30 Second Summary
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the pancreas loses its ability to produce insulin.
- Symptoms include excessive drinking, excessive urination, extreme hunger, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision and skin infections.
- Treatment includes insulin injections, blood glucose monitoring and carbohydrate counting.
- It is the result of a combination of genetic factors and environmental factors.
What is type 1 diabetes?
The body's main nutrients are carbohydrates, fats and protein. Simple sugar, which is among carbohydrates and called glucose, is an important nutrient that is involved in many organs of the body, especially the brain. In order for glucose to be used in metabolism, the pancreas located behind the stomach must secrete the hormone insulin. This hormone breaks down the glucose in the blood into small amounts so that it can be used by the cells. If the hormone insulin is not secreted sufficiently, the body cannot provide the energy it needs.
Type 1 diabetes is the name given to the condition in which beta cells, which are responsible for producing insulin hormone in the pancreas, are damaged for various reasons and therefore cannot secrete enough insulin homone. Type 1 diabetes, which is usually seen in children under the age of 15, can occur in people of all ages. Type 1 diabetes is also called juvenile diabetes because it mostly affects children. The global prevalence of children with type 1 diabetes is not common in any geographical region. However, type 1 diabetes in adults is more common in northern countries.
Insufficient insulin hormone in the body leads to an increase in the level of sugar in the blood and this sugar cannot be used by the body. For this reason, type 1 diabetes can cause serious health problems if left untreated. In the treatment of type 1 diabetes, the main thing is to take the hormone insulin from outside. Patients should also pay attention to their diet and exercise.
Diagnostic criteria for type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is relatively easy to diagnose. Because the increase in the amount of sugar in the blood causes some symptoms in the body. Blood tests also facilitate the diagnosis of the disease.
Blood sugar test
In this test to check the amount of sugar in the blood, patients must give a blood sample on an empty stomach. If the test shows high levels of sugar in the blood, the person is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
Antibody test
Another test to confirm the diagnosis is an antibody test. This test identifies proteins called autoantibodies, which attack the body's tissues when they should not. This test is also used to determine the type of diabetes. Because type 2 diabetes patients do not have autoantibodies.
Urinalysis
Urine tests used in the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes look for ketones in the samples. A high amount of ketones in the urine sample causes the urine to have a more acidic structure. This has a negative impact on the general health of patients.
Arterial blood gas
In this test to compare the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, a blood sample is taken from an arterial vein.
Symptoms of Medicine 1 diabetes
Common symptoms caused by type 1 diabetes include the following:
- Involuntary weight loss
- Dry mouth
- The constant need to drink water
- Increased number of urinations
- Feeling more hungry
- Fatigue
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Skin infections
- Difficulty breathing
- Slow healing of wounds
- Don't be angry
- Vaginal fungi
- Night urination
- Itching
- Difficulty concentrating
- Numbness and tingling sensation in the feet
- Skin dryness
- Acetone-like odor in the mouth
In addition to these symptoms, patients should consult a doctor as soon as possible in case of complaints of the following symptoms.
- Lethargy
- Fruity odor in the mouth
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Rarely loss of consciousness
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in infants
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in infants may not be clearly understood. This is why the results of blood tests are important. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in infants include the following:
- Increased thirst
- More urine output than normal
- Bedwetting in toilet trained children
- Excessive hunger
- Unwanted weight loss
- Burnout
- Irritability
- Behavior changes
- Fruit-scented breath
In addition, type 1 diabetes is diagnosed if the blood tests of the babies are higher than the following values:
- Fasting blood glucose more than 126 mg/dl
- 2-hour blood glucose level 200 mg/dl higher on OGTT
- HbA1c value more than 6.5%
Causes of type 1 diabetes
The root cause of type 1 diabetes is not known. However, there is a genetic predisposition. In people with a family history of type 1 diabetes, the beta cells that produce insulin hormone are completely eliminated due to an autoimmune cause.
It is also known that type 1 diabetes is triggered after viral infections, trauma and stressful events. Since viral infections attack the beta cells in the pancreas, beta cells are damaged.
Type 1 diabetes treatment methods
Since type 1 diabetes patients have no or very little insulin hormone, the most important treatment option is to take insulin hormone from outside. Patients should also pay attention to their diet.
Type 1 diabetes surgery
These surgeries, called metabolic surgery, ensure that the insulin hormone in the body becomes functional. However, the lack of insulin hormone in type 1 diabetes patients prevents successful results from these surgeries. For this reason, type 1 diabetes patients are not subjected to metabolic surgery.
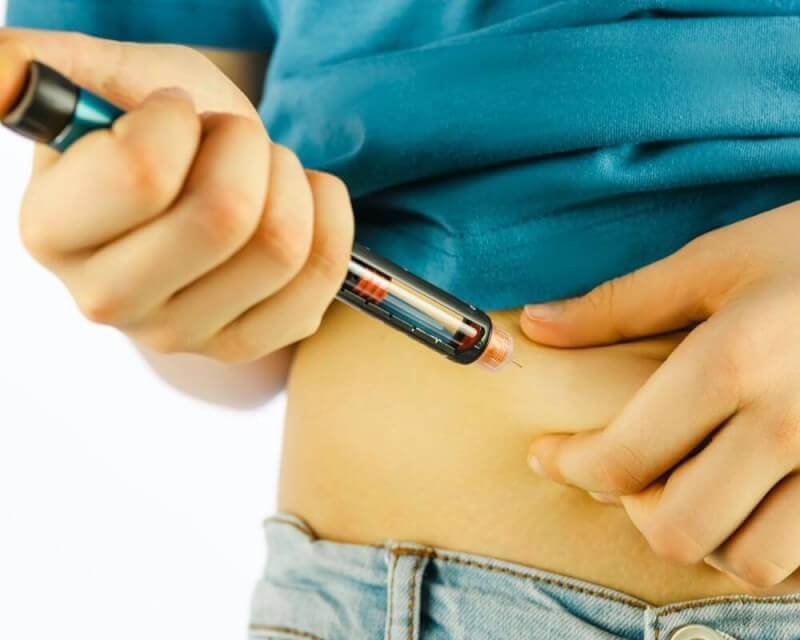
Insulin treatment of type 1 diabetes
The indispensable treatment option for type 1 diabetes patients is insulin therapy. Usually, patients receive insulin treatment in 4 or 6 doses during the day. Insulin types are as follows:
- Multi-day injections
- Fast-acting inhaled insulin
- Insulin pumps
- Insulin pens
Blood sugar monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring is part of insulin therapy. In this method, which can be applied at home with a special measuring device, patients try to keep their blood glucose levels within the required range.
Carbohydrate counting
In order to accurately determine insulin doses, it is necessary to count the amount of carbohydrates in the food and beverages consumed. This is because glucose is produced when carbohydrates are digested. Glucose causes blood sugar levels to rise. For this reason, the amount of carbohydrate consumed during the day is extremely important in determining the insulin dose.
Stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes
Research on stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes patients was announced in 2022. According to these studies, stem cell therapy shows promise, especially in patients with hypoglycemia.
Research has shown that some stem cells transform into insulin-producing cells. In this way, blood sugar levels can be controlled. Studies have shown an increase in C-peptide in the pancreas, which is made together with insulin. C-peptide measurement is one of the important indicators of how much insulin is in the body.
In this treatment with a special implanted device, the devices are designed to maintain long-term and stable blood glucose levels. The device contains a repository of stem cells that are prepared to transform into pancreatic cells after being implanted into the body. Then, when the blood vessels come into contact with this depot, the stem cells are allowed to grow correctly in the device. In order to prevent any reaction of the immune system against the implant, patients should use immunosuppressive drugs.
Is type 1 diabetes genetic?
Type 1 diabetes is a genetically transmitted disease. If a person's mother, father or sibling has type 1 diabetes, the risk of diabetes is high. Ten out of 100 people with a close family history of type 1 diabetes are at risk of developing type 1 diabetes. Studies have shown that if the father has type 1 diabetes, it carries a higher risk than if the mother has type 1 diabetes. According to research on the genetic transmission of type 1 diabetes, the risks are determined as follows:
- In the general population, the probability of type 1 diabetes is 3 or 4 per 1000 people.
- If both parents have type 1 diabetes, 25 out of 100 children have type 1 diabetes.
- If a parent or sibling has type 1 diabetes, 8 out of 100 children have type 1 diabetes.
- If the father has type 1 diabetes, 5 out of 100 children have type 1 diabetes.
- If the mother has type 1 diabetes, 3 out of 100 children have type 1 diabetes.
In addition, although type 1 diabetes carries the risk of genetic transmission, 90 out of 100 children with type 1 diabetes do not have genetic transmission. For this reason, it is possible to say that every child is at risk of type 1 diabetes.
Nutrition in patients with type 1 diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes do not need diabetic foods or diets. A diet suitable for diabetes should be tailored to the individual and attention should be paid to ensure that the foods added to the diet are healthy and that these foods are consumed in a balanced way.
The diet of diabetic patients should be organized in a way that can be easily adapted to their daily lives. The financial situation and culture of the patients should also be taken into account. For this reason, type 1 diabetes patients should seek help from nutritionists in the regulation of their diet.
Type 1 diabetics receive intensive insulin therapy, so their diet can be flexible. However, it is important to calculate the amount of carbohydrates in the diet and their nutritional value in order to adjust the insulin dosage.
What type 1 diabetics should pay attention to in their diet
Nutrition programs for patients with type 1 diabetes should be prepared by specialists. Patients get used to their diet over time and it is easy to implement. Among the points that patients should pay attention to in their nutrition are the following.
- They should always make sure that there is plenty of variety in their diet.
- Foods rich in fiber should be chosen.
- It is important that they avoid processed foods and eat unprocessed or minimally processed foods as much as possible.
- Avoid added sugar, high energy foods and refined grains.
- The main components of their diet are vegetables, legumes, seeds, fruit, whole grain products, fish, low-fat dairy products, low-fat meat products.
- A low-carbohydrate and low-fat diet should be prescribed.
Meal frequency
The number of meals that patients with type 1 diabetes should eat during the day should be determined according to the medical treatment received and the physical activity level of the patients. People with type 1 diabetes who use insulin should eat 3 main meals and 3 snacks. The last snack should be consumed before going to bed at night.
Patients should consume their meals half an hour after the insulin injection. If the waiting time is not respected, blood sugar will rise rapidly after the meal. Another mistake patients make regarding meal consumption is skipping snacks or limiting the amount of food they consume because they do not feel hungry. This causes a drop in blood sugar.
What can be consumed in snacks?
Type 1 diabetics are generally recommended to consume carbohydrate-containing foods in their snacks. In general, 10-15 g of carbohydrate consumption is sufficient. For this reason, breadsticks, popcorn, sugar-free whole wheat biscuits and dairy products that can replace bread can be consumed in snacks.
It is also recommended for type 1 diabetes patients to consume fruit in their snacks. However, fruit should not be consumed alone. Because if fruit is consumed alone, blood sugar rises rapidly.
Carbohydrate counting in type 1 diabetes
Carbohydrate counting, which type 1 diabetics should do at every meal, helps to keep blood sugar under control. Before counting, blood glucose should be measured to find out the amount of carbohydrates people need.
Although foods contain elements such as fat, protein and carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals, carbohydrates are the most effective part on blood sugar. For this reason, people should pay attention to carbohydrate consumption in their diet.
The ideal range of blood sugar varies between patients. For this reason, patients should ask their doctor for the most suitable interval for them. Studies have proven that consuming the right amount of carbohydrates and adjusting the right insulin dose can reduce HbA1c by 1%.
Carbohydrate counting techniques
Portion control is required for carbohydrate counting. Among the methods used to adjust portions are the following:
- Practical kitchen measurements (such as cups, spoons and bowls)
- Hand measurements (such as palm and fist)
- Tags
- Kitchen scale
- Books showing the carbohydrate content of foods
Patients with type 1 diabetes need to determine the most appropriate measurement method for themselves when counting carbohydrates and to keep their diet within these measurements. It will consolidate over time.
Carbohydrate counting is done with 3 different methods. These methods are as follows:
- Counting portions of foods containing carbohydrates
- Carbohydrate option counting
- Carbohydrate gram counting
People who will count carbohydrates should also acquire the habit of reading labels. However, the total values of pulp and sugar alcohols are deducted from carbohydrate values on labels. You should be aware of this method applied to all products except diabetic products and take these values into account when counting carbohydrates.
Baseline carbohydrate counting
Basic carbohydrate counting takes place in 7 stages.
- First of all, people should keep a food diary
- They then need to learn about the amount of carbohydrates in foods.
- In order to measure the amount of carbohydrate, portions need to be learned.
- Checking carbohydrate calculation
- Controlling the amount of carbohydrates in the foods consumed
- Control the amount of carbohydrates that individuals with diabetes should consume on a daily basis
- Evaluation of the effect of carbohydrate intake at each meal on postprandial glucose
For type 1 diabetics, the amount of carbohydrate that should be consumed in a meal is usually 15 g. Among the foods with this amount of carbohydrate value are the following:
- 1 cup soup
- 1 small piece of fresh fruit
- Half a glass of stew
- Half a cup of canned or frozen fruit
- 6 chicken nuggets
- Half a cup of oatmeal
- 1 tablespoon jelly, jam, sugar or honey
- 1 slice of bread
- Half a cup of ice cream
- 3 tablespoons of rice or pasta
- 2 small cookies
- Half a glass of starchy cookies
- 4-6 crackers
- 2/3 cup yogurt
- Small sized potato
Advanced carbohydrate counting
In individuals using multiple insulin injections or insulin pumps, advanced carbohydrate counting used for basal insulin dose adjustment provides an advanced level of glycemia control. This count calculates the ratio of carbohydrate to insulin as well as the insulin sensitivity factor. Patients should also be taught how to perform the calculation and checked at regular intervals. If patients experience an increase in body weight, hypoglycemia or an increase in the frequency of hypoglycemia, the carbohydrate and insulin ratio should be recalculated.
The following steps are used to calculate the carbohydrate and insulin ratio:
- First of all, basal and bolus doses in ratios and the total amount of carbohydrate ingested by patients should be appropriate for individuals.
- For 1 week, patients should take a detailed note of the amount of carbohydrate intake at all meals. In addition, the results of blood glucose counts before and after feeding and the timing and doses of insulin treatment should be recorded regularly.
- By keeping these records, the amount of carbohydrate consumed at meals is evaluated.
- It is necessary to ensure that the results of blood glucose tests performed before and after meals are stable at the targeted level.
The difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
To briefly summarize the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, they can be listed as follows:
- While type 1 diabetes is a rare type of diabetes, type 2 diabetes is common.
- Type 1 diabetes is usually seen in people under the age of 30, especially in childhood and adolescence, while type 2 diabetes is usually seen in people over the age of 30.
- While type 1 diabetes occurs independently of lifestyle, type 2 diabetes is completely lifestyle-related.
- Type 1 diabetes is caused by insulin deficiency, while type 2 diabetes is caused by genetic predisposition.
- Common symptoms seen in patients with type 1 diabetes include dry mouth, weight loss and blurred vision, while type 2 diabetes patients have no or only mild symptoms.
- People with type 1 diabetes are at their ideal weight or underweight. People with type 2 diabetes are usually obese.
- People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin. Patients therefore need to take insulin from outside. Type 2 diabetes patients are treated with pills or insulin injections.