30-Second Summary
- This device uses special X-rays to obtain detailed images of various sections of the body.
- Eating and drinking should be stopped several hours before the CT scan. Additionally, accessories such as hairpins or piercings that may affect image quality should be removed.
- Generally, imaging lasts between a few minutes and 30 minutes.
- Interpreting and reporting the images may take up to 10 days.
What is a CT Scan?
The word tomography comes from the Greek words “tomos” (cut) and “graphein” (to record). It is a medical imaging technique used to create detailed pictures of the body. This device uses special X-rays to obtain detailed images of various body sections. These images are captured from different angles and later combined using software. This allows for the creation of bone, soft tissue, and vascular images.
Why is a CT Scan Performed?
A CT scan is an imaging method used to diagnose many different diseases and health conditions. Common health conditions in which CT scans are used include:
- Bone fractures
- Bone tumors
- Bone deformities
- Various internal organ injuries
- Internal bleeding
- Tumors
- Detecting the location of blood clots
- Infections
- Surgical planning
- Biopsy planning
- Radiation therapy planning
- As a visual guide during needle aspiration or biopsy
- Heart diseases
- Lung nodules
- Liver masses
- Cancer
- Measuring bone density
- Determining the stage of cancer
- Colorectal cancer screening
- Ulcerative colitis
- Kidney stones
- Bladder stones
- Sinusitis
- Assessing the risk of internal bleeding
- Identifying diseases in internal organs
- Detecting metastasis
- Evaluating treatment outcomes
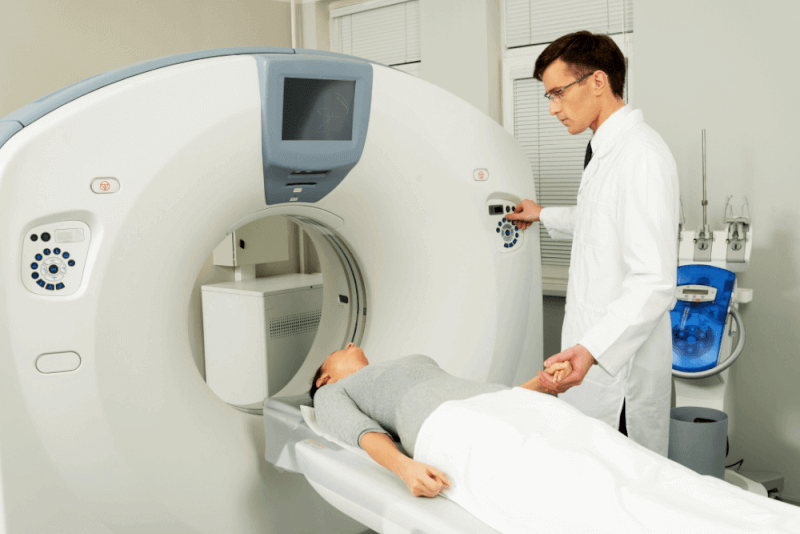
How is a CT Scan Done?
To perform a successful CT scan, there are a few things to consider before and during the procedure. The steps of the scan are as follows:
- Eating and drinking should be stopped several hours before the scan.
- Clothing is removed, and a hospital gown is worn. Accessories such as piercings or hairpins that may affect image quality must be taken off.
- Patients lie on the table of the CT machine during the procedure. Depending on the device, either the table moves while the scanner remains fixed, or the scanner moves around a stationary table.
- Depending on the type of scan, patients may lie face up or face down.
- Patients must remain completely still during the scan. Therefore, being in a comfortable position on the table is very important.
- In some cases, patients may be asked to hold their breath to avoid issues with image quality.
- Foam cushions or straps may be used to ensure patient comfort.
- Various sounds may come from the machine during scanning.
- The patient remains alone in the room during the scan, but the radiology technician can see and communicate with the patient from another room.
How Long Does a CT Scan Take?
The duration of a CT scan depends on the area being imaged. Thanks to advances in CT technology, many scans can now be completed within seconds. Generally, the procedure takes between a few minutes and 30 minutes.
What Is a CT Scan Used For?
The purposes of using a CT scan include the following:
- Providing three-dimensional images of tissues, vessels, organs, and bones
- Capturing images in cross-sectional slices
- Helping to avoid unnecessary interventions
- Assisting with accurate treatment planning
- The procedure is very short in duration
- Quickly distinguishing between damaged and healthy tissue
When Will the CT Scan Results Be Available?
The images obtained from a CT scan are stored digitally. However, interpretation and reporting of the images can take up to 10 days. Afterward, the results are communicated to the patient.
What Is the Difference Between MRI and CT?
CT and MRI are among the most commonly used and trusted imaging systems in modern healthcare. However, there are some key differences between them:
- CT scans use X-rays to obtain images, whereas MRI uses radio waves within a magnetic field.
- MRI is generally used for musculoskeletal, spinal, brain imaging, neurological conditions, or sports injuries, while CT scans provide three-dimensional images of the entire body.
- CT scan results are typically available faster than MRI results.
What Is the Difference Between a CT Scan and a Contrast-Enhanced CT Scan?
The main difference between a standard CT scan and a contrast-enhanced CT scan is that in the latter, contrast material is administered intravenously. Contrast-enhanced CT scans are preferred in the following situations:
- They allow for clearer visualization of soft tissues.
- For esophagus or stomach evaluations, the contrast agent must be swallowed to produce clearer images.
- During detailed intestinal screening, contrast material may be administered rectally.
- After a contrast-enhanced CT scan, patients may need to be monitored for a short period to ensure the contrast agent is expelled. In standard CT scans, such observation is not necessary.
Which Diseases Are Diagnosed Using CT Scans?
CT scans help diagnose many conditions occurring within the body. The scan is named according to the body region being examined.
Lung
Lung CT scans, also known as thoracic CT (CT thorax), are used to diagnose pulmonary conditions and to monitor treatment effectiveness. Their uses include:
- Congenital anomalies
- COVID-19 disease progression
- Lung tumors
- Aortic diseases
- Chest trauma
- Screening individuals at risk due to family history of lung diseases
- Pneumonia
- Detection and monitoring of lung nodules
- Bronchitis
- COPD
- Emphysema
- Blockage in lung vessels
- Pulmonary embolism
Abdomen
The term abdomen refers to the belly area, which houses nearly all internal organs. Abdominal CT is often used to examine these organs, which include:
- Small intestine
- Colon
- Bladder
- Gallbladder
- Uterus
- Ovaries
- Prostate
- Stomach
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Gallbladder
- Spleen
- Adrenal glands
Abdominal CT is used to diagnose diseases in these organs. Common reasons for using abdominal CT include:
- Aortic diseases
- Trauma
- Risk of internal bleeding
- Vascular obstructions
- Tumors in internal organs
- Stones in the urinary tract, bladder, or kidneys
- Inflammatory diseases such as kidney infection or appendicitis
Head
A head CT scan provides a detailed examination of the brain. Also known as brain CT, it is frequently used for the following purposes:
- Tumors
- Stroke
- Head trauma
- Brain hemorrhage
- Neurological diseases
- Aneurysm
- Severe headaches
- Numbness
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Memory loss
- Sensory loss
Temporal Bone CT
Temporal bone CT is a specialized scan used for the following reasons:
- Examining tissues in the middle and inner ear
- Infections in the middle and inner ear
- Cerebrospinal fluid leakage into the ear
- Facial nerve paralysis
Cardiac CT
Also known as coronary CT angiography, this scan is used for the following purposes:
- Identifying issues in the coronary arteries
- Detecting arterial narrowing
- Coronary heart disease
- Pericardial diseases
- Congenital heart muscle disorders
Types of CT Scans
With technological advancements, CT scanners now provide higher image quality and thinner slices. CT devices are categorized based on their features, and the main types include:
Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT)
Multidetector CT scanners, with 16 to 64 slices, can scan the entire body in just 15–20 seconds. They also produce high-quality 3D images.
They are especially used for imaging coronary arteries, the heart, and lungs. These devices help detect very small findings that are difficult to see with the naked eye, enabling earlier diagnosis of diseases.
It can also be used in CT angiography procedures, especially for virtual colonoscopy and comprehensive vascular imaging.
Dual-source multidetector CT (DSCT):
These 128-slice systems can image the heart within 5–6 seconds, regardless of heart rate. They allow evaluation of all body regions with 3D and multiplanar images. The imaging applications include:
- Virtual colonoscopy
- Whole-body angiography
- Virtual bronchoscopy
- Large intestine
- Bronchi
- Blood vessels
These scanners are also used to detect vascular narrowing and analyze internal organs. They are particularly effective in identifying small lesions in the lungs.
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
SPECT uses gamma rays to create nuclear tomographic images. A camera captures 3D images from multiple angles, and these are reconstructed digitally. It is commonly used in scintigraphy of the following organs:
- Brain
- Heart
- Perfusion
- Myocardium
- Lungs
- Kidneys
- Liver
- Bones
PET/CT
Positron emission tomography combined with CT is used primarily for cancer diagnosis and treatment monitoring, as well as for many other conditions, including:
- Fever of unknown origin
- Infection
- Detection of viable tissue in heart disease
- Differentiation of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease
- As a guide for biopsy
Harms of CT Scanning
Computed tomography uses X-rays, which are a form of radiation. Since CT scans provide more detailed images than standard X-rays, the radiation exposure is higher. However, with technological advancements, scan durations have decreased, thereby reducing radiation exposure.
Studies have shown that the probability of developing a fatal cancer due to CT scanning is approximately 1 in 2,000. However, CT scans pose greater risks for children in their growth phase. This is because cells in growing children divide more rapidly. For this reason, children under the age of 15 who undergo CT scans have a higher risk of developing leukemia or brain tumors within the next 10 years.