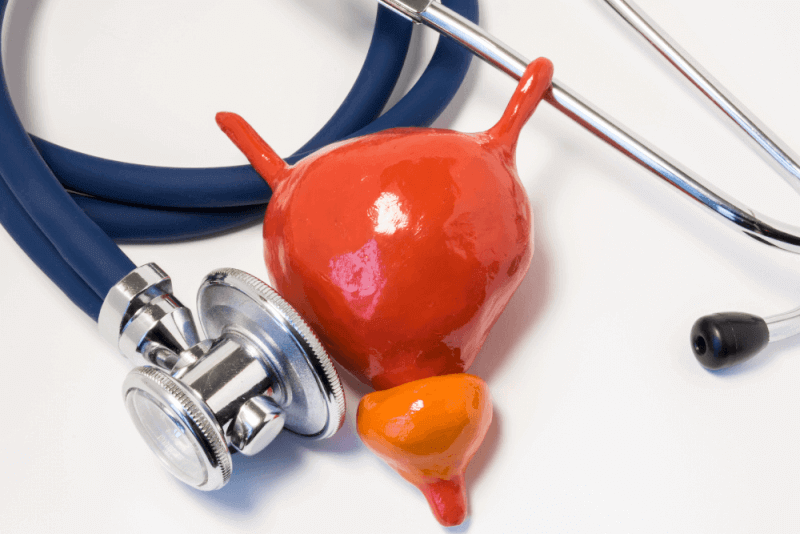
What is Neurogenic Bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is a disease that occurs due to injuries or diseases at different levels of the nervous system, resulting in the inability to fully perform the storage and emptying functions of the bladder. The muscles in the bladder wall constantly contract or relax, causing problems with urination.
Neurogenic bladder occurs due to damage to the peripheral nerves that control urination or problems in the central nervous system. There are different types of neurogenic bladder depending on the way it manifests and the changes in the bladder muscles.
Diagnosis of Neurogenic Bladder
- The patient's health problems and symptoms are evaluated, and a physical examination is performed.
- Urinalysis is performed to detect urinary tract infections and different urinary problems.
- The bladder is imaged with ultrasound to check the bladder volume and urine accumulation rate.
- Urodynamic tests are used to evaluate the bladder muscles and sphincter function.
- Imaging methods such as MRI or CT are used to examine abnormalities in the nervous system.
Symptoms of Neurogenic Bladder
Symptoms of neurogenic bladder can vary depending on how the disease manifests and its location. The severity and progression of the symptoms can vary based on the underlying cause of the disorder. Some symptoms are as follows;
- Frequent urination with small amounts
- Urinary incontinence
- Sudden urge to urinate
- Loss of sensation of bladder fullness
- Difficulty urinating
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Sweating and increased blood pressure while urinating
- Stone formation in advanced stages
Causes of Neurogenic Bladder
The general cause of neurogenic bladder is the damage to the nerves that control the bladder in the nervous system. However, the reason for the damage to these nerves can vary. Some causes of neurogenic bladder are as follows;
- Dementia and Alzheimer's
- Brain trauma
- Stroke
- Brain tumor
- Hydrocephalus
- Cerebral palsy
- Parkinson's
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord injuries
- Disc diseases
- Childbirth
- Diabetes
- Aging
- Pernicious anemia
Treatment Methods for Neurogenic Bladder
- Medications can be used to help the bladder contract.
- Catheterization can be used to completely empty the bladder. Self-catheterization involves inserting a catheter into the bladder to completely empty it.
- Bladder training can be used to develop a habit of regular urination along with urinary retention.
- Botox injections can be used to treat muscle spasms in the bladder.
- Surgery can be performed to increase bladder capacity or redirect urine flow.
Types of Neurogenic Bladder
There are different types of neurogenic bladder depending on how it manifests and the changes in the bladder muscles.& nbsp;
Overactive bladder
Patients with overactive bladder experience involuntary bladder contractions. Even if there is a small amount of urine in the bladder or no urine at all, the person has the urge to urinate.
Underactive bladder
In patients with underactive bladder, the bladder muscles cannot contract fully, and the sphincter region that allows urine retention cannot relax properly. As urine accumulates, the bladder expands, and because the sphincter cannot hold the urine, it drips out.
How Should Nutrition Be in Neurogenic Bladder?
- Alcohol and caffeine should not be consumed.
- Spicy, hot, and saucy foods should not be consumed.
- Smoking should be avoided.
- A diet rich in fiber should be preferred.
- Eating and drinking should be stopped 2 hours before sleeping.
- Being overweight puts pressure on the bladder and increases neurogenic bladder symptoms. Therefore, weight control should be maintained.
- Consuming fiber-rich foods can reduce the risk of overactive bladder.