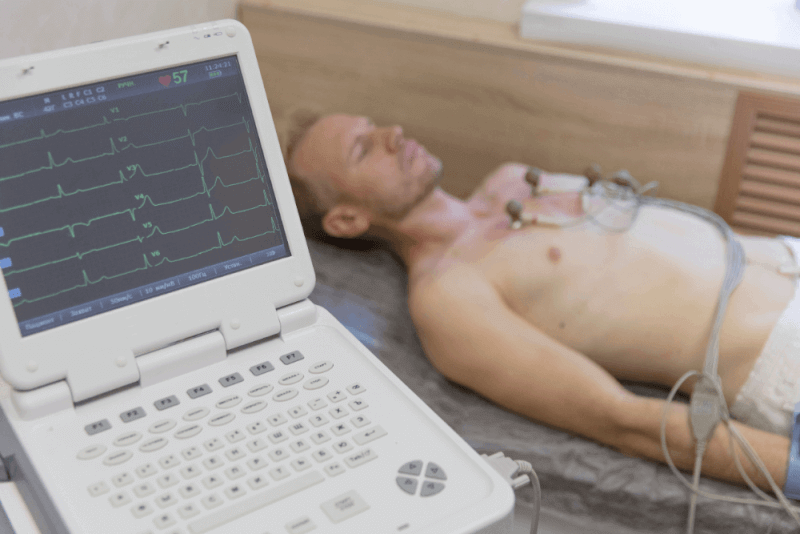
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
It is the most commonly used method to diagnose tachycardia. In this test, electrodes are attached to the patient's arms, chest and legs to measure the electrical activity of the heart. The ECG records the timing and strength of electrical signals as they circulate through the heart.
Holter Monitor
For 24 hours, a Holter monitor worn by the patient records the activity of the heart. This allows a comprehensive examination of the heart rhythm.
Event Monitoring
This device, which allows monitoring of cardiac activity from one week to several months, is worn on the patient all day, but patients activate the device as soon as they feel signs of tachycardia.
Other Portable Devices
Devices such as smartwatches, which are used by many people in today's technology, are also daily devices that are frequently used to check the heart rhythms of patients.
Cardiac Imaging
Cardiac imaging can be used to determine whether tachycardia is caused by a structural problem.
MRI
Irregularities are diagnosed with MRI, which allows visualization of how blood flows to the heart.
CT
CT scans provide a more detailed view of the heart.
Echocardiography
Blood flow is analyzed with this imaging method that creates an image of the heart using sound waves.
Coronary Angiography
It is used both to monitor blood flow and to identify possible abnormalities and blockages.
Chest X-ray
It is used to find out if the heart is larger than normal.
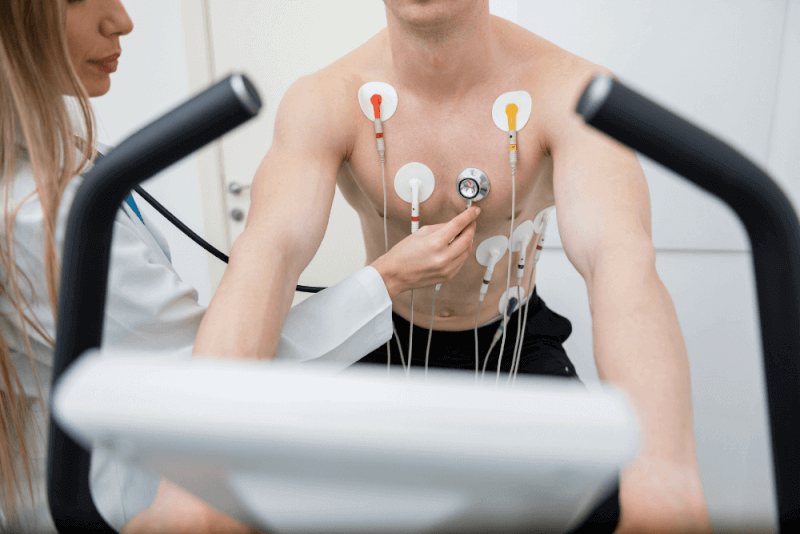
Stress Test
The stress test examines how the patient functions under intense exercise. Patients are given medication for this. Afterwards, heart rates are monitored with electrodes while patients exercise.
Inclined Table Test
After a tachycardia-inducing drug is administered to the patient, they are fixed on a moving table and monitor how their nervous system and heart respond to these changes.
Tachycardia Treatment
Treatment planning for tachycardia is based on the general health and age of the patients, and its main aim is the regulation of rapid heart rate. The treatment is also aimed at preventing future complications caused by tachycardia.
Vagal Maneuvers
In vagal maneuver treatment, judges require patients to do some physical activity during attacks. These include pushing, coughing or placing an ice pack on the face.
Medicines
In some patients, vagal maneuvers are insufficient. For this reason, these patients are started on medication. The group of drugs used in the treatment of tachycardia are anti-arrhythmatic drugs.
Cardioversion
Cardioversion is a treatment method applied in emergency situations when other treatment methods are not sufficient. In this treatment method, patients are given electric current through a spoon or pad.
Defibrillation
It is a treatment method applied in cases where the pulse is dirhythmic in patients. A possible dirhythmic pulse is a medical emergency. For this reason, it is especially applied in ventricular tachycardia where there is no blood flow to the body.
Other Treatment Methods
Other treatment methods used to treat tachycardia include the following.
- Catheter ablation,
- Pacemaker
- Implantable cardioverter,
- Open heart surgery,
- Labyrinth procedure,
What should the tachycardia limit be according to age groups?
In order to talk about the presence of tachycardia, a heart rate above the normal heart rate limits must be obtained. The heart rate should be taken at rest. Heart rates that are considered normal by age are as follows.
- In the first 6 months, babies should have a heart rate between 90 and 180. The average heart rate is 145.
- Babies between 6 months and 1 year of age have a heart rate between 106 and 185, with an average heart rate of 145.
- Babies between 1 and 2 years of age have a heart rate between 105 and 170, with an average heart rate of 132.
- Children between 2 and 4 years of age have a heart rate between 90 and 150, with an average heart rate of 120.
- Children between 4 and 6 years of age have a heart rate range of 72 to 135, with an average heart rate of 108.
- Children between 6 and 10 years of age have a heart rate range of 65 to 3 135. The average heart rate is 100.
- In children between 10 and 14 years of age, the heart rate range is between 65 and 130, with an average heart rate of 90.
- People over 14 years of age have a heart rate range of 60 to 120, with an average heart rate of 85.