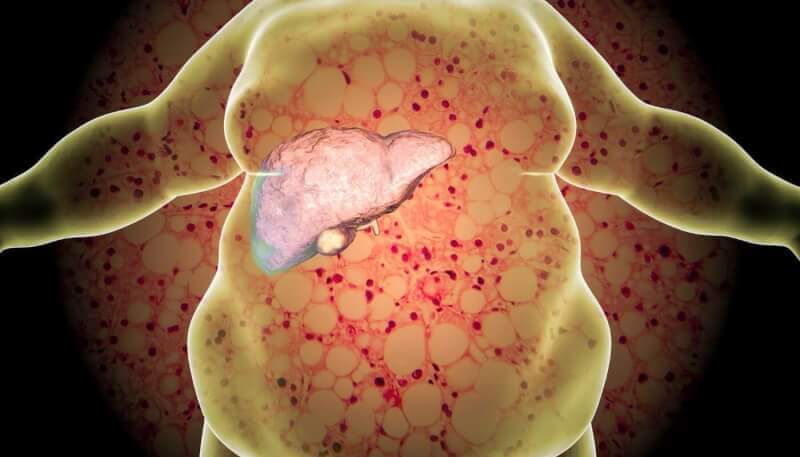
What is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease is a health problem caused by the storage of excess fat in the liver. It is usually asymptomatic and does not cause serious health problems. However, in some cases it can cause liver damage. Liver damage causes serious health problems.
Fatty liver disease is also called steatosis. A healthy liver also contains some fat. However, if the amount of fat in the liver reaches between 5 and 10% of the total weight of the liver, fatty liver disease is mentioned.
The liver usually does not cause serious complications. However, in 7-30% of people with fatty liver disease, it tends to worsen over time. Fatty liver disease occurs in three stages. These stages include the following:
- The liver becomes inflamed. That's why it swells. This causes damage to liver tissue. This stage of the liver is called steatohepatitis.
- In the second stage of fatty liver disease, scar tissue begins to form in the areas where the tissue is damaged. This stage is called fibrosis.
- In the final stage, extensive scar tissue replaces healthy tissue. This stage is called liver cirrhosis. Cirrhosis of the liver means that serious damage to the liver has occurred. At this stage, the hard scar tissue prevents the liver from functioning properly. This leads to complete inhibition of the liver. This can lead to liver cirrhosis, liver failure or cancer.
Forms of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease is divided into two different groups. The first of these groups is alcohol-induced fatty liver disease. This type is seen in people who regularly consume alcohol. The other form of fatty liver disease is non-alcohol-related liver disease. This form has nothing to do with alcohol and is the most common form in both children and adults. Although the cause of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not known exactly, it is thought that people's diet and obesity are effective.
Diagnostic criteria for fatty liver disease
Since fatty liver disease does not cause any symptoms, it is usually detected during a routine examination or investigation of another disease. Elevated levels of liver enzymes, especially in blood tests to investigate another disease, indicate liver injury. In this case, doctors may also order different tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests include the following:
- Ultrasound
- Computed tomography
- Biopsy to understand how far the disease has progressed
- A special type of ultrasound called fibroscan can also be used instead of a liver biopsy to find the amount of fat and scar tissue in the liver.
- Magnetic resonance
- Measurement of liver stiffness by transient elastography
- Magnetic resonance elastography
In addition to these tests, some blood tests are also requested to rule out other diseases and to obtain information about liver damage. These blood tests include the following:
- Complete blood count
- Celiac disease screening test
- The amount of iron in the blood
- Chronic viral hepatitis tests
- Liver enzymes
- Liver function tests
- Lipid profile
- Fasting blood glucose
- Hemoglobin A1C
Causes of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease can occur even in people who have never had any health problems before. However, some risk factors have been identified that may increase the risk of fatty liver disease. These risk factors include the following:
- Being overweight or obese
- Type 2 diabetes
- Insulin resistance
- Metabolic syndrome
- Some medicines such as amiodarone, diltiazen, tamoxifen and steroids
- Hispanic or Asian origin
- Completion of menopause
- High amounts of abdominal fat
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Genetics
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Underactive thyroid gland
- Underactive pituitary gland or hypopituitarism
- Over 50 years of age
Symptoms of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver usually does not cause any symptoms until it progresses to cirrhosis of the liver. However, some patients may experience symptoms. Among the most common symptoms of fatty liver disease are the following:
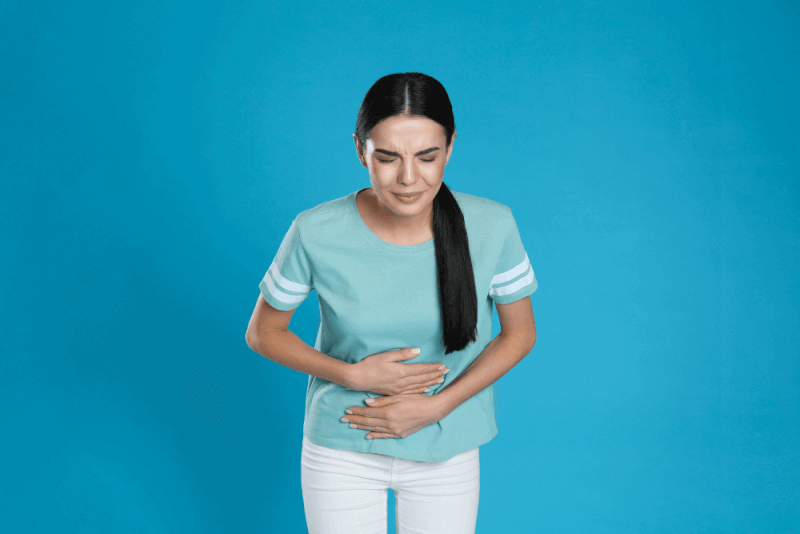
- Abdominal pain
- Feeling of fullness in the right upper abdomen
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Mental confusion
- Weakness
- Burnout
- Feeling depressed
If scar tissue forms in the liver due to fatty liver disease or if cirrhosis develops, the symptoms that can be seen include the following:
- Skin itching
- Jaundice
- Abdominal swelling called ascites
- Red palms
- Shortness of breath
- Fine blood vessels visible through the skin surface
Fatty liver disease treatment methods
There are no medicines developed for the treatment of fatty liver disease. However, medications can be used to treat health problems that contribute to fatty liver disease. In addition, lifestyle changes are essential for the elimination of fatty liver disease. For this, the lifestyle changes that will be requested primarily from patients include the following.
- Not drinking alcohol
- Taking the necessary medications to manage cholesterol, diabetes and triglycerides
- Lose weight
- Some cases use vitamin E and thiazolidinediones.
How to prevent fatty liver disease?
A healthy lifestyle is the key to preventing fatty liver disease. For this, the main things to be done are the following.
- Staying at a healthy weight
- Slow weight loss for people with excess weight
- Regular exercise
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Use of medicines as prescribed
Drug treatment of fatty liver disease
There are no approved medicines to treat fatty liver disease. For this reason, doctors can prescribe vitamin E supplements and pioglitazone, which is used in diabetes, among the drugs that doctors can recommend in fatty liver disease. However, these medicines have side effects. Besides, they are not suitable options for every patient. For this reason, lifestyle changes are necessary for the problem of fatty liver disease. Work on medicines is ongoing.
How does fatty liver disease go away?
The liver is the second most important organ of the body. It is therefore extremely important to maintain liver health. In order to maintain liver health, it is necessary to adopt a healthy diet and eat a low-calorie diet. In addition, the following foods can be added to the diet to protect liver health.
- Consuming apple cider vinegar by mixing it in hot water or adding it to salads is extremely effective in eliminating fatty liver.
- One of the vitamins that is important for the liver to be healthy is vitamin C. For this reason, it is recommended to consume lemon, which is also rich in antioxidants.
- Papaya fruit and seeds help to eliminate fatty liver.
- Nuts consumed in the right portions during the day are also recommended for the elimination of fatty liver disease.
Skin manifestations of fatty liver disease
The effects of some problems occurring in the liver can be seen on the skin. Knowing these effects helps to diagnose liver diseases at an early stage. Among the skin symptoms caused by liver diseases due to fatty liver disease are the following:
- The level of bilirubin in the blood increases because the liver is unable to function. This causes the skin to take on a yellowish color.
- If the liver tissue is damaged, itching of the skin occurs because bile salts cannot be secreted and toxic substances in the blood cannot be filtered.
- Punctate rashes on the face and trunk. These rashes are caused by dilated capillaries.
- Flushing of the palms, which occurs in 24% of people with cirrhosis of the liver.
- Bruising even in minor strokes due to blood clotting problems in liver diseases
- Skin tone inequalities due to protein accumulation in the liver.
Stages of fatty liver disease
Failure to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease can cause it to progress. Fatty liver disease is divided into 4 stages according to its degree.
Phase 1
The first stage of fatty liver disease is also known as simple fatty liver disease or steatosis. There is no inflammation or scarring in the liver at this stage. Since it is an early stage, patients do not show any symptoms. For this reason, most patients do not know they have fatty liver disease. At this stage, the fat in the liver is between 5% and 33% of the liver weight. It is quite common in the community and usually does not progress. In addition, lifestyle changes are sufficient to treat the first stage.
Phase 2
The second stage of fatty liver disease is also called non-alcoholic stestohepatitis. This stage occurs because inflammation occurs as the liver repairs damaged tissues. If there is an increase in damaged tissue in the liver, the liver cannot repair itself sufficiently and inflammation can leave scars.
Stage 2 symptoms
Symptoms that can be seen in patients in the second stage of fatty liver disease include the following:
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Swelling of the legs and abdomen
- Fatigue and weakness
- Yellowish skin color
- Yellowing of the pupils
- Pain in the upper right region of the abdomen
Phase 3
The third stage of fatty liver disease is also called fibrosis. At this stage, permanent scar tissue forms in the liver and the blood vessels around the liver. The liver also functions well in the third stage. By removing the cause of the inflammation and treating the inflammation, the growth of scar tissue is prevented and the damage can even be reversed, as the liver is a self-repairing organ. However, if left untreated, scar tissue may replace liver tissue over time, causing liver function to be affected.
Stage 3 symptoms
Symptoms that can be seen in third degree fatty liver disease include the following.
- Prolonged anorexia
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Pain in the lower right side of the abdomen
- Pale skin
- Yellowness of the whites of the eyes
- Angiomas on the skin
- Rapid weight loss
Phase 4
The fourth stage of fatty liver disease is called cirrhosis of the liver. When fatty liver disease reaches this stage, the liver is unable to perform its functions to a significant extent. In the case of liver cirrhosis, the scar tissue that forms in the liver is difficult to remove. Only when the cause of liver damage is eliminated can the progression of scar tissue be halted. This is the most serious stage of fatty liver disease as it can completely stop liver function.
Stage 4 symptoms
Symptoms that can be seen in the fourth stage of fatty liver disease include the following.
- Pale skin
- Pain in the right lower part of the ribs
- Swelling
- Bleeding
Nutrition in fatty liver disease
If fatty liver disease is seen due to alcohol or without alcohol, nutrition comes to the forefront in its treatment. In addition to proper nutrition, regular exercise and reaching the ideal weight are the key points in the treatment of fatty liver disease.
In the diet of people with fatty liver disease, foods that fight cell damage, reduce inflammation and enable the body to use insulin more easily should be preferred.
In addition, since the nutritional requirements of each person are different, it is necessary to seek help from nutritionists in the regulation of nutrition.
Foods that can help treat fatty liver disease
Although the Mediterranean diet is not a dietary principle created for fatty liver disease, it is also beneficial for fatty liver disease because this diet consists of foods with reduced fat. The foods in this diet are as follows.
- Fish and seafood
- Avacado
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Olive Oil
- Hazelnut
- Legumes
Choosing the right oils
People with fatty liver disease usually also have insulin resistance. In case of insulin resistance, the insulin level in the blood rises, but the body cannot use this insulin and the liver converts insulin into fat, causing fatty liver.
If the right fats are chosen, insulin in the blood can be used more efficiently. The cells can then take up glucose and the liver does not need to convert insulin in the blood into fat. For this reason, among the fats that liver patients should add to their diet are the following.
- Fish, nuts and flaxseed containing omega-3 fatty acids
- Olive Oil
- Hazelnut oil
- Plant-based and monounsaturated fats such as avocado
Fats to avoid
There are some types of fat that should be avoided to prevent further fat accumulation in the liver. Unsaturated fats are the most important of these. Foods rich in unborn fat include the following.
- Poultry, except lean white meat
- Sugar
- Full-fat cheese
- Red meat
- Full-fat yogurt
- High fructose corn syrup
- Baked or fried products made with palm or coconut oil
Antioxidant supplements
If nutrients are not broken down properly, they damage cells. This leads to fat accumulation in the liver. On the other hand, antioxidants help protect cells from this damage. Among the foods rich in antioxidants are the following.
- Coffee
- Vegetables
- Green tea
- Fruits
- Raw garlic
- Sunflower, almond, olive oil, canola oil, which are rich in vitamin E
Vitamins
In addition to the above-mentioned foods, it is recommended to add the following nutritional supplements to the diet.
- Vitamin D to protect against low vitamin D levels, which cause severe liver damage
- Potassium is considered to be one of the causes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. For this reason, a diet rich in potassium or supplements should be taken.
- Betaine is another mineral that protects against fatty liver disease.
Is fatty liver disease dangerous?
Fatty liver usually does not cause any serious problems. However, if the condition progresses to liver cirrhosis, people may face serious health problems. If liver cirrhosis is left untreated, the disease can progress to liver failure or liver cancer.
In addition, the liver is an organ that has the ability to repair itself. For this reason, starting to live in a healthy way will ensure that fatty liver disease is eliminated and you will have a healthy liver.
Does stress cause fatty liver disease?
Stress is the body's natural response to challenging conditions. However, prolonged or chronic stress can affect many organs and metabolism, especially the liver.
The hormone cortisol secreted from the liver due to stress may be related to insulin resistance and inflammation. This can lead to an increase in the amount of fat stored in the liver cells.
Complications of fatty liver disease
Liver damage occurs when there is severe scar tissue in the liver due to fatty liver disease or cirrhosis of the liver. If liver damage is left untreated, the following complications may occur
- Fluid accumulation in the stomach area called ascites
- Swelling and varicose veins in the esophagus. Over time, the vessels may rupture and bleeding may occur.
- Confusion
- Persistent sleepiness
- Slurred speech
- Overactive spleen, which can cause too few blood platelets
- Liver cancer
- End-stage liver failure

















S** S** | 25 Oct 2023
C** C** | 29 Nov 2023