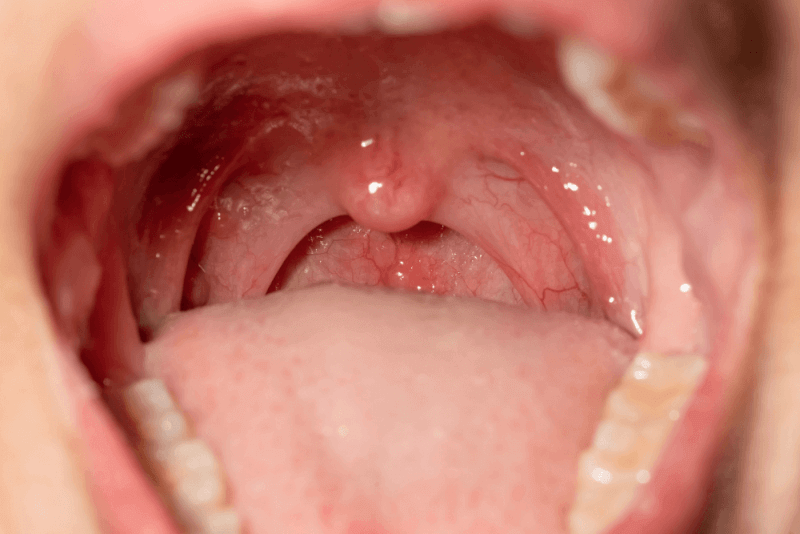
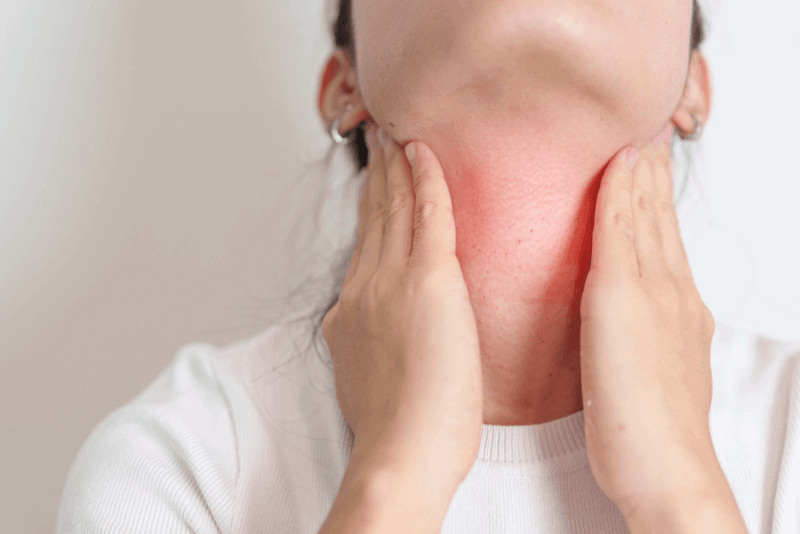
What is Pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis, often associated with the common cold, causes difficulty swallowing, throat pain, burning, and itching in patients. It is simply defined as the inflammation of the back part of the pharynx, a structure in the throat. Commonly known as a sore throat or throat inflammation, pharyngitis is more frequently seen during the cold winter months. It spreads quickly among people in close contact, as it can be caused by viral or bacterial infections.
Pharyngitis presents with symptoms such as sore throat, fever, difficulty swallowing, and post-nasal drip, and it is important to see a doctor for treatment as soon as possible. If left untreated, pharyngitis can lead to airway obstruction and abscess formation at the back of the throat. Additionally, untreated pharyngitis may lead to more serious conditions such as kidney disease and rheumatic heart disease. However, with timely diagnosis, treatment is very easy and quick.
Chronic Pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis is caused by the continuous irritation of the throat or pharyngeal area, often leading to symptoms such as a persistent cough, a feeling of something stuck in the throat, and dry cough. Chronic pharyngitis, which describes long-term cases of pharyngitis, has several different causes.
Acute Pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis cases are typically shorter in duration. Common symptoms of acute pharyngitis include fever, throat burning, and throat pain. It can be caused by bacterial or viral infections.
Pharyngitis Symptoms
The symptoms of pharyngitis vary depending on the cause. The incubation period of pharyngitis ranges from 2 to 5 days, and the general symptoms include:
- Sore throat
- High fever
- Runny nose
- Body aches
- Headache
- Cough
In addition to a sore throat, pharyngitis can also present with mononucleosis symptoms, which include:
- Loss of appetite
- General weakness
- Muscle aches
- Fever
- Severe fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
If the cause of pharyngitis is bacterial, the symptoms may include:
- General weakness
- Unusual taste in the mouth
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- White or gray patches in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing
Chronic Pharyngitis Symptoms
Chronic pharyngitis symptoms are generally milder compared to acute pharyngitis symptoms. Chronic pharyngitis symptoms include:
- Mild sore throat
- Cough
- Pain while swallowing
Acute Pharyngitis Symptoms
Acute pharyngitis symptoms are more severe. These symptoms include:
- Sensation of something stuck in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Runny nose
- Weakness
- Fever
- Sore throat
Causes of Pharyngitis
The causes of pharyngitis vary depending on its type, with different factors contributing to acute and chronic pharyngitis.
Causes of Chronic Pharyngitis
The primary cause of chronic pharyngitis is irritation of the throat. Chronic pharyngitis persists as long as the irritating factor remains. For instance, patients with nasal septum deviation often breathe through their mouth, leading to prolonged throat dryness and irritation. Other factors contributing to chronic pharyngitis include:
- Sinusitis
- Allergies
- Conditions causing swelling of the adenoids
- Hay fever
- Consumption of spicy foods
- Smoking
- Consumption of excessively hot or cold foods
- Inadequate fluid intake
- Occupations requiring constant speaking, such as teaching
Causes of Acute Pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis is generally caused by bacteria or viruses, with viral causes being more common. Other causes of acute pharyngitis include:
- Common cold
- Infections
- Exposure to cold environments
- Being in the same environment as sick individuals
- Dry air
- Constant exposure to chemicals
- Influenza virus
- Infectious mononucleosis, also known as the kissing disease
- Adenovirus
- Beta infection
- Whooping cough
- Croup
- Chickenpox
- Measles
Diagnosis and Tests for Pharyngitis
A diagnosis of pharyngitis cannot be made solely based on a sore throat or irritation. Patients must present with additional symptoms. Pharyngitis is diagnosed under two categories: acute and chronic. Additionally, patients must answer questions about their daily routines, work environment, and daily water intake. A physical examination is then conducted to diagnose pharyngitis.
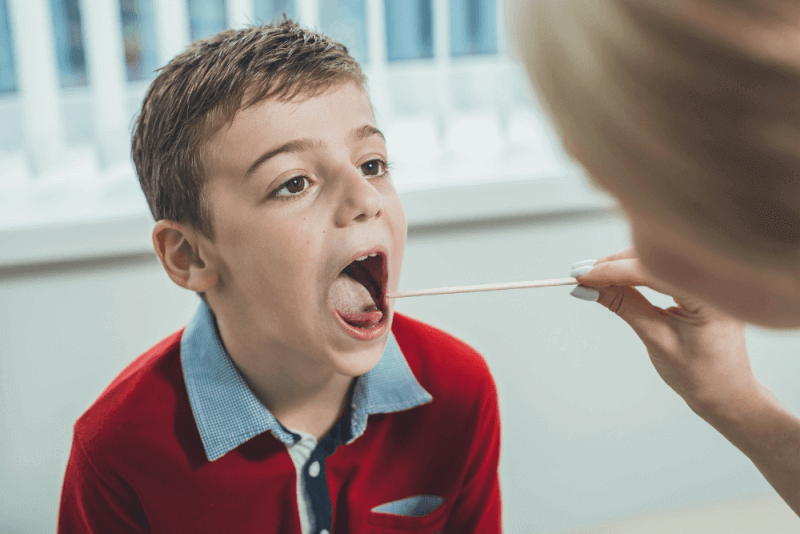
Generally, tests are not required for diagnosing pharyngitis. However, in certain cases, doctors may request blood tests, throat swabs, chest X-rays, and culture antibiogram tests. Throat culture, which helps identify the bacteria causing pharyngitis, is a simple procedure where a swab is taken from the patient's throat. Patients do not feel pain or discomfort during this process.
Treatment Methods for Pharyngitis
To treat pharyngitis, it is essential to identify the underlying cause. If pharyngitis is bacterial, antibiotics are used in treatment. Other medications, such as pain relievers and sprays, may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms quickly.
If pharyngitis is viral, antibiotics are not prescribed. Treating chronic pharyngitis is a more challenging and lengthy process. Patients should quit smoking, avoid inhaling dust and chemicals, and ensure their environment is well-ventilated.
Pharyngitis and Medication Treatment
The medications used to treat pharyngitis vary depending on the underlying cause. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial pharyngitis,
If pharyngitis is caused by acid reflux, anti-acid medications are prescribed to reduce the severity of reflux. For allergic pharyngitis, antihistamines are prescribed to control allergy-related symptoms.
How Does Pharyngitis Heal?
In the treatment of viral pharyngitis, medications are prescribed to alleviate symptoms. There are also natural remedies that patients can use at home to speed up recovery. Some of these include:
- Humidifying the room
- Bed rest
- Gargling with warm saltwater
- Drinking broths and soups
- Drinking plenty of fluids
- To relieve throat pain and itching, consuming sage and Echinacea tea is recommended. Sage also helps reduce throat inflammation.
- Using garlic can support the treatment of bacterial pharyngitis, as garlic has powerful antibacterial properties.
- Chewing mint helps alleviate dry cough and throat pain caused by pharyngitis.
Is Pharyngitis Contagious?
The viruses and bacteria that cause pharyngitis tend to live in the throat and nose, making it highly contagious. Pharyngitis can spread through:
- Consumption of contaminated food and beverages
- Touching one's face with dirty hands
- Coughing or sneezing by an infected person
How to Prevent Pharyngitis?
To reduce the risk of contracting pharyngitis, the following precautions should be taken:
- Avoid exposure to chemicals and irritants
- Ensure that living and working spaces are well-ventilated
- Use sanitizing agents on commonly used surfaces
- Avoid consuming excessively hot or cold foods
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Stay away from people with viral or bacterial infections
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Wash your hands regularly and thoroughly
Differences Between Pharyngitis and Laryngitis
Pharyngitis and laryngitis are often confused due to their similar symptoms. The key difference between the two conditions is the location of the inflammation in the throat. Pharyngitis refers to inflammation at the back of the pharyngeal tissue in the throat, while laryngitis involves inflammation in the larynx or vocal cords. Therefore, the distinguishing symptom of laryngitis is hoarseness.
Differences Between Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis
Another condition often mistaken for pharyngitis is tonsillitis, an infection that affects the tonsils. Additionally, pharyngitis and tonsillitis can occur together, a condition known as pharyngotonsillitis.
The Relationship Between Reflux and Pharyngitis
Reflux occurs when stomach acid reaches the throat via the esophagus due to the malfunctioning of the esophageal valve. Stomach acid is one of the body's strongest acids, and its presence in the throat poses a significant risk for chronic pharyngitis.
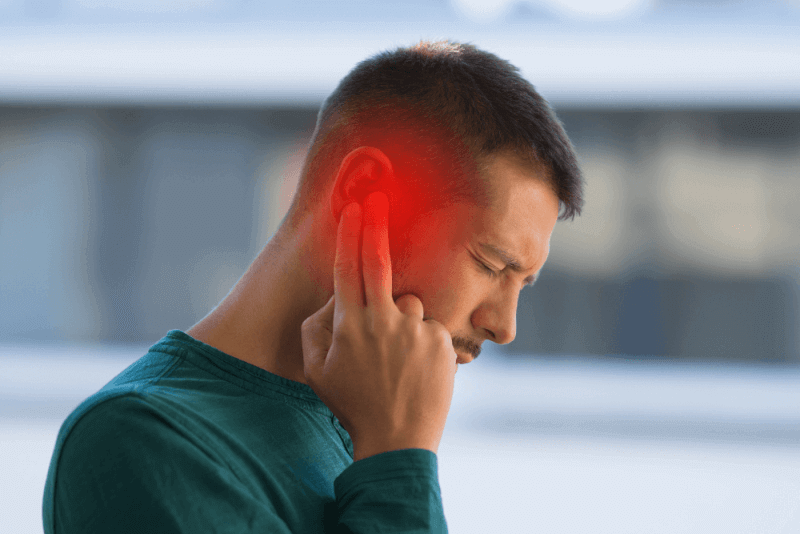
Does Pharyngitis Cause Shortness of Breath?
Pharyngitis can cause inflammation and swelling of the throat, which can sometimes obstruct breathing. Although rare, some pharyngitis patients may experience difficulty breathing. In such cases, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Is Pharyngitis Contagious?
Whether pharyngitis is contagious depends on its cause. Pharyngitis caused by allergies or reflux is not contagious, whereas bacterial pharyngitis is. The bacteria that cause pharyngitis are usually transmitted through the respiratory tract.
Does Pharyngitis Cause Fever?
If the cause of pharyngitis is bacterial, the immune system activates, and the body temperature may rise to kill the bacteria. Therefore, fever is one of the symptoms associated with pharyngitis.