30 Second Summary
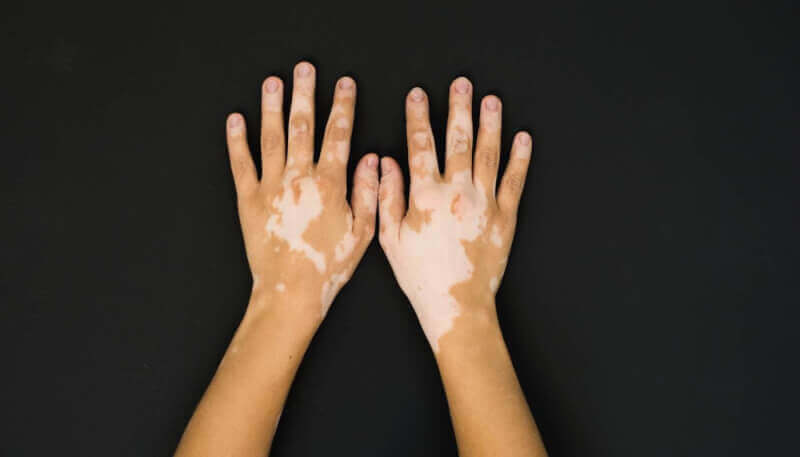
- Vitiligo is a skin disease caused by damage to skin cells called melanocytes.
- It appears as white spots anywhere on the body.
- Methods such as light therapy, creams, immunosuppressive drugs and depigmentation can be used in the treatment of vitiligo.
- Vitiligo is a lifelong disease, but symptoms can be alleviated with treatments.
- There is no definitive cure for vitiligo, but treatments are available.
Commonly seen vitiligo is also called ala or pied among the people. Although vitiligo is seen in approximately one in every 100 people, it usually shows the first symptoms under the age of 20. The size of vitiligo, which only affects the color of the skin and does not cause any physiological problems, varies according to the patients.
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is caused by damage to melanocyte cells in the body, which are responsible for the production of pigments that give the skin its color. Damage to melanocyte cells for any reason causes changes in the color of the skin. Treatment should be started as soon as the first spots of vitiligo, which only affects patients psychologically due to their appearance, are seen.
Classification of Vitiligo
Vitiligo is divided into different classes according to the incidence, location and spread of the spots.
Local Vitiligo
Local vitiligo is divided into two types. The first type of local vitiligo is focal. Although patients with focal vitiligo have one or more lesions, they do not show segmental features.
Another type of local vitiligo with one or more patches is segmental vitiligo, which differs from focal vitiligo in that it is located on certain lines of the body. Segmental vitiligo, which can be seen at any age, is especially seen between the ages of 5 and 30. It starts in a specific anatomical area and remains limited within this area. In men, it is mostly seen on the face, neck, extremities and scalp, respectively. In women, it is mostly seen on the face, neck, arms and legs, respectively.
Spotting that starts in one breast is usually a sign of segmental vitiligo. Factors that are effective in increasing vitiligo are not effective in segmental vitiligo. On the other hand, autoimmune diseases are less common in segmental vitiligo. However, segmental vitiligo is accompanied by more allergic symptoms.
Generalized Vitiligo
Generalized vitiligo is also divided into two subtypes. The first subtype of generalized vitiligo is acrofacial vitiligo. Acrofacial vitiligo is a type of vitiligo that involves the face and hands and has multiple lesions.
Another subtype of generalized vitiligo is diffuse. In these patients, the lesions have a widespread distribution but are also irregular.
Universal Vitiligo
Except for a few areas of normal skin, depigmentation is seen on the entire skin of patients.
Mixed Vitiligo
The combination of more than one type of vitiligo is called mixed vitiligo. The areas most affected by mixed vitiligo include the face, neck and scalp. It is also frequently seen in skin folds. In addition to these, lesions are frequently seen in the areas where the bones protrude, which are constantly exposed to traumas. These areas include the elbows, gums, outer forearm, inner wrist, inner wrist, finger and back of the hand.
Causes of Vitiligo
While the exact cause of vitiligo is not known, some factors that increase the risk of its occurrence are known. For vitiligo to occur in the majority of patients, more than one risk factor usually needs to be present together.
The first risk factor for vitiligo is the autoimmune mechanism. The immune system that attacks melanocytes causes damage to the membranes of the cells. In this case, vitiligo occurs because it affects pigment production. Other risk factors of vitiligo include the following.
- Severe trauma,
- Sunburn,
- Febrile diseases,
- Stress,
- Otoimmune goiter diseases,
- Soriasis,
- Diabetes,
- Anemia,
In addition, vitiligo is also thought to be genetically inherited. Because 30% of vitiligo patients have the same disease in their family.
The Course of Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a lifelong disease. Vitiligo, which enters periods of exacerbation from time to time, shows a development specific to each patient. For this reason, some patients develop a small number of plaques and these plaques do not change throughout their lives, while in some patients, the spots can grow and spread in a short time and cover the entire skin.
Vitiligo Symptoms
Symptoms of vitiligo can be seen in people of all ages, starting from childhood to adulthood. The first symptoms are usually seen on the areas of the skin that are most exposed to the sun. For this reason, the first spots appear on the hands, arms, legs, neck and face. White spots on the skin are more prominent in women than in men due to the difference in skin colors.
The first and most common symptom of vitiligo is the sudden appearance of a white spot anywhere on the skin. In the progressive process, this spot grows and spreads. Vitiligo, which does not affect any organ, shows no other symptoms.
Vitiligo Treatment Methods
The vitiligo treatment to be applied is determined by the extent of the affected skin area, which area is affected and how fast the condition progresses.
Although results vary, the medications and radiation used in the treatment are designed to improve skin tone and even out skin tone. In addition, some treatments applied in vitiligo treatment have serious side effects. Due to these side effects, experts recommend that skin tone inequalities should first be covered with cosmetic products such as concealer and bronzer.
Treatment options such as medication, therapy and surgery are evaluated according to the tests performed and the general health status of the patients. Several trials may be necessary to find the most appropriate treatment for patients.
In addition, even if vitiligo treatments are successful for a while, there is no certainty that the results obtained will be permanent. In addition, it is possible to see new patches outside the treated area. Experts can prescribe preventive medications for the formation of new patches.
Medication
Currently, no medication can compensate for the loss of pigment in the cells. However, some drugs can be used in combination with radiotherapy to restore some skin color.
Medications that control inflammation
The use of corticosteroid creams on the affected area can restore some of the skin color, and the effects of these extremely easy-to-use drugs can be seen within a few months. The side effects of these medications include thinning and streaking of the skin.
Mild forms of corticosteroid medication are prescribed for pediatric patients or for patients who require long-term use. Pills are prescribed instead of creams for those with rapid progression of the disease.
Medicines that affect the immune system
Calcineurin inhibitor ointments are effective in removing small patches, especially on the face. However, these drugs have been proven to be associated with lymphoma and skin cancer.
Therapies
Some types of therapy applied in the treatment of vitiligo can remove depigmentation and slow the progression of the disease. These treatments include the following.
Light therapy
Phototherapy with UVB is known to slow down the disease. If this therapy is used in combination with medications, its effectiveness increases. Light therapy requires participation in sessions 2 to 3 times a week. Patients can see the difference between 1 and 3 months. In order to see the full effect, the treatment should continue for 6 months.
Because of the link between the drugs used in treatment and skin cancer, it is necessary to discuss the benefits and side effects of treatment with the doctor before treatment.
Patients who are unable to attend sessions may be offered portable UVB devices designed to be applied at home. Possible side effects of the treatment include burning, redness and itching. However, these symptoms disappear a few hours after the session.
Combining xoralen and light therapy
This treatment combines phototherapy with a plant-based substance called psoralen. After the oral administration of psoralen and its effect, phototherapy with UVA rays is applied. This treatment helps to restore skin color. However, due to the difficulty of its application, UVB rays are usually used instead of UVA rays.
Removal of residual color
Depigmentation is applied if the spots caused by vitiligo are very common or if other treatments do not produce the expected results. In this application, a depigmenting agent is applied to the areas of the skin that are not affected by the disease. In this way, the skin tone gradually becomes paler and the entire skin takes the same color as the patches. Depigmentation treatment should last at least 9 months. The application is performed 2 times a day.
Side effects of the treatment include itching, swelling and dryness.
Surgery
In cases where medication and therapies do not work, various surgical methods can be applied if the patient's general health condition is stable. The aim of these surgeries is to restore the old color of the skin.
Skin grafting
In the skin grafting process, cells that retain their pigment are removed and patches that have lost their pigment are injected. It is especially used in cases where the spots are small.
Side effects of the treatment include infection, spotty color, scar patchy appearance and discoloration of the area.
Blister vaccination
In the blister grafting method, surgeons first create blisters on the skin by suction. Afterwards, patches are transplanted on the upper part of the blisters.
Possible risks of this treatment include scarring, patchy appearance and discoloration of the area. In addition, new vitiligo patches may appear in the area where tissue is removed due to suction.
Cellular suspension transplantation
In this surgical method, tissue is removed from the pigmented skin. This tissue is then placed in a special solution and when the tissue is ready, it is transplanted into the patches. The results of this procedure can be seen 4 weeks after the operation.
Possible side effects of the treatment include scarring, uneven skin tone and infection.
Treatments under investigation
Among the treatment methods being studied for the treatment of vitiligo are the following.
Drug that stimulates color-producing cells
In this treatment method called Afsmelsnoid, an implant is placed under the skin to stimulate the growth of melanocytes.
Medication to help control melanocytes
Prostagladin E2 aims to restore skin color in patients with uncommon or small patches.
How Should Vitiligo Patients Eat?
Vitiligo is not a disease caused by allergies. For this reason, it is not possible to control the disease. However, since vitiligo patients are more affected by the harmful rays of the sun, attention should be paid to a diet rich in vitamins A, E and B, which have antioxidant properties.