30 Second Summary
- It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to visualize and treat the inside of joints.
- Arthroscopy is performed through smaller incisions than open surgery and shortens recovery time.
- It can be used in joints such as the knee, shoulder, hip, elbow and ankle.
- After arthroscopy, patients are usually discharged the same day and can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
What is Arthroscopy?
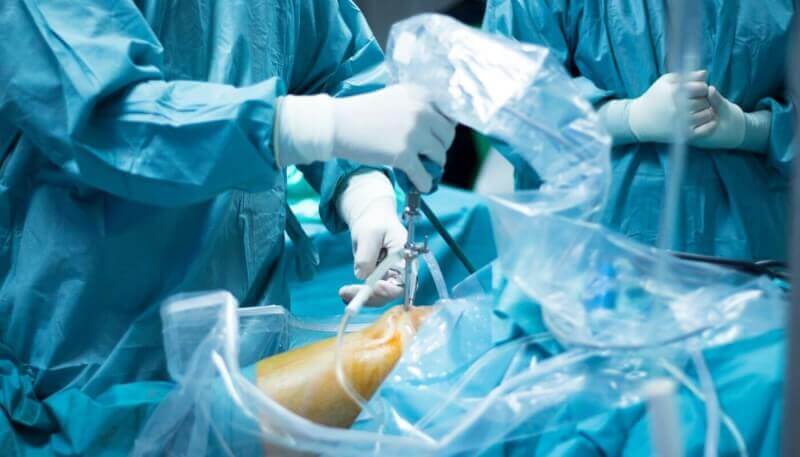
When we look at the word arthroscopy, "arthro" means joint. In its entirety, we can say that arthroscopy means looking inside the knee or joint. This procedure shows how the advancement of technology has had an impact on medicine. Because in this way, fiber optic cameras are used to view the knee or joint areas and the area in question is examined in this way. Better than this is closed arthroscopy. In the closed arthroscopy method, no scars or incision marks are visible. Because with this method, no part of the body is cut and this prevents the occurrence of conditions such as disability, disease or pain due to infection after the examination.
Types of Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy, which is used to diagnose and, if necessary, treat various problems in the joints, varies according to the region of application.
Knee arthroscopy
In knee arthroscopy, specialists can view the inside of the knee joint through an arthroscope without making a large incision on the flat. This camera, which is extended into the knee joint through a small incision, transfers images inside the knee to the monitor. In this way, problems that are not noticed in other imaging methods can be diagnosed.
In addition, arthroscopy is also used when surgical intervention is required for treatment. However, surgical procedures may require 2 or more incisions. It is generally preferred because it has a lower complication rate and faster recovery compared to open surgeries.
Ankle arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy, which allows various ankle problems to be solved, is a procedure with a low risk of complications and allows patients to be discharged on the same day. It not only diagnoses but also treats problems in the ankle. It is applied in case of ankle pain that does not respond to other treatments.
Shoulder arthroscopy
Shoulder arthroscopy, which has been practiced since the 1970s, is often preferred by patients because of its faster recovery after surgery. Thanks to the continuous development of new equipment and techniques, shoulder arthroscopy is one of the treatment options for more health problems. In addition, shoulder arthroscopy is also used to understand problems in the shoulder.
Elbow arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy is a procedure that has been performed since the 80s. It is used for diagnostic as well as therapeutic purposes. Thanks to the use of this method in treatment, patients experience less pain and joint stiffness after the operation. Common elbow arthroscopy procedures include the following
- Tennis elbow
- Removing loose objects
- Releasing scar tissue to improve range of motion
- Fracture treatment
- Osteochondritis dissecans
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
Wrist arthroscopy
Another type of arthroscopy used for both diagnosis and treatment is wrist arthroscopy. Wrist arthroscopy is recommended if other imaging methods fail to yield results or if symptoms persist despite treatment.
Wrist arthroscopy can also be used to treat health problems in the wrist. With the arthroscope, which is approximately the size of a pen, the problem is first detected and then treatment procedures are applied with additional equipment. Since it is a procedure performed under local anesthesia and the risk of complications is very low, patients can be discharged after the procedure.
Hip arthroscopy
Although hip arthroscopy has been practiced for many years, it is not as common as knee and shoulder arthroscopy. Hip arthroscopy, which can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, helps to treat damage to the labrum, articular cartilage and other soft tissues surrounding the joint, reducing the symptoms seen in patients.
Arthroscopy Advantages
Arthroscopy has many advantages over open surgery. One of them is that since very small (approximately 1 centimeter) incisions are made in the body, these areas do not prevent the patient from returning to normal life after surgery. At the same time, very small instruments are used in these procedures. The instruments are small and the incisions are small. For this reason, it is a procedure that almost does not affect the patient's life. After the examination, the cleft closes in a short time and there is no scar.
The arthroscopy method of examination is much more advantageous than normal open surgery. Because in this way, there is no permanent scar or damage to the body. The patient can resume normal life in a short time as if nothing had happened. The fact that the instruments and wounds are small means that the pain is also small. For this reason, arthroscopy is a preferred method of examination.
Where is arthroscopy used in the body?
Arthroscopy lives up to its name and is usually used on the knee and joint areas. These include the wrists and ankles, elbows, knees, shoulders and hips. Problems such as tightness and strain in these areas can be easily treated with arthroscopy.
What are the side effects of arthroscopy?
As with anything else, arthroscopy can of course have side effects. In fact, there are no special side effects of arthroscopy. Because it is a human procedure, it carries the same risks as any surgery or examination. One of these is infection.
Albeit much, much less likely than open surgery, it is still possible. Even though arthroscopy is performed with small instruments and incisions no more than 1 centimeter long, there is a possibility that the tiny incision can become infected. This is enough to make it one of the side effects of arthroscopy.
Another side effect of arthroscopy is blockage of the veins. Although this is also rare, we can count it among the side effects because it is still within the possibilities such as infection.
Another side effect of arthroscopy is actually an accident. This side effect is when the joint surfaces are bruised or damaged in any way by the instruments used. This is not normally seen, but since it is a human being who performs this procedure and every human being has the right to make mistakes, accidents can happen, even if they are simple. This is more related to the doctor's attention.
Other side effects of arthroscopy may also include extremely simple, rare problems that disappear in a short period of time, such as failure of the repaired tissue to heal or injury to the nerves.
Exercises After Arthroscopy
Although arthroscopy is a simple procedure, there is no harm in doing exercises afterwards. These exercises will always make the patient healthier.
It is recommended to do exercises regularly to restore the knee to its former mobility and strength. It is also useful to pay attention when doing the exercises listed below. It can be done 2-3 times a day for 20 or 25 minutes. It can also be done together with walking.
If there is an unexpected condition such as severe pain, swelling or redness in the knee or the aforementioned joint area during or after exercises, the area should be wrapped with a bandage (without squeezing too tightly and blocking blood flow) and shown to the doctor.
Back Muscle Group
Lie flat on your back. Then we pull our feet towards our hips. There is no need for full contact. After the angle in the knee is about 30 degrees, we straighten our legs again. We hold for 5 seconds and do the same process again and when we pull, we wait for 5 seconds again. The 30-degree angle we have determined in the knee is not maximum or minimum. It can be pulled until it reaches the pain limit. Repeat this 10 times.
Front Muscle Group
This time we lie face down. One of the exercises performed after arthroscopy is this exercise, which aims to train the anterior muscle group.
We put something like a rolled towel or a pillow at the ankle level. Then we put pressure there with our foot. This pressure lasts for about 5 seconds and then we pull it back. We do it 10 times calmly, waiting 5 seconds each. In this way, we ensure that the knee muscles contract.
Straight Leg Raise
Lie on your back like the first exercise. After lying flat, this time we do not pull our feet to ourselves. Without bending the knee, we bring the feet up and hold them for 5 seconds and then lower them. We repeat this again 10 times or 15 times. It is enough for the foot to go up about 20 centimeters.
Difference Between Arthroscopy and Open Surgery
As mentioned above, the difference between arthroscopy and open surgery is the amount of incisions. In open surgery, large wounds are made and the risk increases. At the same time, the patient's return to normal life is delayed and scars remain. Arthroscopy eliminates this problem. The examination is completed with the help of optical fiber cameras through extremely small incisions. In summary, the biggest difference between arthroscopy and open surgery is the length of the incision in the body.
What to Consider After Arthroscopy Surgery
After arthroscopy, as after any other surgery, sudden movements should be avoided. Although arthroscopy may seem like a much simpler, plainer and smaller procedure than open surgery, it is not worth risking your health. Therefore, care should be taken not to make any sudden movements after arthroscopy. At the same time, it is important to avoid putting a load on the area or any behavior that may cause the wound to become dirty and infected, even if it is small. The wound should be kept clean and allowed to breathe.
Paying attention to the cleanliness and safety of the wound after arthroscopy, preventing the area from being hit, and performing post-procedure exercises are among the biggest factors that will accelerate the return to normal life.
Summary of Surgery
Surgery Duration: 30 minutes -2 hours
Anesthesia Method: Local,Spinal
Hospitalization Period: 1 Day
Return to Work: 1-6 Weeks