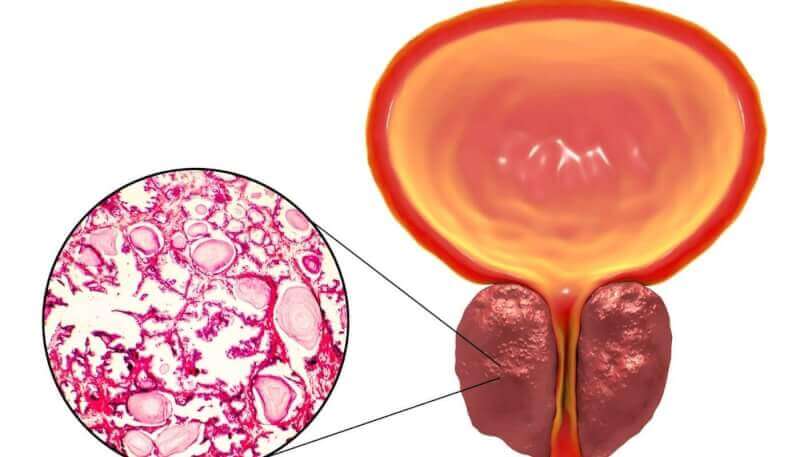
What is prostate enlargement?
Benign prostate enlargement, which becomes common with age, occurs in the prostate gland, a small gland that helps produce sperm. Located just below the bladder, the enlargement of this gland can block the flow of urine. This condition can lead to health problems in the bladder, kidneys, and urinary tract.
Benign prostate enlargement
Common symptoms of benign prostate enlargement include:
- Frequent and urgent need to urinate
- More frequent urination at night
- Weak urine flow
- Interrupted urine flow
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Urinary leakage
- Pain during or after urination
- Changes in urine color
- Urine odor
Less common symptoms of benign prostate enlargement include:
- Blood in urine
- Inability to urinate
- Urinary tract infection
The symptoms of benign prostate enlargement tend to worsen slowly. However, in some patients, the severity of symptoms may remain stable for a long time. Additionally, the severity of symptoms is not directly related to the size of the prostate. Therefore, even a small enlargement of the prostate can cause severe symptoms. In some patients, no symptoms of prostate enlargement may be observed.
Causes of prostate enlargement?
The exact cause of prostate enlargement is not yet understood. One theory suggests that the prostate enlarges due to a decrease in testosterone levels while estrogen levels remain constant as men age. Another theory is that the prostate gland continues to grow throughout a man’s life. Lastly, individuals with benign prostate enlargement have high levels of DHT, a more potent form of testosterone that contributes to prostate growth.
Symptoms of prostate enlargement
Symptoms caused by prostate enlargement include:
- Delayed start of urine flow
- Formation of bladder stones
- Frequent need to urinate
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Dribbling after urination
- Delayed bladder emptying
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
Diagnosis criteria for prostate enlargement
The most common cause of prostate enlargement is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). However, it may also be caused by a malignant tumor. Therefore, all possible causes should be evaluated. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient's symptoms are first examined. In addition, it is important to take into account any medications the patient is using, as some drugs can mimic the symptoms of prostate enlargement. After symptoms are recorded and medications are ruled out, a physical examination should be performed.
In this examination, the size and texture of the prostate gland are evaluated. A physical examination is conducted via a rectal exam. Afterward, a urine test is performed to assess the presence of a prostate issue and determine if there is a urinary tract infection. Additionally, it helps rule out other potential health problems the doctor may suspect. To determine if the prostate enlargement is malignant, PSA levels are checked. Prostate cancer can cause an increase in PSA levels.
However, PSA testing is not performed on every patient, as it has both advantages and disadvantages. If benign prostate enlargement is suspected, the urine flow rate per second is evaluated using a special device. Additionally, ultrasound can be used to measure the size of the prostate.
Treatment methods for prostate cancer
Benign prostate enlargement generally does not require urgent treatment. However, some patients may develop symptoms such as sudden inability to urinate, which requires immediate treatment. In these cases, a catheter is placed in the bladder to drain it. A few days after the catheter procedure, surgery to reduce the size of the prostate may be performed to improve urine flow.
In patients who do not require urgent treatment, the advantages and disadvantages of different treatment options should be considered before deciding on a treatment. Especially when evaluating surgical options, long-term considerations should be taken into account. The treatment options for prostate enlargement include:
Observation
For patients with mild symptoms and no complications, observation is one of the best options. Patients only need to visit the doctor once a year. Additionally, some lifestyle changes may be recommended.
Herbal medicines
There are herbal medicines available over the counter that help alleviate the symptoms of prostate enlargement. However, there is not enough research on their side effects and effectiveness. Therefore, they should be used under a doctor's supervision.
Medical drugs
Prescription drugs for prostate enlargement help relax the muscles of the bladder and prostate, allowing patients to urinate more efficiently.
Prostate reduction surgeries
Surgical options may be necessary due to the various complications of prostate enlargement. Conditions that may require surgery include recurrent urinary tract infections, urinary retention, and symptoms that cannot be alleviated with medication.
HoLEP
Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) is a type of surgery used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BPH causes the prostate to enlarge, leading to pressure on the urinary tract. To relieve this pressure and restore urine flow, the tissue obstructing the urinary tract must be removed, which is often done using the HoLEP method.
Before HoLEP surgery
Before undergoing HoLEP surgery, patients undergo several tests to determine if they are suitable candidates for the procedure. These tests include:
- Tests to evaluate urine volume and flow
- Transrectal ultrasound to help determine the size of the prostate
- Computed tomography (CT scan)
- Cystoscopy to evaluate the prostate for signs of cancer, infection, or obstruction
- Urodynamic tests to assess bladder function and determine if removing prostate tissue will help reduce symptoms
In addition to these tests, certain medications should be discontinued before surgery. Therefore, it is important for patients to inform their doctor about any medications they are taking.
HoLEP procedure
This procedure is performed under general anesthesia. However, if general anesthesia is not possible, spinal anesthesia may be used. Additionally, antibiotics are administered to reduce the risk of infection. The steps of the procedure are as follows:
- The patient is positioned on their back with their legs raised.
- A surgical instrument called a resectoscope is inserted into the urethra. This instrument includes a camera that allows the surgeon to view the prostate gland.
- A laser is then inserted into the resectoscope, and laser beams are directed at the prostate to cut away the tissue blocking urine flow.
- Next, blood vessels are sealed with the laser.
- After the laser procedure is complete, the resectoscope is removed and replaced with a morcellator. This device removes the remaining prostate tissue from the bladder.
- Before the surgery ends, the resectoscope is removed and a urinary catheter is inserted.
After HoLEP
Patients are usually discharged a few hours after surgery. However, if there are concerns about bleeding or other issues, the patient may need to stay in the hospital for a few days. Post-surgery conditions that patients may experience include:
- Fluid will be drained from the catheter to clear the blood from the urine. As long as the urine is light pink or light red, the patient cannot be discharged.
- Although rare, excessive bleeding can occur. Once the bleeding is controlled, the catheter is removed. The patient is then expected to urinate 2-3 times. If no issues are observed, the patient is discharged. If urination does not occur after the catheter is removed, it is reinserted.
- After surgery, urination may be painful for patients. Therefore, certain medications are prescribed. It is normal for blood to be present in the urine for a few weeks after surgery. The amount of blood may vary depending on fluid intake and activity level. Therefore, it is recommended that patients drink plenty of fluids after surgery.
- It may take several months for issues such as increased frequency of urination, sudden urges to urinate, and nighttime urination to resolve after surgery. This is because the bladder needs time to adjust to the removal of prostate tissue, and pelvic muscle control may be weak after surgery.
- A burning sensation for a few weeks after surgery is considered normal. Pain relievers can be used to manage this.
Summary of Surgery
Duration of Surgery: 1-1.3 Hours
Anesthesia Method: General, Spinal
Hospital Stay: 1-3 Days
Return to Work: 2-4 Weeks
Prostate enlargement and sexuality
Men with benign prostate enlargement may experience erectile dysfunction and ejaculation problems. While BPH itself does not cause these issues, they can be side effects of certain medications used in treatment. For example, 3.7% of men taking anti-testosterone drugs prescribed for treatment experience erectile dysfunction, and 3.3% experience a decrease in libido.
Does prostate enlargement cause impotence?
Erectile dysfunction is observed in 25% of patients with prostate enlargement. Additionally, a decrease in sexual desire and satisfaction may occur in these patients. Sudden onset erectile dysfunction is considered a possible symptom of prostate cancer. However, more detailed tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis.
In men with benign prostate enlargement, erectile dysfunction or ejaculation problems are more likely due to the medications used in treatment rather than the enlargement of the prostate itself.
Is prostate enlargement dangerous?
If prostate enlargement is not treated, it can lead to a blockage of the urinary tract. In this case, the symptoms of prostate enlargement become more severe, and serious conditions requiring surgical intervention may develop. These conditions include:
- Complete blockage of the urethra
- Kidney damage
- Urinary tract infection
- Bladder stones
- Bladder infections
Symptoms that may result from these issues include:
- Pain in the back or lower abdomen
- Inability to urinate
- Painful urination
- Fever
- Chills
- Blood in the urine
How to prevent prostate enlargement?
There is no definitive evidence on how to prevent prostate enlargement. However, paying attention to the following points may help reduce the risk of prostate enlargement:
- Maintaining balanced levels of testosterone and estrogen
- Regular exercise
- Balanced diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables
- Stress management techniques such as meditation and leisure activities to reduce inflammation in the body